By Sandeep Chaudhary
Banks and Financial Institutions Show Mixed Trends in Outstanding Credit

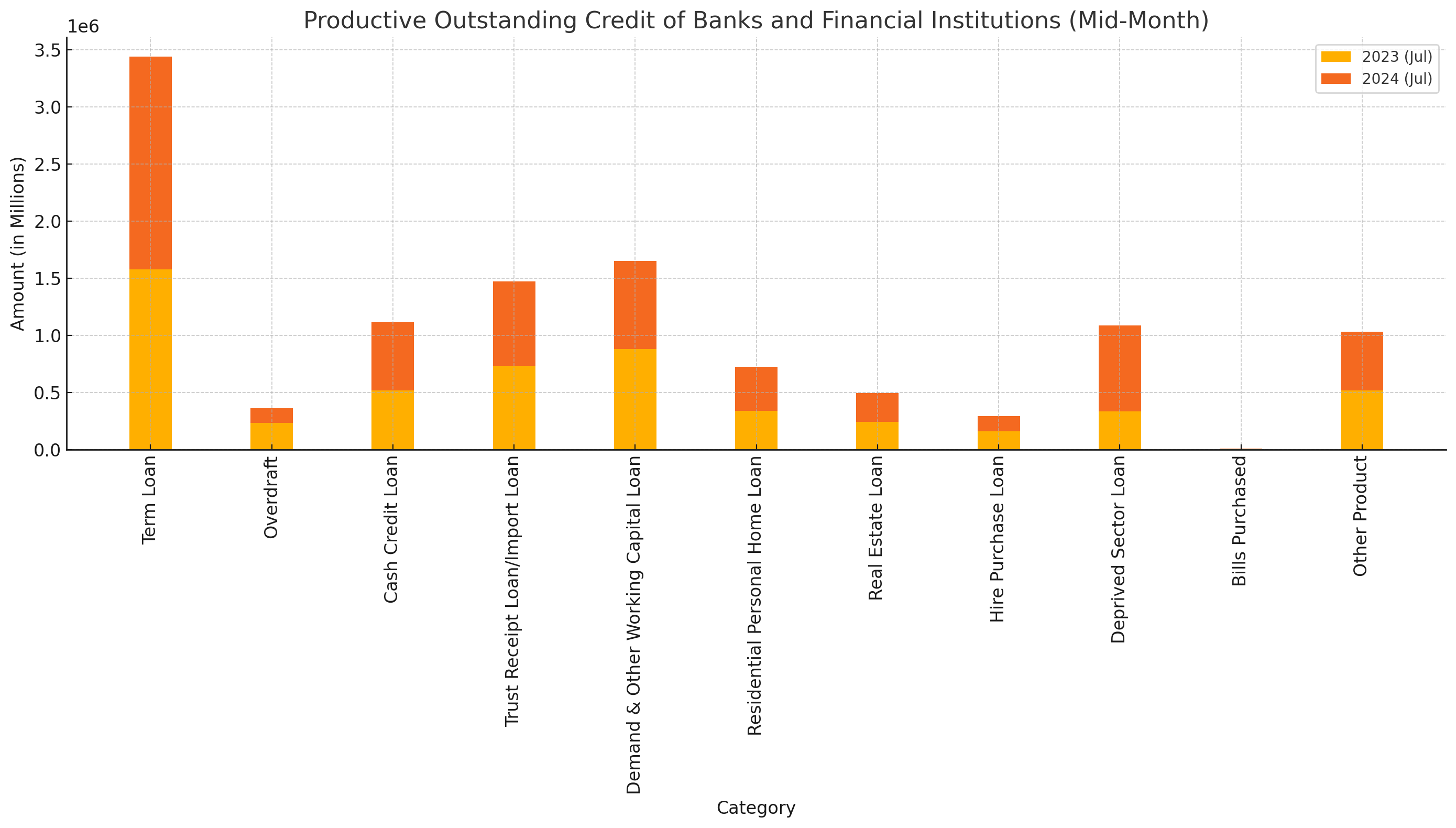
Kathmandu, June 7, 2024 - The latest report from the Nepal Rastra Bank, showcasing the productive outstanding credit of banks and financial institutions, reveals a mixed bag of growth and decline across various sectors. The data, updated to mid-month, presents insightful trends over the past three years.
Significant Highlights:
Term Loans:
The total outstanding term loans reached NPR 18,602,502 million in mid-July 2024, showing an 8.4% increase from the previous year. This growth was primarily driven by business institutions, which saw a substantial rise of 18.3%.
Industrial institutions experienced a 6.2% increase, while service sector institutions observed a modest growth of 4.9%.
Overdrafts:
Overdraft facilities showed a significant decrease of 43.7%, falling from NPR 231,886 million in mid-July 2023 to NPR 130,581 million in mid-July 2024. This decline indicates a tightening in the availability or demand for short-term credit.
Cash Credit Loans:
There has been a notable increase in cash credit loans, rising by 16.3% to NPR 601,203 million. This reflects an increased reliance on short-term borrowing by businesses to manage their operational needs.
Trust Receipt Loans/Import Loans:
Import financing, including trust receipt loans, saw a 3.2% rise, totaling NPR 734,018 million. This trend is indicative of the country's ongoing need to finance imports amid a challenging economic environment.
Demand and Other Working Capital Loans:
Working capital loans experienced a marginal decline of 2.3%, falling to NPR 771,925 million. The drop suggests a possible slowdown in business activities or a shift towards other forms of credit.
Residential Personal Home Loans:
The demand for personal home loans surged by 6.1%, reaching NPR 386,323 million. This rise underscores the continued growth in the real estate market, with more individuals investing in residential properties.
Real Estate Loans:
Loans for real estate, excluding residential personal home loans, increased by 1.2% to NPR 252,062 million. The data highlights sustained investment in the real estate sector, albeit at a slower pace compared to personal home loans.
Hire Purchase Loans:
A significant decline of 16.9% was observed in hire purchase loans, with the total falling to NPR 132,352 million. This decrease could be attributed to changing consumer behaviors or stricter lending policies.
Deprived Sector Loans:
Loans aimed at the deprived sector saw a robust growth of 7.4%, totaling NPR 752,911 million. This increase reflects ongoing efforts to support financially marginalized groups.
Bills Purchased:
There was a sharp 51.1% increase in bills purchased, indicating a higher volume of trade and commercial transactions requiring financing.
Other Products and Services:
The report also highlights growth in other loan categories, with a notable 12.5% increase in the total outstanding credit, amounting to NPR 512,487 million.
Interpretation:
The data from the Nepal Rastra Bank suggests that while there has been a substantial increase in certain types of loans, particularly those related to business and real estate, there are significant declines in areas such as overdrafts and hire purchase loans. This mixed trend could be reflective of broader economic conditions, including changing consumer behaviors, business dynamics, and possibly tighter lending regulations.
The growth in residential personal home loans and deprived sector loans is encouraging, indicating that financial institutions are supporting both individual homebuyers and marginalized communities. However, the decline in overdraft facilities and hire purchase loans might signal caution in consumer spending and a shift in borrowing preferences.
As the economy navigates through these changes, the financial sector's adaptability will be crucial in maintaining stability and fostering growth across various sectors.









