By Sandeep Chaudhary
Nepal’s Expanding Financial Access Landscape as of Baisakh End 2082
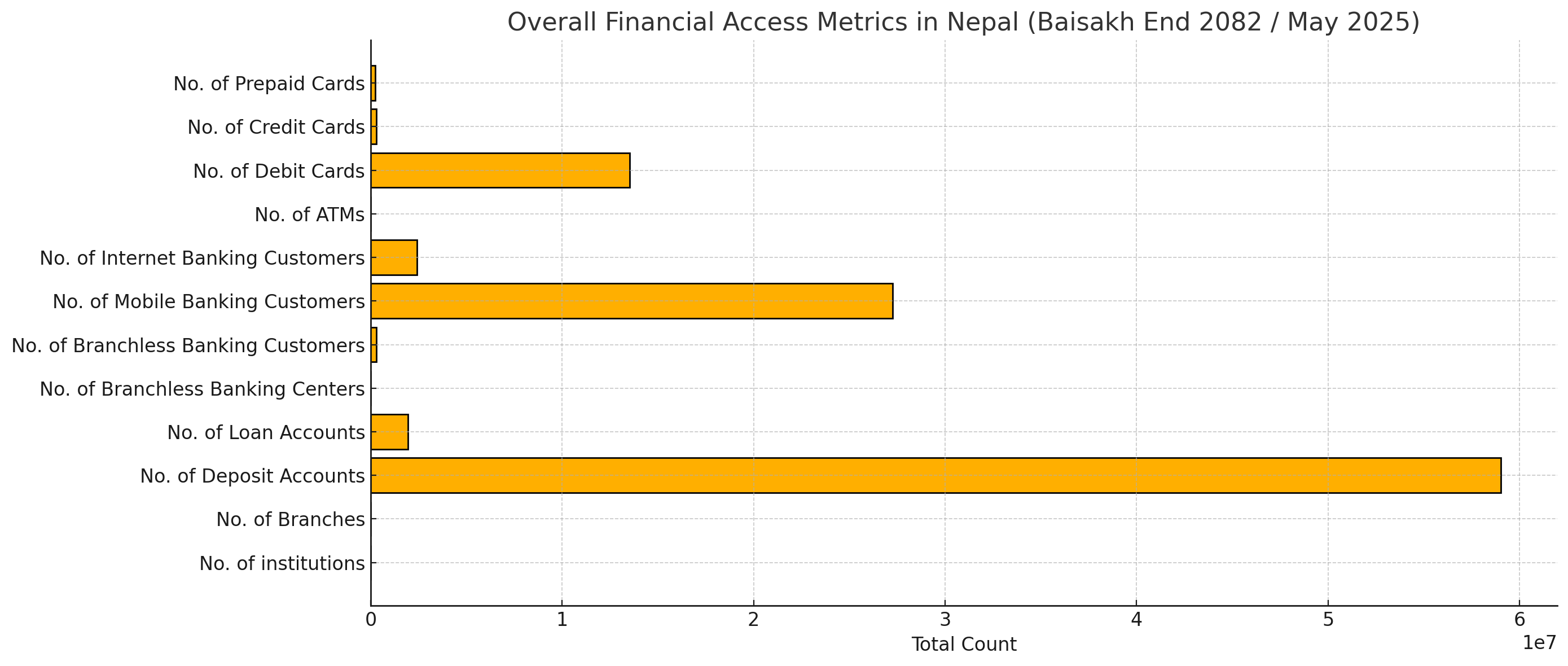
Nepal’s banking and financial sector has seen a significant expansion in terms of financial access and customer outreach, as highlighted by recent data from Nepal Rastra Bank for the period ending Baisakh 2082 (Mid-May 2025). The report covers 54 licensed institutions, including 20 Class “A” commercial banks, 17 Class “B” development banks, and 17 Class “C” finance companies.
A total of 6,507 branches are operational nationwide, dominated by Class "A" banks with 5,083 outlets, followed by Class "B" with 1,133 and Class "C" with 291. This extensive network supports a massive 59 million deposit accounts, with commercial banks alone accounting for over 50 million of these.
Loan accessibility has also expanded, with 19.53 lakh loan accounts across all classes of institutions. Class “A” banks again lead with over 16 lakh loan accounts, followed by development banks (2.72 lakh) and finance companies (47,656).
Innovative banking models like branchless banking are gaining traction, although their spread is still limited. There are 951 branchless banking centers serving nearly 2.88 lakh customers, almost all of which are handled by Class “A” banks.
In terms of digital banking, adoption continues to rise. Mobile banking users have reached 27.26 million, with the largest base under Class “A” banks. Similarly, internet banking services have been accessed by over 2.4 million users, again with a dominant share under commercial banks.
ATM networks have expanded, with 5,266 ATMs installed across the country—4,881 by Class "A" alone. The use of plastic money has also grown, with 13.5 million debit cards, over 3 lakh credit cards, and 2.4 lakh prepaid cardscurrently in circulation.
This data indicates that Nepal’s financial institutions are rapidly expanding their physical and digital presence to cater to a growing customer base. The dominance of Class “A” commercial banks in almost every metric also highlights their pivotal role in financial inclusion. However, Class “B” and “C” institutions are also contributing significantly, especially in rural and underserved segments.
Overall, the numbers reflect a positive trajectory toward broader financial access, digital banking penetration, and a more inclusive financial ecosystem across Nepal.









