By Sandeep Chaudhary
Analyzing Nepal's Inflation Trends: A Rollercoaster of Economic Pressures

Date: June 17, 2024
In recent years, Nepal has experienced fluctuating inflation rates, as evidenced by the Consumer Price Index (CPI) data from 2018/19 to mid-May 2023/24. The CPI, a critical indicator of inflation, has shown a rollercoaster pattern reflecting the diverse economic pressures the country has faced.
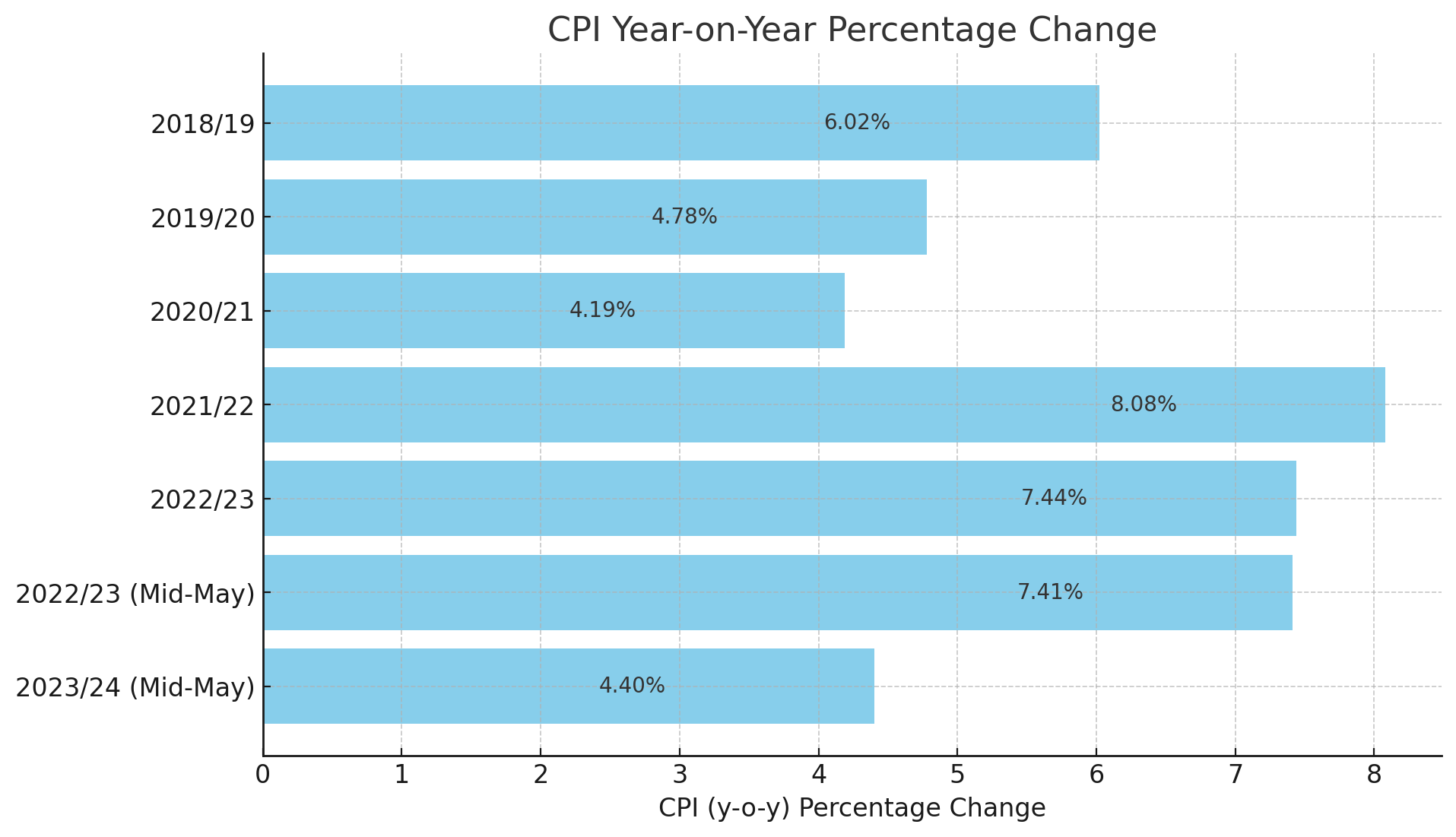
Annual CPI Analysis:
2018/19: The year-on-year CPI was recorded at 6.02%, indicating a moderate level of inflation. This period was characterized by stable economic growth and controlled price levels.
2019/20: Inflation dropped to 4.78%, showcasing an improved economic environment with better price stability.
2020/21: The CPI further declined to 4.19%, the lowest in the observed period. This could be attributed to improved agricultural outputs and effective monetary policies that kept price levels in check.
2021/22: However, inflation surged dramatically to 8.08%. This spike can be linked to global economic disruptions, supply chain issues, and increased import costs due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
2022/23: The inflation rate slightly decreased to 7.44%, yet remained high due to ongoing economic recovery challenges and persistent supply-side constraints.
Mid-May CPI Analysis:
2022/23: As of mid-May, the CPI was at 7.41%, indicating consistent inflationary pressures from the previous year.
2023/24: The most recent data shows a significant reduction in the CPI to 4.40%. This decrease suggests a possible easing of supply chain issues, stabilization of global markets, and effective domestic economic policies aimed at controlling inflation.
Interpretation: The data paints a picture of a volatile economic landscape in Nepal. The sharp rise in CPI during 2021/22 underscores the vulnerability of Nepal’s economy to global shocks and supply chain disruptions. The subsequent decline in inflation to 4.40% by mid-May 2023/24 is a positive sign, indicating that corrective measures might be taking effect.
However, the persistent high inflation rates in the years leading up to 2023/24 have had significant impacts on the cost of living, reducing the purchasing power of consumers. Policymakers need to continue focusing on stabilizing the economy by addressing supply chain vulnerabilities, promoting domestic production, and ensuring that inflationary pressures are kept in check to foster sustainable economic growth.
This analysis of Nepal’s inflation trends highlights the importance of adaptive economic strategies to mitigate the impacts of global economic fluctuations and maintain price stability for the benefit of all Nepalis.









