By Sandeep Chaudhary
Understanding EPS Variants: EPS-TTM, EPS-Adjusted, EPS-Diluted, and EPS-Annualized

Earnings Per Share (EPS) Variants:
Earnings Per Share (EPS) has several variants that provide different insights into a company's profitability. These include EPS-TTM, EPS-Adjusted, EPS-Diluted, and EPS-Annualized. Each variant serves a specific purpose and caters to different analytical needs.
1. EPS-TTM (Earnings Per Share - Trailing Twelve Months)
EPS-TTM provides an earnings snapshot over the past twelve months. This measure is useful for evaluating a company's recent performance without being influenced by seasonality or single-quarter anomalies.
Formula:

Explanation:
Net Income (TTM): Sum of net income for the past four quarters.
Preferred Dividends (TTM): Sum of preferred dividends paid over the past four quarters.
Weighted Average Shares Outstanding (TTM): Average number of shares outstanding over the past twelve months.
2. EPS-Adjusted
EPS-Adjusted excludes one-time gains, losses, and other non-recurring items to provide a clearer picture of a company’s ongoing profitability.
Formula:

Explanation:
Adjusted Net Income: Net income adjusted for non-recurring items, such as asset sales, restructuring costs, or litigation expenses.
Preferred Dividends: Dividends promised to preferred shareholders.
Weighted Average Shares Outstanding: Average number of shares outstanding during the period.
3. EPS-Diluted
EPS-Diluted accounts for all potential shares that could be created through convertible securities, options, and warrants, providing a conservative view of earnings per share.
Formula:
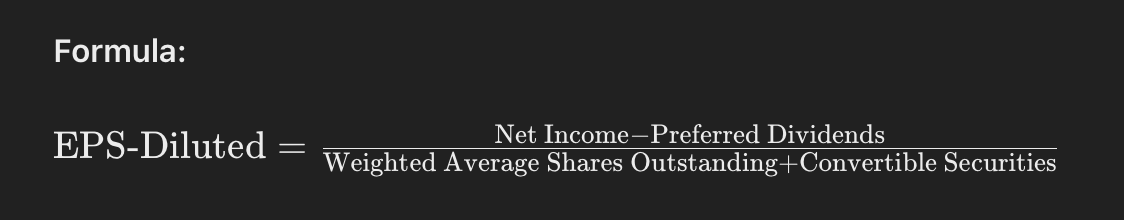
Explanation:
Net Income: Total profit after all expenses and taxes.
Preferred Dividends: Dividends promised to preferred shareholders.
Weighted Average Shares Outstanding: Average number of shares outstanding.
Convertible Securities: Potential shares from options, warrants, and convertible bonds.
4. EPS-Annualized
EPS-Annualized projects a company's earnings over a full year based on its most recent performance, useful for companies with seasonal earnings.
Formula:

Explanation:
EPS (most recent period): EPS calculated for the most recent quarter or half-year.
Number of Months in the Period: The duration of the period used to calculate the recent EPS.
Summary:
Each variant of EPS offers a unique perspective:
EPS-TTM provides a recent historical view.
EPS-Adjusted offers a clearer picture by excluding non-recurring items.
EPS-Diluted presents a conservative measure considering potential share dilution.
EPS-Annualized projects earnings over a full year based on recent performance.
Understanding these variants helps investors make more informed decisions by providing a comprehensive view of a company's profitability.









