By Sandeep Chaudhary
Analysis of Nepal Banking Sector Net Liquidity Percentages As on Chait end, 2080 (Mid-April 2024)

Understanding Bank Net Liquidity
Net Liquidity Percentage, calculated as Net Liquid Assets to Total Deposits, is a critical measure of a bank's financial health and stability. This ratio indicates a bank's ability to meet its short-term obligations and is essential for maintaining depositor confidence and regulatory compliance. In Nepal, the minimum required net liquidity percentage is set at 20%.
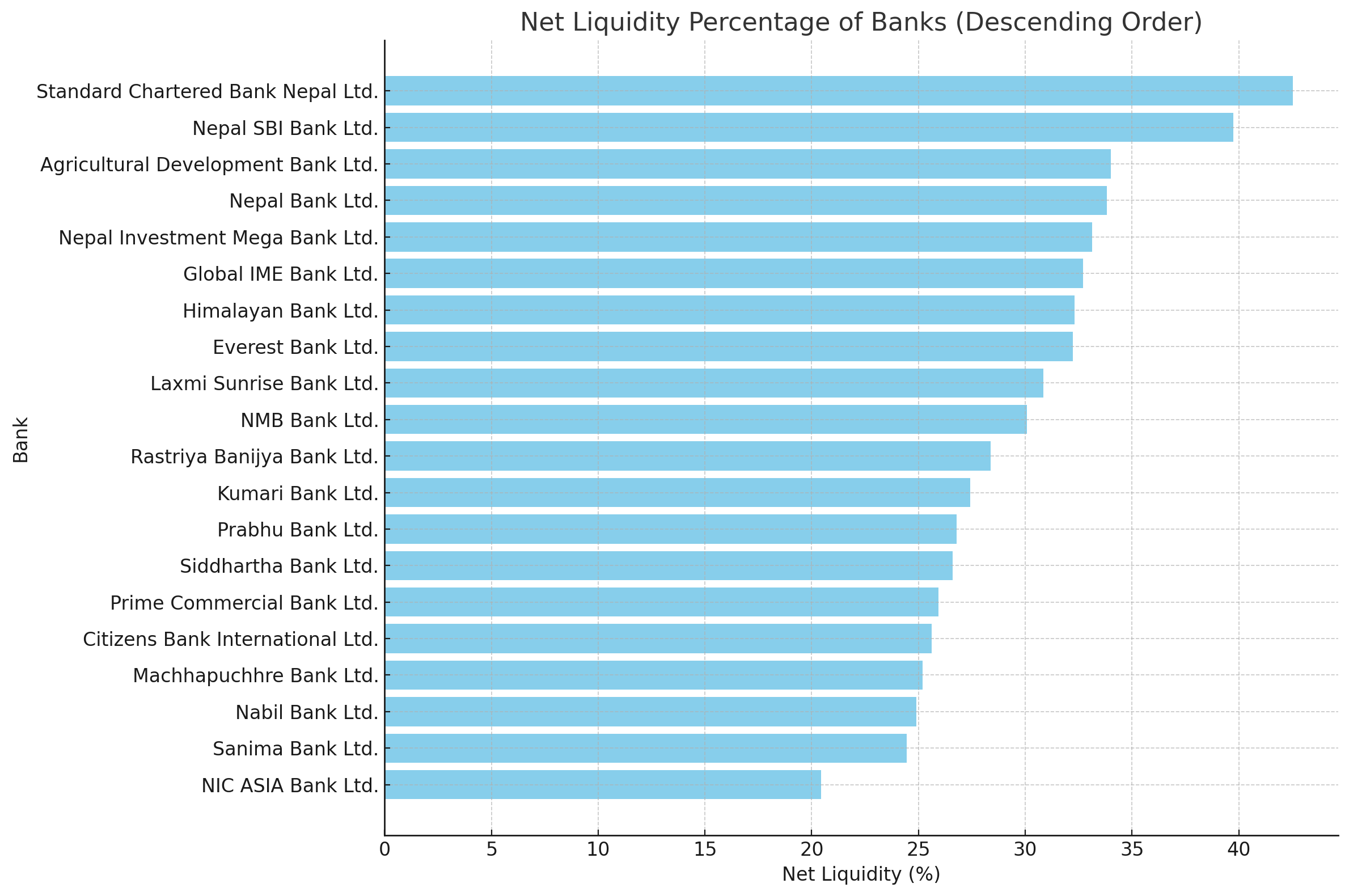
Banks with the Highest Liquidity
The latest data reveals that several banks have significantly exceeded the minimum liquidity requirement, showcasing robust financial management and resilience. Standard Chartered Bank Nepal Ltd. leads the chart with an impressive net liquidity percentage of 42.53%, followed by Nepal SBI Bank Ltd. at 39.75%. These banks have demonstrated exceptional liquidity management, ensuring they have sufficient liquid assets to cover any immediate withdrawal demands from their depositors.
Performance of Other Banks
Other notable performers include the Agricultural Development Bank Ltd. with a net liquidity of 34.02% and Nepal Bank Ltd. at 33.83%. These figures indicate a strong liquidity position, reflecting prudent asset management and a conservative approach to risk.
Banks like Nepal Investment Mega Bank Ltd. (33.12%), Global IME Bank Ltd. (32.71%), and Himalayan Bank Ltd. (32.32%) also show commendable liquidity levels, comfortably surpassing the regulatory threshold.
Areas of Concern
However, not all banks are performing equally well. NIC ASIA Bank Ltd., with a net liquidity percentage of 20.44%, barely meets the minimum requirement. This close margin suggests potential vulnerabilities that could pose risks during financial stress. Banks like Machhapuchhre Bank Ltd. (25.18%) and Nabil Bank Ltd. (24.90%) also have lower liquidity percentages, indicating the need for improved asset management strategies.
Conclusion
Overall, while many banks in Nepal exhibit strong liquidity positions, ensuring they can meet depositor demands and regulatory requirements, some banks need to enhance their liquidity management practices. Maintaining a healthy net liquidity percentage is crucial for sustaining depositor confidence and achieving long-term financial stability.
As the banking sector continues to navigate economic challenges, maintaining and improving net liquidity ratios will remain a top priority for financial institutions to ensure resilience and trust in the system.









