By Dipesh Ghimire
KBL Faces Declining Financial Performance Challenges

News Article: Declining Earnings Trend for KBL Raises Concerns
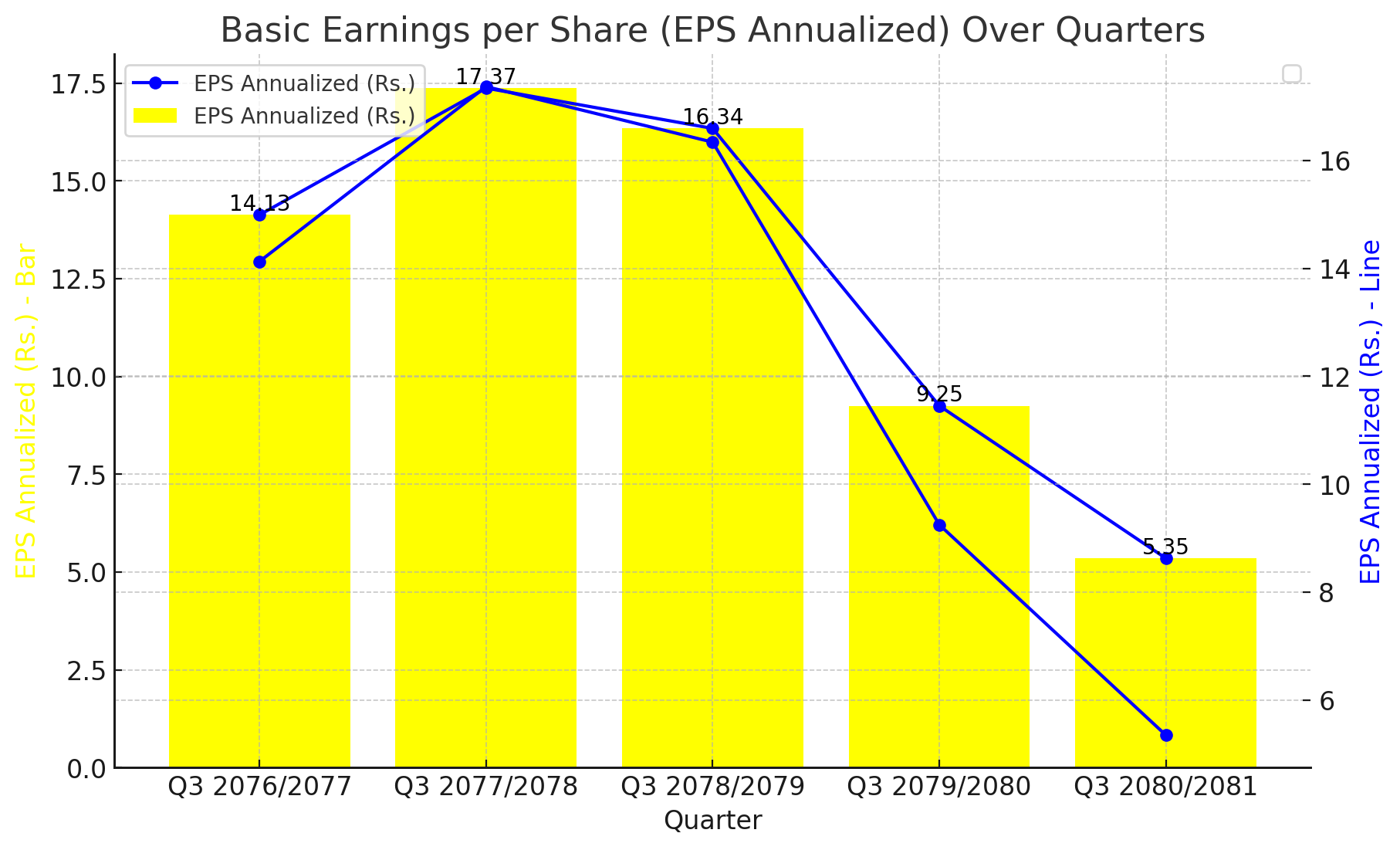
In a concerning development for investors, the Basic Earnings per Share (EPS) for KBL, a prominent player in the banking sector, has shown a consistent decline over the past five years. The latest financial data, ending in Q3 2080/2081, reveals a notable drop in annualized EPS, which has decreased from 17.37 in Q3 2077/2078 to a mere 5.35 in the most recent quarter.
