By Sandeep Chaudhary
Understanding the Credit-Deposit (CD) Ratio According to NRB Guidelines

The Credit-Deposit (CD) Ratio is a fundamental measure of a bank's liquidity and efficiency in managing its deposits and lending activities. According to the guidelines set by Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB), maintaining an optimal CD Ratio is vital for ensuring financial stability and operational efficiency in the banking sector.
The CD Ratio indicates the proportion of a bank's deposits that are used for lending. A higher CD Ratio means that a significant portion of deposits is being utilized for loans, which can enhance profitability but also increase the risk of liquidity shortages. On the other hand, a lower CD Ratio suggests that the bank is holding onto more deposits, potentially reflecting inefficiency in fund utilization.
As per NRB guidelines, banks are required to maintain their CD Ratio within a specified range to ensure they have enough liquid assets to meet withdrawal demands and other obligations. This regulatory measure helps in balancing the dual objectives of profitability and liquidity management.
To calculate the CD Ratio, the NRB uses a simple formula:
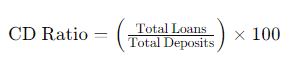
This formula highlights the relationship between the total loans disbursed by the bank and the total deposits it has mobilized. By keeping this ratio within the prescribed limits, banks can ensure they are neither over-leveraging their deposits nor underutilizing their resources.
In conclusion, the CD Ratio is a crucial metric for assessing a bank's financial health and operational efficiency. By adhering to NRB guidelines, banks can effectively manage their liquidity, mitigate risks, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards, thereby promoting a stable and robust banking environment.









