By Sandeep Chaudhary
Foreign Currency Transactions and IC Purchases: A Comparative Analysis

The recently released data on the purchase and sale of foreign currency for the fiscal years 2022/23 and 2023/24 reveals significant insights into the economic activities and currency management practices of the central bank.
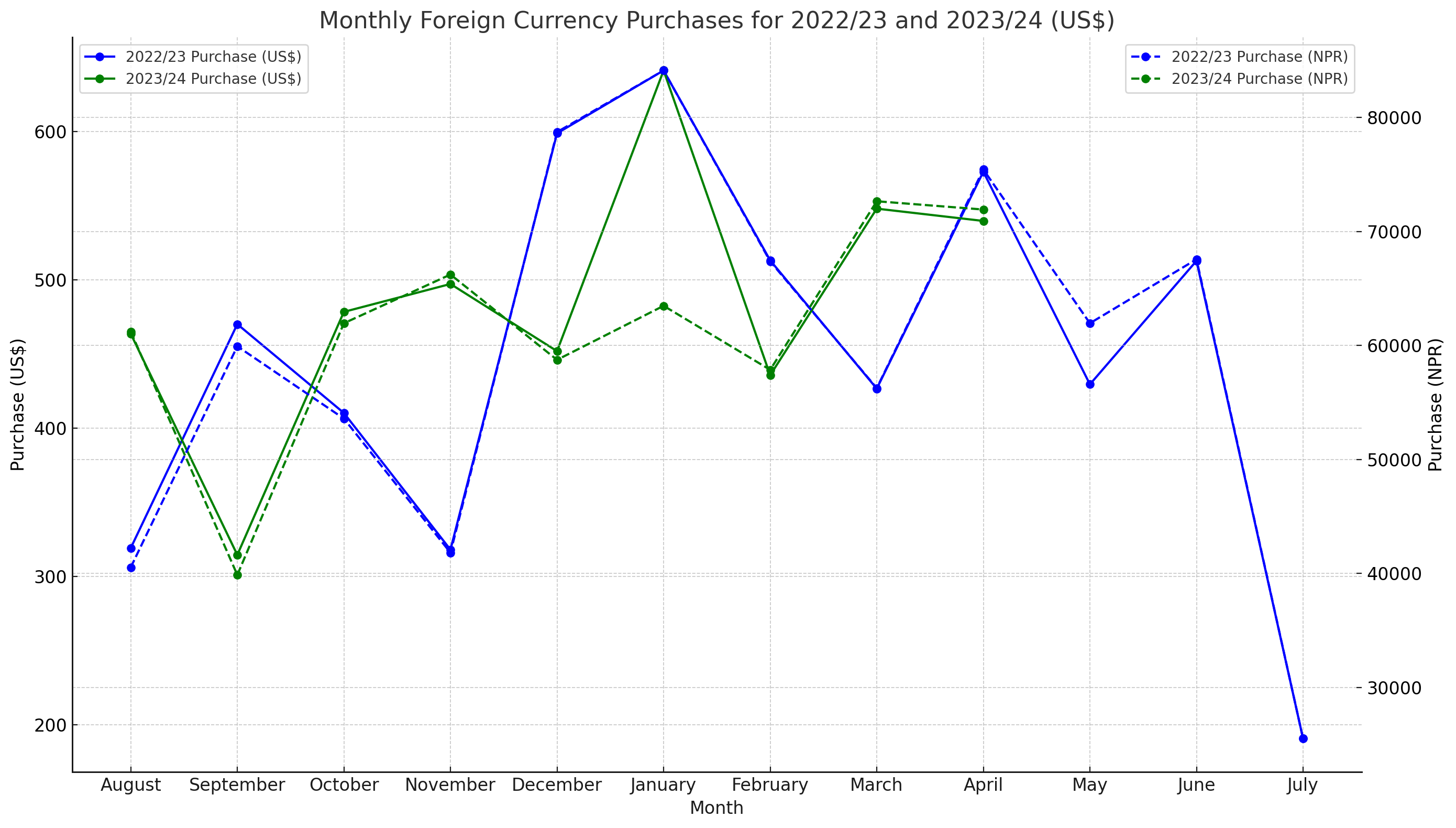
Here's the visual chart depicting the monthly foreign currency purchases for the fiscal years 2022/23 and 2023/24. The chart includes the values in both US dollars and Nepalese Rupees (NPR).
Interpretation of the Chart:
The solid lines represent the purchases in US dollars for each month in both fiscal years.
The dashed lines represent the corresponding purchases in Nepalese Rupees.
There is a noticeable pattern of higher purchases in January for both fiscal years.
The overall trend for 2023/24 appears to follow a similar trajectory to 2022/23, though some monthly variations are observed, particularly in March and April.
This visualization aids in understanding the monthly dynamics of foreign currency purchases and their corresponding value in the local currency, offering a clear comparative view between the two fiscal years.
Purchase and Sale of Convertible Currency
2022/23 Highlights:
The total purchase of convertible currency amounted to US$ 5,447.3 million, equivalent to NPR 712,500.3 million.
The net injection of convertible currency was equal to the total purchase, indicating no sales during this period.
2023/24 Highlights:
Up to the mid-month of July 2023, the total purchase of convertible currency was US$ 4,278.9 million, which equates to NPR 568,581.0 million.
Similar to the previous fiscal year, there were no sales of convertible currency, resulting in the net injection being equal to the total purchase.
IC (Indian Currency) Purchases
2022/23 Highlights:
The central bank purchased IC worth NPR 372,730.8 million.
The sale of IC was significantly lower at NPR 4,560.0 million, highlighting a net accumulation of Indian currency.
2023/24 Highlights:
Up to July 2023, the purchase of IC has drastically reduced to NPR 229,368.6 million.
The sales have remained low at NPR 2,760.0 million, continuing the trend of net accumulation of Indian currency.
Monthly Trends
2022/23:
Peak purchases of convertible currency were observed in January and April, with amounts of US$ 641.3 million and US$ 573.0 million, respectively.
Notably, the highest IC purchase was recorded in January at NPR 38,050.2 million, while the highest sale occurred in October at NPR 3,270.0 million.
2023/24:
For the ongoing fiscal year, January saw the highest purchase of convertible currency at US$ 641.3 million, while the peak for IC purchases was observed in October at NPR 10,617.6 million.
Sales activities for both currencies have remained minimal, reflecting a strategy of accumulation rather than liquidation.
Interpretation and Implications
The data suggests a strategic accumulation of both convertible and Indian currencies by the central bank. The lack of sales indicates an intent to bolster foreign currency reserves, which can provide a buffer against economic shocks and enhance the country's ability to meet its international obligations.
The reduced purchase and sale volumes in the ongoing fiscal year compared to the previous year could be indicative of a cautious approach amidst global economic uncertainties. Additionally, the higher net injection of foreign currencies supports the stability of the domestic currency, potentially mitigating inflationary pressures.
Overall, the central bank's currency management appears to be focused on maintaining a robust reserve position while managing liquidity effectively. This strategy is crucial for sustaining economic stability and fostering confidence among investors and stakeholders.