By Sandeep Chaudhary
Imports of Major Commodities from China Show Diverse Trends in 2023/24

Kathmandu, Nepal - June 10, 2024
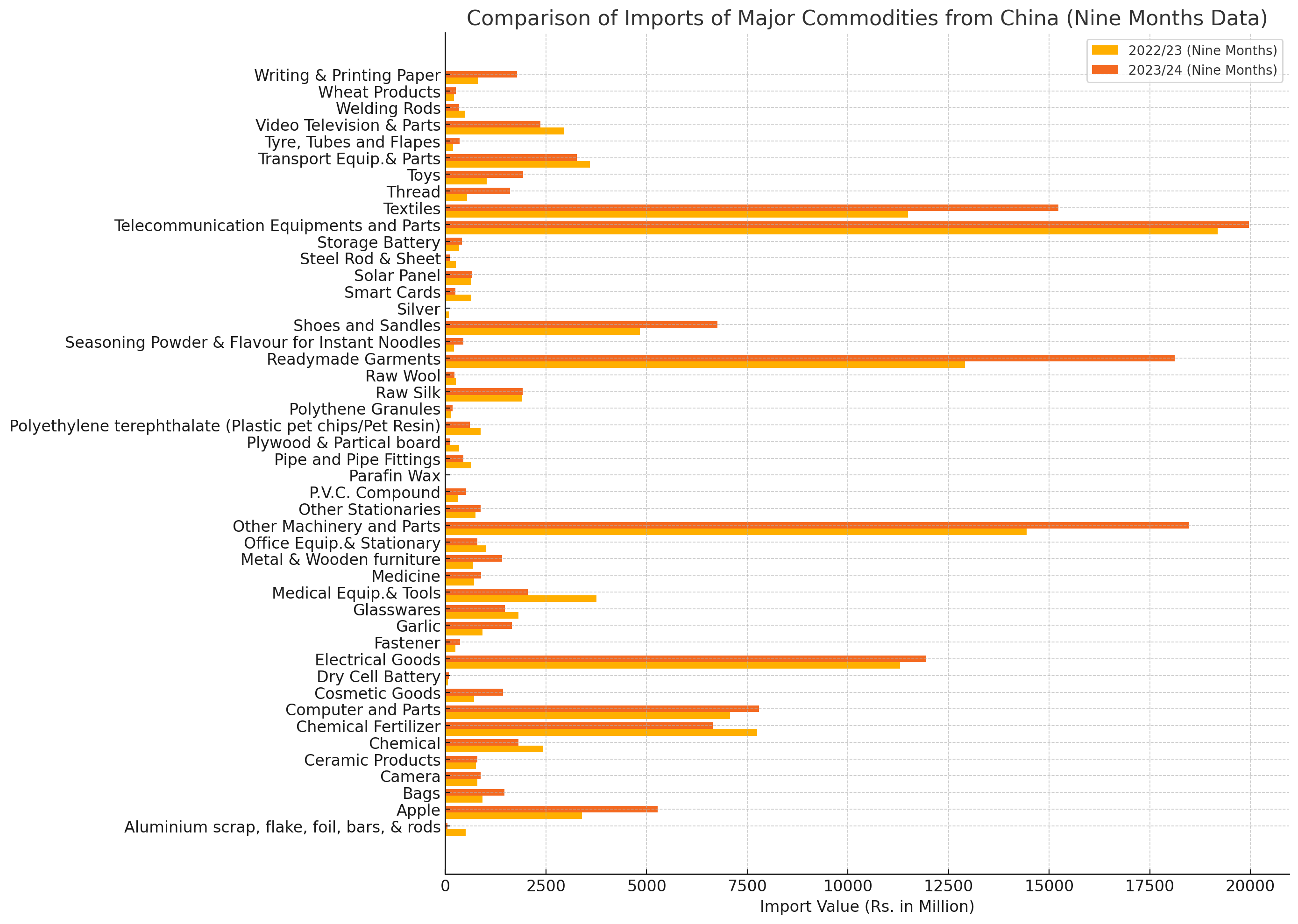
The latest data on imports of major commodities from China reveals a mixed landscape, with significant variations across different categories. The overall trend for the nine months of the fiscal year 2023/24 indicates a 15.4% increase in imports, amounting to Rs. 144,103 million compared to Rs. 124,925.1 million during the same period in the previous fiscal year.
Key highlights from the report include:
Apple Imports Surge: Apple imports have seen a notable rise by 55.4%, reaching Rs. 5,274.3 million from Rs. 3,393.2 million. This increase is reflective of the growing demand for imported fruits.
Garlic Imports Increase: Garlic imports have surged by 77.7%, indicating a significant rise from Rs. 927.5 million to Rs. 1,648.3 million. This may be attributed to higher domestic consumption and culinary trends.
Readymade Garments: Imports of readymade garments have increased by 40.3%, with figures rising from Rs. 12,907.6 million to Rs. 18,115.8 million. This growth highlights the robust demand for Chinese apparel in Nepal.
Writing and Printing Paper: The import of writing and printing paper has seen a staggering increase of 121.2%, amounting to Rs. 1,779.5 million, up from Rs. 804.6 million. This significant rise could be due to increased educational and office activities.
Chemical Fertilizer: The import of chemical fertilizers decreased by 14.2%, from Rs. 7,747.8 million to Rs. 6,648.4 million, reflecting a possible shift towards organic farming practices or changes in agricultural policies.
Medical Equipment and Tools: Imports in this category dropped drastically by 45.3%, indicating a decline from Rs. 3,748.9 million to Rs. 2,049.0 million. This might be due to a stabilization post-pandemic or increased local production.
Cosmetic Goods: There was a notable increase of 101.0% in the import of cosmetic goods, from Rs. 711.3 million to Rs. 1,429.8 million, reflecting rising consumer interest in beauty and personal care products.
Telecommunication Equipment and Parts: The import of telecommunication equipment and parts experienced a slight increase of 4.1%, amounting to Rs. 19,962.8 million from Rs. 19,180.7 million, showcasing steady growth in the telecommunication sector.
Tyre, Tubes, and Flaps: This category saw an 87.3% increase, growing from Rs. 189.6 million to Rs. 355.0 million, indicating higher demand for automotive parts.
Seasoning Powder and Flavor for Instant Noodles: Imports in this category grew by 103.6%, from Rs. 220.5 million to Rs. 448.8 million, highlighting the popularity of instant noodles and associated seasonings.
While some categories showed impressive growth, others faced significant declines. For instance, the import of aluminium scrap, flake, foil, bars, and rods plummeted by 89.3%, and imports of video television and parts dropped by 20.2%.
Overall, the data portrays a dynamic trade relationship with China, reflecting changing consumption patterns and economic activities within Nepal. The diverse trends in imports signify shifts in market demands, technological advancements, and potential policy impacts.
As the fiscal year progresses, these figures will be crucial for policymakers and businesses to understand the evolving economic landscape and to strategize accordingly.