Financial Performance Analysis:
Q3 2080/2081: The EPS has plunged to 5.35, reflecting the lowest point in the five-year span.
Q3 2079/2080: A sharp decline is evident with the EPS recorded at 9.25, significantly lower than the previous years.
Q3 2078/2079: Despite a decline from the peak, the EPS was still robust at 16.34.
Q3 2077/2078: This period marked the highest EPS at 17.37, showcasing a period of strong profitability.
Q3 2076/2077: The EPS stood at 14.13, indicating a period of steady growth before the peak.
Interpretation and Implications: The steady decline in KBL's EPS over the recent years signals potential underlying issues within the bank's operational efficiency, market conditions, or management strategies. This downward trend could be attributed to several factors, including increased competition in the banking sector, higher operating costs, or external economic challenges such as fluctuating interest rates and regulatory changes.
Investors and stakeholders must take note of this trend as it impacts the bank's profitability and, consequently, the return on their investments. A declining EPS generally indicates that a company's earnings are falling, which might result in lower dividends and reduced stock prices, affecting shareholder value.
Strategic Considerations for KBL:
Cost Management: KBL needs to evaluate its operational costs and identify areas for cost reduction to improve profitability.
Revenue Diversification: Exploring new revenue streams and innovative banking solutions could help mitigate the impact of market saturation and competition.
Operational Efficiency: Enhancing operational efficiency through technology and streamlined processes could bolster the bank’s financial health.
Regulatory Adaptation: Proactively adapting to regulatory changes and economic policies will be crucial in maintaining financial stability.
Conclusion: The declining EPS trend is a clear signal that KBL must reassess its strategic approach to ensure long-term sustainability and growth. While the bank has faced challenges, there are opportunities for recovery and improvement through targeted strategies and robust financial management.
Investors are advised to closely monitor KBL's future financial statements and strategic initiatives to make informed decisions regarding their investments in the banking sector.
Rising NPL Ratio Poses Challenges for KBL
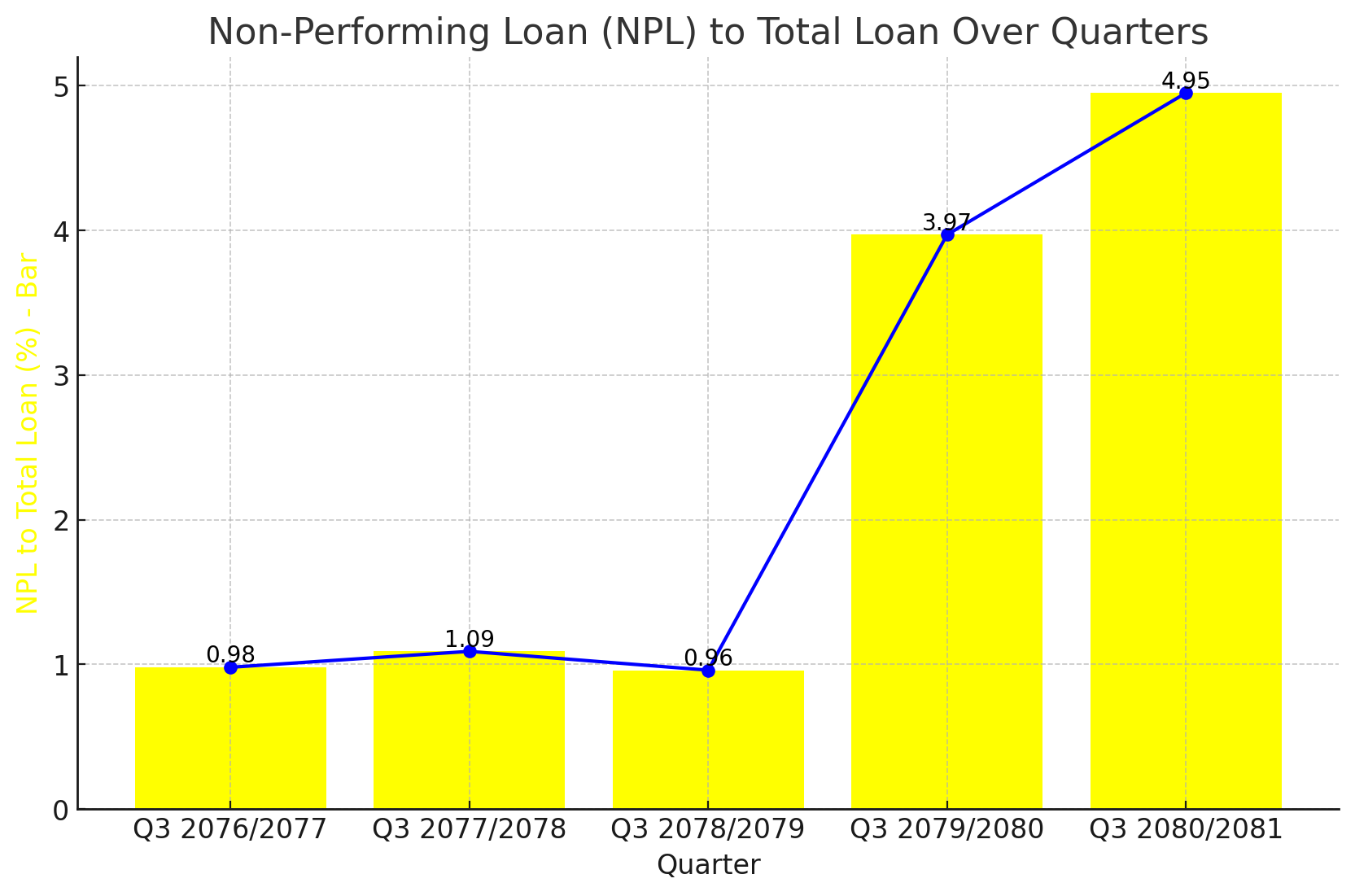
