By Sandeep Chaudhary
Deposits and Private Sector Credit Continue to Rise in Nepal’s Banking Sector
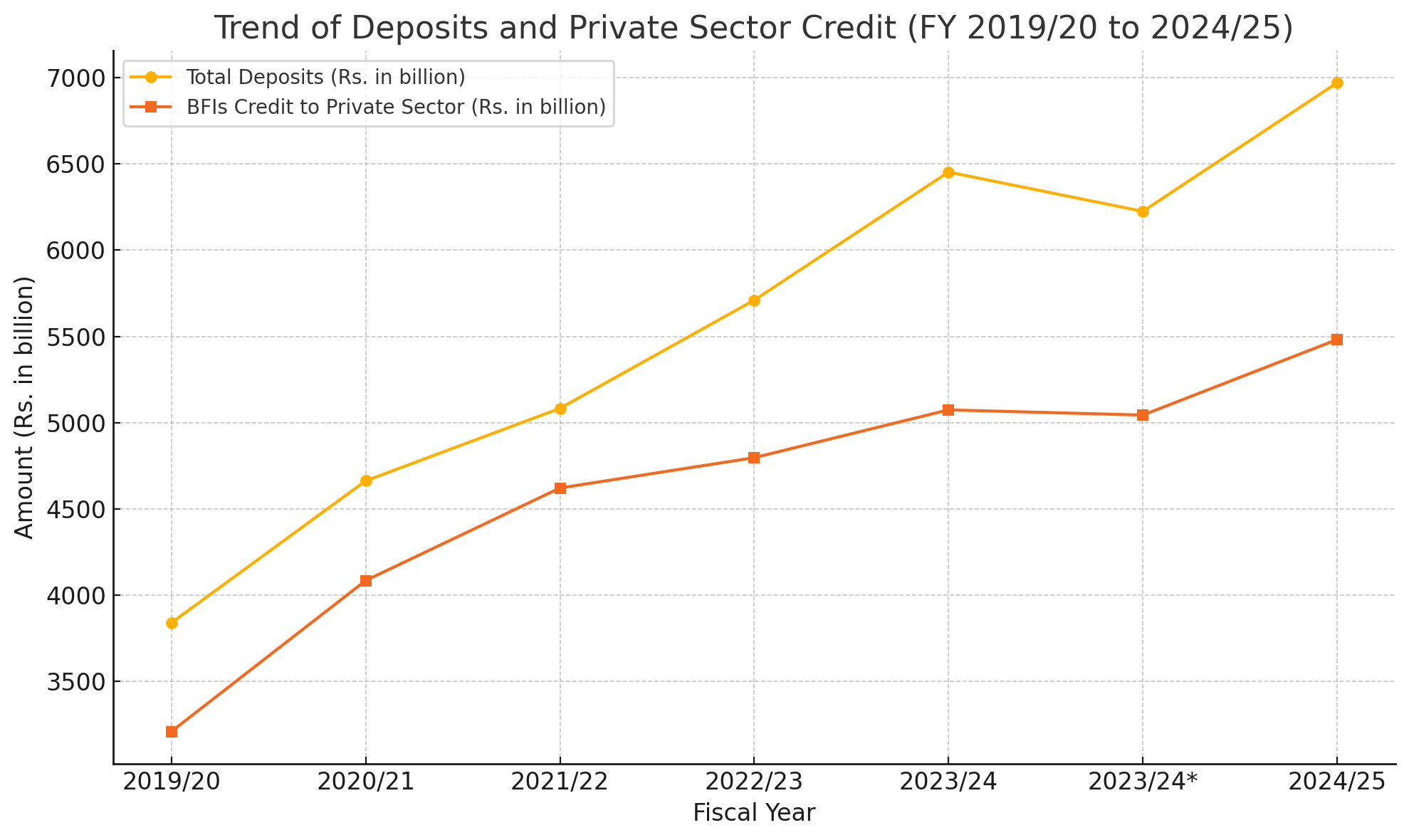
Nepal's banking sector has witnessed a consistent and healthy growth in both total deposits and credit disbursed to the private sector, according to the latest monetary data. The figures reveal that total deposits in the banking and financial institutions (BFIs) surged from Rs. 3,839.7 billion in FY 2019/20 to Rs. 6,970.0 billion in FY 2024/25. This marks a substantial increment of over Rs. 3,130 billion within six years, reflecting increased public trust in the banking system, growth in savings culture, and the gradual expansion of formal financial access.
Parallel to this, credit extended by BFIs to the private sector also climbed significantly, from Rs. 3,209.8 billion in FY 2019/20 to Rs. 5,481.6 billion in FY 2024/25. While the credit growth has been robust, it has trailed behind deposit growth in recent years, particularly after FY 2022/23. This could be indicative of tighter lending practices, risk aversion amidst economic uncertainty, or slower-than-expected demand for credit in certain sectors.
Notably, between FY 2022/23 and FY 2023/24, total deposits slightly decreased from Rs. 6,452.4 billion to Rs. 6,224.6 billion, before bouncing back to Rs. 6,970.0 billion in FY 2024/25. A similar trend was observed in private sector credit, which dipped slightly in the same period from Rs. 5,074.0 billion to Rs. 5,043.8 billion, and then recovered to Rs. 5,481.6 billion. This temporary contraction likely reflects the impact of liquidity constraints or policy tightening aimed at controlling inflation and stabilizing the financial system.
The widening gap between total deposits and private sector credit in recent years may also suggest a buildup of excess liquidity in the banking system, raising questions about investment absorption capacity and the effectiveness of financial intermediation. This scenario presents both a challenge and an opportunity for policymakers—to channel these funds into productive sectors while maintaining financial stability.
In summary, Nepal’s banking sector remains resilient with rising deposit mobilization and credit extension, though recent trends signal the need for targeted interventions to optimize credit flow, support economic growth, and ensure balanced monetary expansion.









