By Sandeep Chaudhary
Analysis of Export Trends of Major Commodities from Nepal to India

Overall Decline in Exports
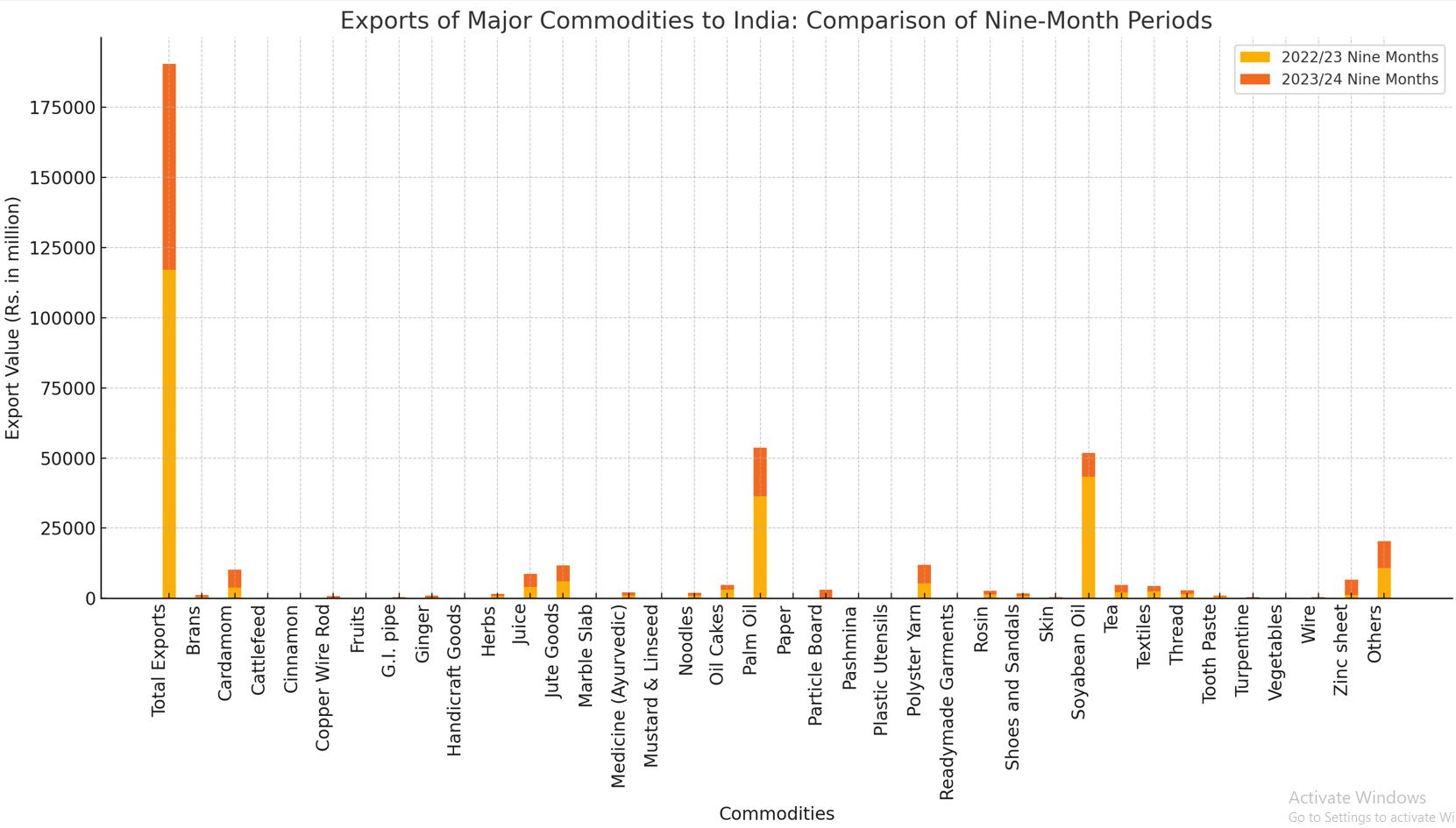
The total export value of major commodities has significantly declined over the observed periods. From an annual value of Rs. 140,697.9 million in 2021/22, exports fell to Rs. 93,287.0 million in 2022/23 and further dropped to Rs. 62,020.2 million in the first nine months of 2023/24. This represents a decrease of 37.4% from 2021/22 to 2022/23 and a further 15.4% decline in the latest nine-month period.
Key Commodities with Significant Changes
Soyabean Oil and Palm Oil: Both commodities experienced drastic reductions in export values. Soyabean oil exports dropped by 80.5% in 2022/23 and a staggering 90.2% in the first nine months of 2023/24. Similarly, palm oil saw a 52.5% decrease in 2022/23 and a further 67.0% decline in 2023/24.
Textiles and Readymade Garments: The textiles category showed a decline of 26.5% in 2022/23, but only a marginal increase of 0.8% in 2023/24. Readymade garments, however, have shown growth, with a 29.5% increase in 2022/23 and a further 17.4% increase in the latest period.
Cardamom: Exports of cardamom increased significantly by 66.0% in 2022/23. However, this upward trend reversed slightly in 2023/24, showing a minor decrease of 0.8%.
Ginger and Herbs: Ginger exports saw a significant rise of 154.9% in 2022/23, followed by a 38.9% increase in the recent nine months. Similarly, herbs experienced an 11.7% increase in 2022/23 and a substantial 28.0% rise in 2023/24.
Copper Wire Rod: This commodity displayed a positive trend with a 66.7% increase in 2022/23 and a further 47.5% rise in the latest period.
Commodities with Mixed Trends
Juice: Juice exports increased by 13.3% in 2022/23 and saw a further 37.6% rise in 2023/24.
Pashmina: Pashmina exports showed a significant rise of 223.7% in 2022/23 and continued to grow by 16.6% in 2023/24.
Wire and Zinc Sheet: Both commodities experienced substantial growth, with wire exports increasing by 145.4% and zinc sheet exports growing by 58.1% in the latest period.
Notable Declines
Brans and Cattlefeed: Both these commodities experienced significant declines. Brans saw an 86.6% increase in 2022/23 but a drastic fall of 50.8% in 2023/24. Cattlefeed exports plummeted by 61.2% in 2022/23 and further by 99.9% in 2023/24.
Mustard & Linseed, Noodles, and Oil Cakes: Mustard & linseed exports ceased entirely in the observed periods. Noodles saw a decrease of 17.9% and 20.9% in consecutive periods. Oil cakes exports fell by 41.8% in 2022/23 but showed a recovery with a 23.0% increase in 2023/24.
Overall Interpretation
The data highlights a concerning trend of declining exports to India across several key commodities. While certain categories such as ginger, herbs, and specific manufactured goods have shown growth, the overall export performance reflects significant challenges. The drastic declines in major export commodities like soyabean oil and palm oil have heavily impacted the total export values.
Strategic measures and interventions may be required to address these declines and revitalize the export sector. Exploring new markets, enhancing product quality, and addressing trade barriers could be pivotal steps in reversing the current downward trend.