KBL, a notable entity in the banking sector, is currently facing a rising trend in its Non-Performing Loan (NPL) to Total Loan ratio. The latest financial data up to Q3 2080/2081 reveals an increase in the NPL ratio to 4.95%, a significant rise from the previous years.
Financial Performance Analysis:
Q3 2080/2081: The NPL ratio has surged to 4.95%, the highest in the recorded period.
Q3 2079/2080: The ratio increased dramatically to 3.97%.
Q3 2078/2079: A notably lower NPL ratio of 0.96% was recorded.
Q3 2077/2078: The ratio slightly increased to 1.09%.
Q3 2076/2077: The NPL ratio was at 0.98%, indicating a relatively stable period.
Interpretation and Implications: The rising NPL ratio is a red flag for the financial health of KBL. An increasing NPL ratio indicates that a higher proportion of the bank’s loans are not being repaid on time, which could lead to financial strain and decreased profitability. This trend is concerning for investors and stakeholders as it reflects potential weaknesses in the bank's credit management practices and economic challenges faced by borrowers.
Several factors could be contributing to this increase, including:
Economic Downturn: Adverse economic conditions can lead to higher default rates as borrowers struggle to meet their financial obligations.
Credit Management Practices: Inefficiencies or laxity in credit appraisal and monitoring could lead to higher non-performing assets.
Sectoral Issues: Specific sectors facing downturns can contribute significantly to the rise in NPLs if the bank has substantial exposure to those sectors.
Strategic Considerations for KBL:
Strengthening Credit Assessment: KBL should enhance its credit appraisal mechanisms to ensure robust evaluation of borrowers' repayment capacities.
Focused Recovery Efforts: Implementing targeted recovery strategies and engaging with defaulting borrowers can help in reducing the NPL ratio.
Diversification of Loan Portfolio: Reducing concentration risk by diversifying the loan portfolio across various sectors and borrower profiles.
Conclusion: The rising NPL ratio poses a significant challenge for KBL, necessitating immediate strategic interventions to mitigate risks and ensure financial stability. Investors and stakeholders should closely monitor the bank's measures to address this issue and its impact on overall performance.
By addressing the underlying causes and implementing effective risk management strategies, KBL can navigate through these challenges and work towards restoring its financial health.
