By Sandeep Chaudhary
Significant Changes in Sectorwise Outstanding Credit of Banks and Financial Institutions

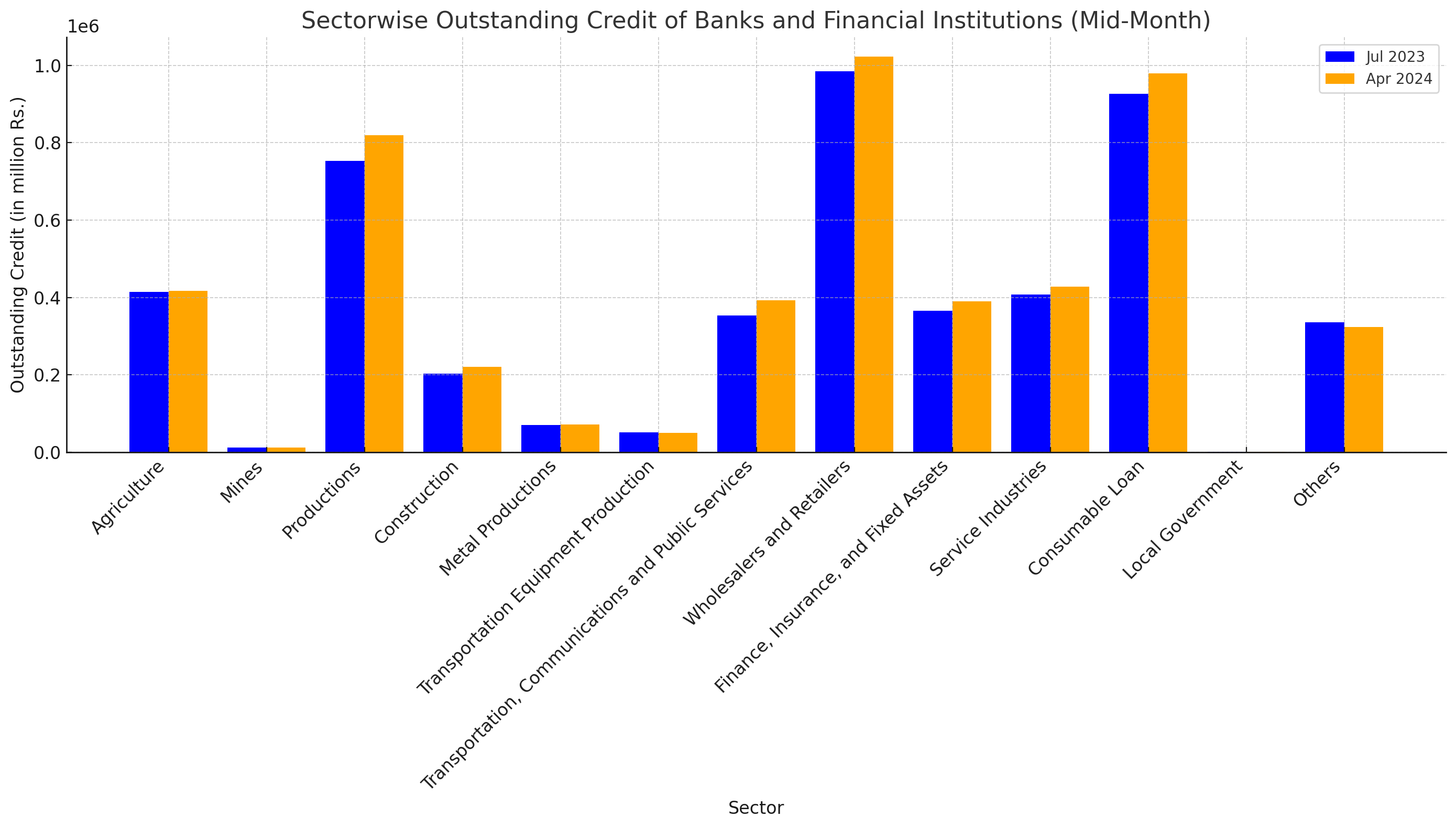
In the latest data released for mid-month 2024, the sectorwise outstanding credit of banks and financial institutions reveals notable trends and shifts across various sectors of the economy. This data, spanning from July 2022 to April 2024, offers insights into the evolving landscape of credit distribution among different industries. Here's an in-depth analysis of the key findings:
Agriculture Sector
The agriculture sector experienced a modest increase in outstanding credit, rising from Rs. 414,661.3 million in July 2023 to Rs. 417,567.8 million in April 2024, marking a growth of 0.7%. However, certain sub-sectors faced declines; for instance, Forest, Fish Farming, and Slaughter dropped significantly by 24.2%, and Tea witnessed a reduction of 6.1%.
Mines Sector
Credit to the mines sector saw a slight increase of 3.0% from July 2023 to April 2024. Noteworthy is the substantial increase in credit to Metals (Iron, Lead, etc.), which grew by 15.1%, while Oil and Gas Extraction faced a significant decline of 26.4%.
Productions Sector
The productions sector recorded an impressive increase of 8.8% in outstanding credit, reaching Rs. 819,010.6 million by April 2024. This growth was driven by sub-sectors like Food Production, which saw an 11.1% rise, and Agriculture and Forest Production, with an 18.0% increase. The Metals - Basic Iron and Steel Plants sub-sector experienced a significant surge of 22.3%.
Construction Sector
The construction sector showed a notable increase of 8.7% in credit, with residential construction experiencing a marginal rise of 1.2%. However, the non-residential construction sub-sector saw a significant increase of 23.9%, reflecting a robust expansion in this area.
Transportation and Public Services
This sector witnessed an 11.0% increase in outstanding credit, with significant contributions from the Electricity sub-sector, which rose by 14.5%. Conversely, the Railways and Passengers Vehicles sub-sector experienced a decline of 11.5%.
Wholesalers and Retailers
The wholesalers and retailers sector recorded a 3.8% increase in credit, with Wholesale Business - Durable Commodities seeing a notable rise of 12.9%. However, Other Retail Business faced a decline of 3.0%.
Finance, Insurance, and Fixed Assets
Credit in this sector increased by 6.7%, driven by sub-sectors like Microfinance Financial Institutions, which saw a 7.0% rise. Non-Financial Government Institutions also experienced substantial growth of 37.5%.
Service Industries
Service industries saw a 4.9% increase in outstanding credit, with significant contributions from the Hotel sub-sector, which grew by 8.5%, and the Hospitals and Health Services sub-sector, which increased by 2.9%.
Consumable Loans
Consumable loans sector experienced a 5.7% increase, with sub-sectors like Credit Card loans seeing an 18.9% rise, reflecting an increase in consumer spending and borrowing.
Local Government
Credit to local government also increased by 8.4%, indicating a growing reliance on credit for local government activities and projects.
Overall Trends
Overall, the total outstanding credit across all sectors increased by 5.1% from July 2023 to April 2024, reflecting a healthy growth trajectory in the economy. This growth highlights the continued expansion and diversification of credit across various sectors, supporting economic development and resilience.
The data underscores the dynamic nature of credit distribution in the economy, with certain sectors experiencing significant growth while others face challenges. These trends provide valuable insights for policymakers, financial institutions, and investors, helping them make informed decisions in the evolving economic landscape.









