By Sandeep Chaudhary
Hydropower Investment by Commercial Banks Exceeds Regulatory Requirements

In a significant boost to the energy sector, commercial banks in Nepal have shown a commendable increase in their investments in hydropower and energy projects. According to recent data, several banks have already exceeded the regulatory requirements set by the Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB) for sectoral lending.
The NRB mandates that commercial banks allocate a minimum of 6 percent of their total credit to the energy sector by mid-July 2022. This requirement increases incrementally to 7 percent by mid-July 2023, 8 percent by mid-July 2024, and 10 percent by mid-July 2025. As of mid-April 2022, the average lending to this sector was 5.51 percent, amounting to Rs. 220.08 billion.
Leading the Charge in Hydropower Investment
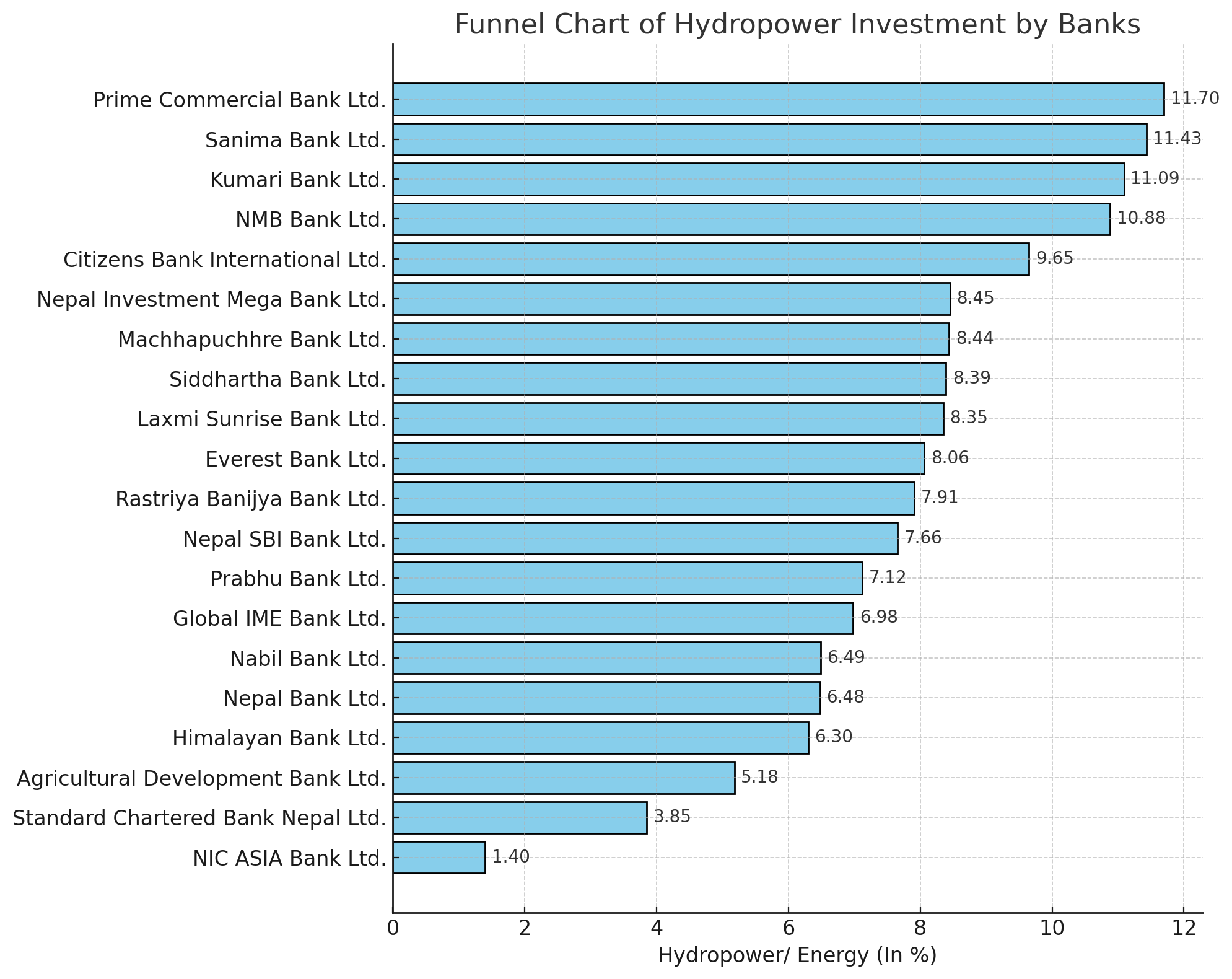
Prime Commercial Bank Ltd. tops the list with an impressive 11.70 percent of its total credit allocated to the hydropower sector. Following closely is Sanima Bank Ltd. with 11.43 percent, and Kumari Bank Ltd. at 11.09 percent. These banks have significantly surpassed the initial requirement of 6 percent, showcasing their commitment to supporting the country's energy infrastructure.
Other notable contributors include NMB Bank Ltd. at 10.88 percent, Citizens Bank International Ltd. at 9.65 percent, and Nepal Investment Mega Bank Ltd. at 8.45 percent. These banks have also made substantial investments, reflecting a strong industry trend towards prioritizing energy sector financing.
Meeting and Exceeding Regulatory Requirements
The data indicates a positive trajectory for future compliance with the NRB's escalating requirements. Many banks are already well-positioned to meet the upcoming thresholds of 7 percent by mid-July 2023 and 8 percent by mid-July 2024.
However, some banks are still catching up. For instance, Standard Chartered Bank Nepal Ltd. and NIC ASIA Bank Ltd. are at the lower end of the spectrum, with 3.85 percent and 1.40 percent, respectively. These banks will need to significantly increase their investments to meet the regulatory targets in the coming years.
Encouraging Trends and Future Prospects
The overall trend is encouraging, as the average lending to the energy sector is expected to continue its upward trajectory. This shift not only aligns with regulatory mandates but also supports the national agenda of enhancing energy production and sustainability.
The concerted efforts of these banks in increasing their hydropower investments are likely to have far-reaching impacts on Nepal's energy landscape. With a robust financial backing from the banking sector, the country can look forward to significant advancements in its hydropower capabilities, contributing to economic growth and energy security.
In conclusion, the proactive approach of Nepal's commercial banks towards meeting and exceeding regulatory requirements for hydropower investment is a positive development. It highlights the crucial role of the banking sector in supporting national infrastructure projects and fostering sustainable economic growth.