Stable Networth per Share for KBL Despite Minor Fluctuations
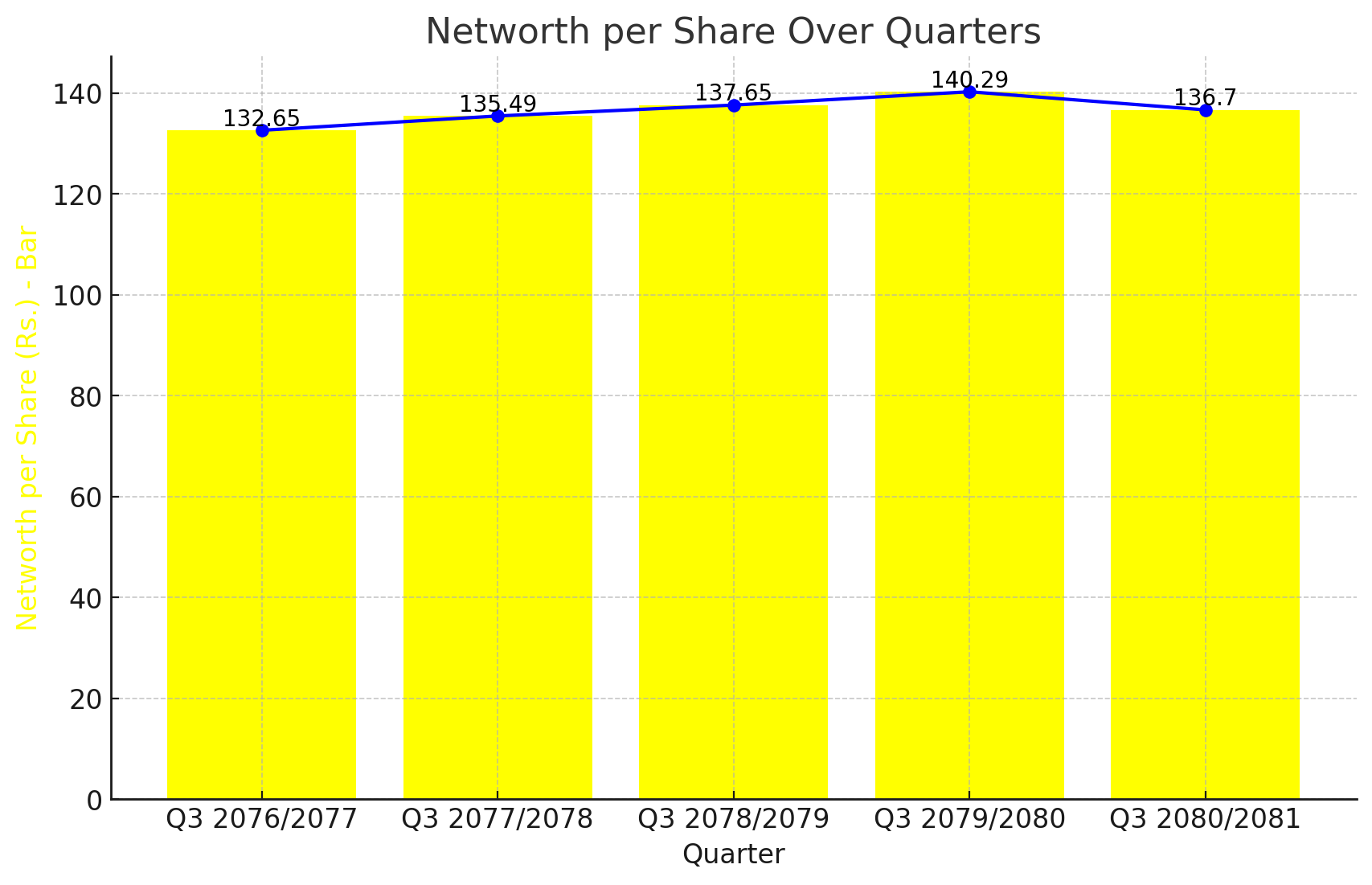
KBL, a leading entity in the banking sector, has demonstrated stability in its Networth per Share over the past five years. The latest financial data up to Q3 2080/2081 shows a Networth per Share of Rs. 136.7, reflecting minor fluctuations but overall stability in the bank's financial health.
Financial Performance Analysis:
Q3 2080/2081: The Networth per Share stands at Rs. 136.7, indicating a slight decrease from the previous year.
Q3 2079/2080: The Networth per Share reached its peak at Rs. 140.29.
Q3 2078/2079: A slightly lower value of Rs. 137.65 was recorded.
Q3 2077/2078: The Networth per Share was Rs. 135.49, reflecting steady growth.
Q3 2076/2077: The value stood at Rs. 132.65, marking the beginning of a steady increase over the years.
Interpretation and Implications: The relatively stable Networth per Share indicates that KBL has maintained its financial health despite minor fluctuations. The Networth per Share represents the value of the company’s equity on a per-share basis, which is a crucial indicator of financial stability and shareholder value.
The slight decrease in the latest quarter could be attributed to several factors, including:
Economic Conditions: Variations in the economic environment can affect the overall net worth of the bank.
Asset Revaluation: Changes in the value of assets and liabilities due to market conditions can impact net worth.
Dividend Payouts: Higher dividend payouts can reduce the net worth as profits are distributed to shareholders.
Strategic Considerations for KBL:
Asset Management: Effective management and revaluation of assets to ensure accurate representation of net worth.
Capital Allocation: Strategic allocation of capital to growth areas to enhance overall financial health.
Stakeholder Communication: Transparent communication with stakeholders regarding financial health and future prospects.
Conclusion: KBL’s stable Networth per Share reflects its resilience and effective financial management over the years. The minor fluctuations observed are within a reasonable range, indicating consistent performance and stability. Investors and stakeholders can take confidence in the bank's ability to maintain its financial health, providing a strong foundation for future growth.
By continuing to focus on effective asset management and strategic capital allocation, KBL can further enhance its financial stability and shareholder value.
Significant Decline in Return on Equity for KBL
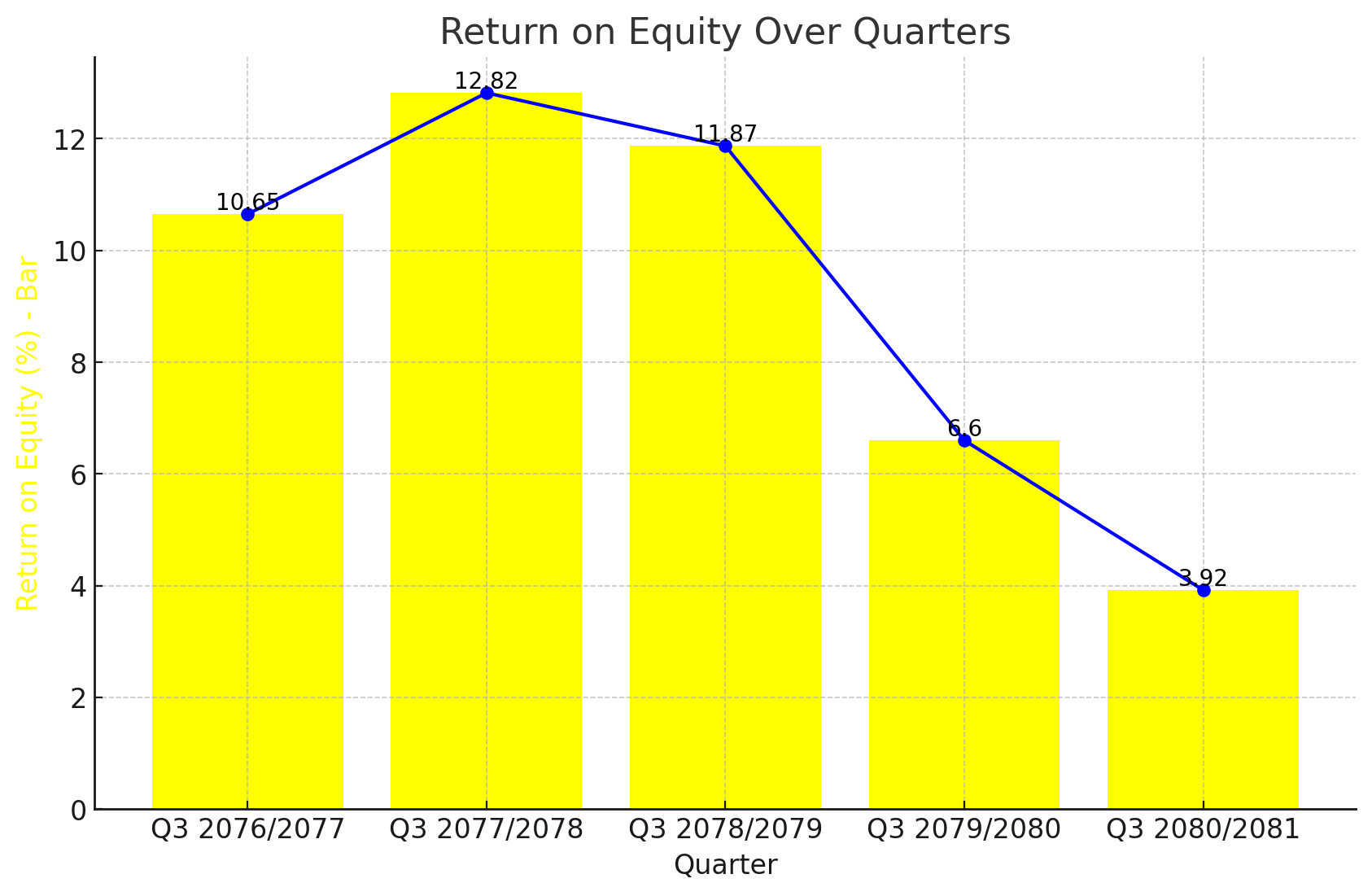
KBL, a major player in the banking sector, has seen a significant decline in its Return on Equity (ROE) over the past five years. The latest financial data up to Q3 2080/2081 shows an ROE of 3.92%, which is a sharp decrease from the 12.82% recorded in Q3 2077/2078.
Financial Performance Analysis:
Q3 2080/2081: The ROE has dropped to 3.92%, indicating a concerning trend.
Q3 2079/2080: The ROE was recorded at 6.6%, showing a steady decline from previous years.
Q3 2078/2079: A higher ROE of 11.87% was observed.
Q3 2077/2078: The peak ROE during this period was 12.82%.
Q3 2076/2077: The ROE was 10.65%, indicating strong performance.
Interpretation and Implications: The declining Return on Equity is a worrying indicator of KBL’s profitability and efficiency in generating returns for shareholders. ROE measures a company's ability to generate profits from shareholders' equity and is a critical metric for assessing financial performance.
Several factors could be contributing to this decline, including:
Profitability Issues: Lower net income due to reduced revenue or increased costs can impact ROE.
Economic Conditions: Adverse economic conditions can affect the bank’s ability to generate profits.
Operational Efficiency: Inefficiencies in operations and higher operational costs can reduce profitability.
Strategic Considerations for KBL:
Improving Profit Margins: Focusing on cost reduction and increasing revenue streams can help improve profitability.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency: Streamlining operations and improving efficiency can contribute to higher profitability.
Strategic Investments: Investing in growth areas and high-return opportunities can boost overall returns.
Conclusion: The significant decline in KBL’s Return on Equity highlights the need for strategic interventions to address profitability and operational efficiency issues. Investors and stakeholders should monitor the bank's performance closely and assess the effectiveness of its strategies to improve financial health.
By focusing on improving profit margins, enhancing operational efficiency, and making strategic investments, KBL can work towards reversing the declining trend and restoring shareholder value.
Drastic Decline in Distributable Profit per Share for KBL
KBL, a prominent bank in the banking sector, has experienced a drastic decline in its Distributable Profit per Share over the past five years. The latest financial data up to Q3 2080/2081 shows a negative distributable profit per share of -16.03, a stark contrast from the positive values recorded in previous years.
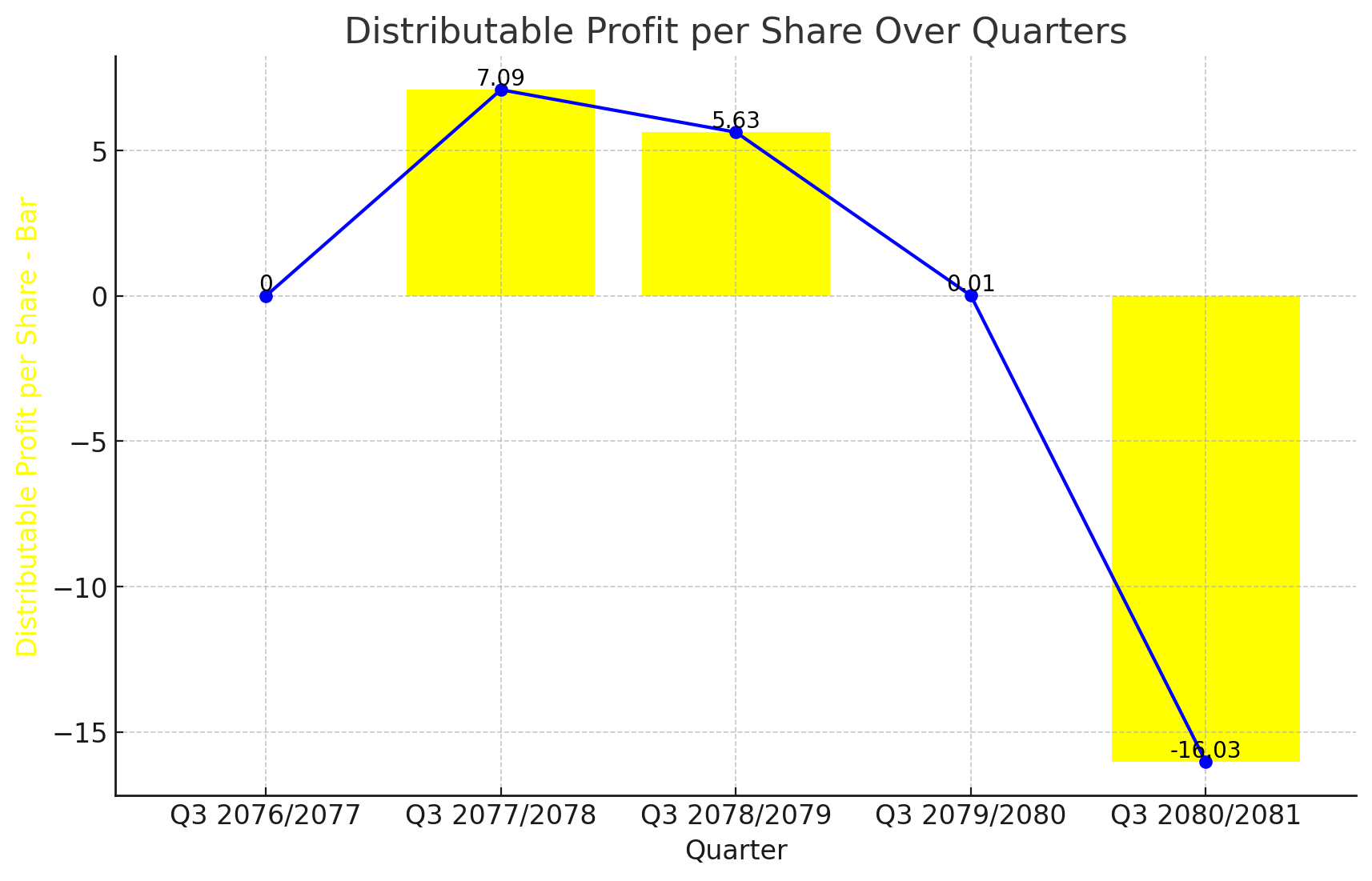
Financial Performance Analysis:
Q3 2080/2081: The distributable profit per share is -16.03, indicating a significant loss.
Q3 2079/2080: A negligible profit of 0.01 per share was recorded.
Q3 2078/2079: The distributable profit per share was 5.63, showing a positive return.
Q3 2077/2078: The profit per share reached 7.09, the highest in this period.
Q3 2076/2077: There was no distributable profit recorded.
Interpretation and Implications: The significant negative value in the latest quarter is alarming and indicates potential financial distress within KBL. Distributable profit per share reflects the portion of profit available for distribution to shareholders, and a negative value suggests that the bank has incurred substantial losses.
Several factors could be contributing to this decline, including:
Revenue Decline: A significant drop in revenue could lead to losses.
Increased Expenses: Higher operational costs without corresponding revenue increases can impact profitability.
Economic Downturn: Adverse economic conditions may lead to reduced income and higher default rates on loans.
Strategic Considerations for KBL:
Cost Management: Implementing stringent cost management measures to control operational expenses.
Revenue Enhancement: Exploring new revenue streams and enhancing existing ones to boost income.
Financial Restructuring: Considering financial restructuring to improve financial health and restore profitability.
Conclusion: The drastic decline in KBL’s Distributable Profit per Share is a significant concern for investors and stakeholders. Immediate strategic interventions are required to address the underlying issues and restore financial stability.
By focusing on effective cost management, revenue enhancement, and potential financial restructuring, KBL can work towards reversing the negative trend and improving shareholder value.









