By Sandeep Chaudhary
Analyzing Nepal's Banking Sector: Key Financial Indicators and Trends

As of the end of Baisakh 2081 (mid-May 2024), the latest financial indicators reveal a robust performance across various classes of banks in Nepal. The data highlights significant trends in deposit, credit, liquidity, capital adequacy, financial access, and interest rates, reflecting the overall health and resilience of the banking sector.
Credit and Deposit Ratios
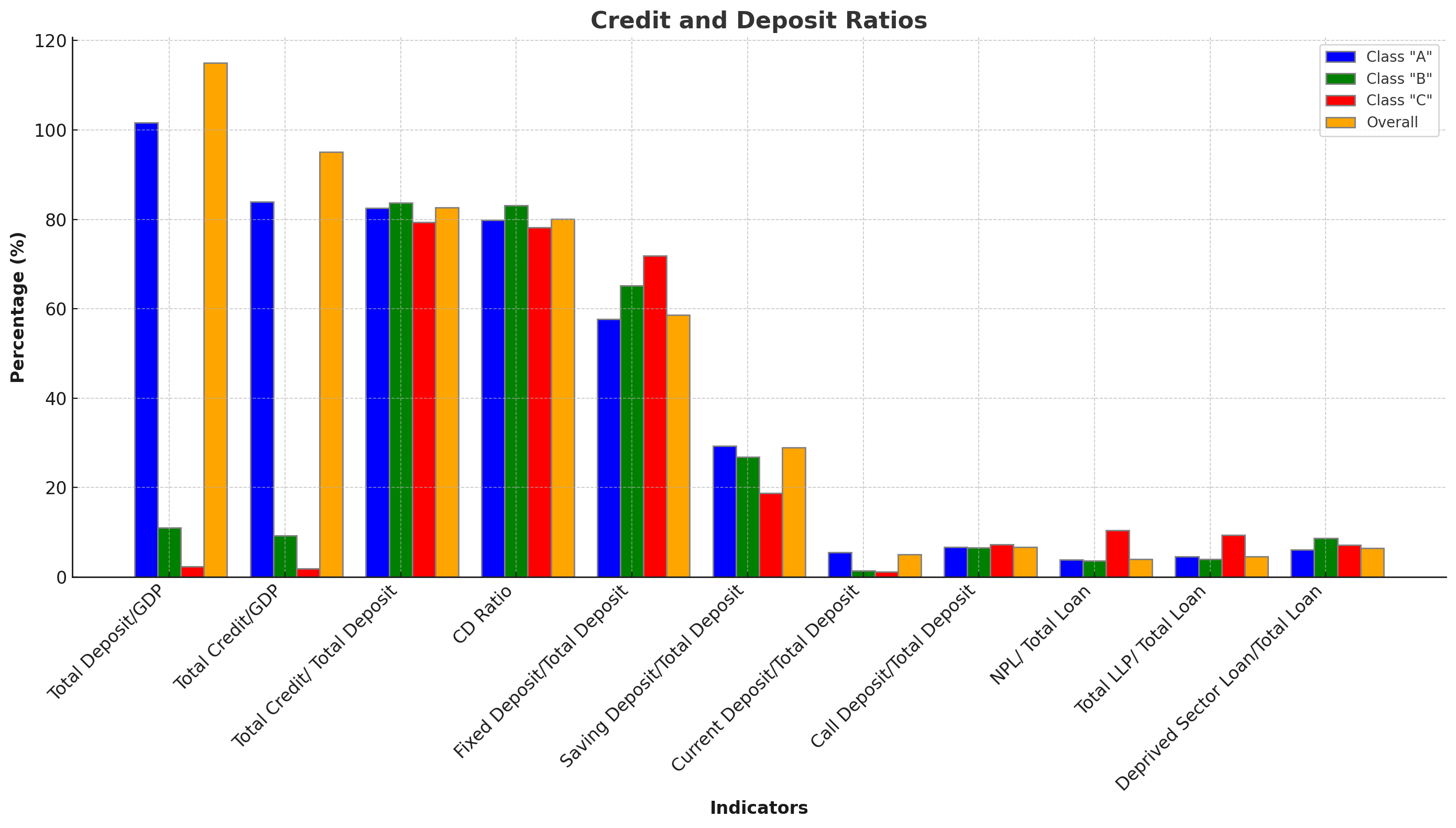
Here is a visual representation of the Credit and Deposit Ratios for Class "A", Class "B", Class "C" banks, and the overall figures. The chart illustrates the performance of various credit and deposit indicators, helping to provide a clear understanding of the financial health of different bank classes
The total deposit to GDP ratio stands impressively at 115.03%, indicating a strong deposit base relative to the size of the economy. Class "A" banks lead with a deposit to GDP ratio of 101.69%, followed by Class "B" and Class "C" banks with 11.03% and 2.31%, respectively. This strong deposit base provides a solid foundation for lending activities.
The total credit to GDP ratio is also robust at 95.01%, showcasing the banking sector's vital role in providing credit to the economy. Class "A" banks account for 83.95% of this figure, demonstrating their dominance in credit distribution.
Liquidity
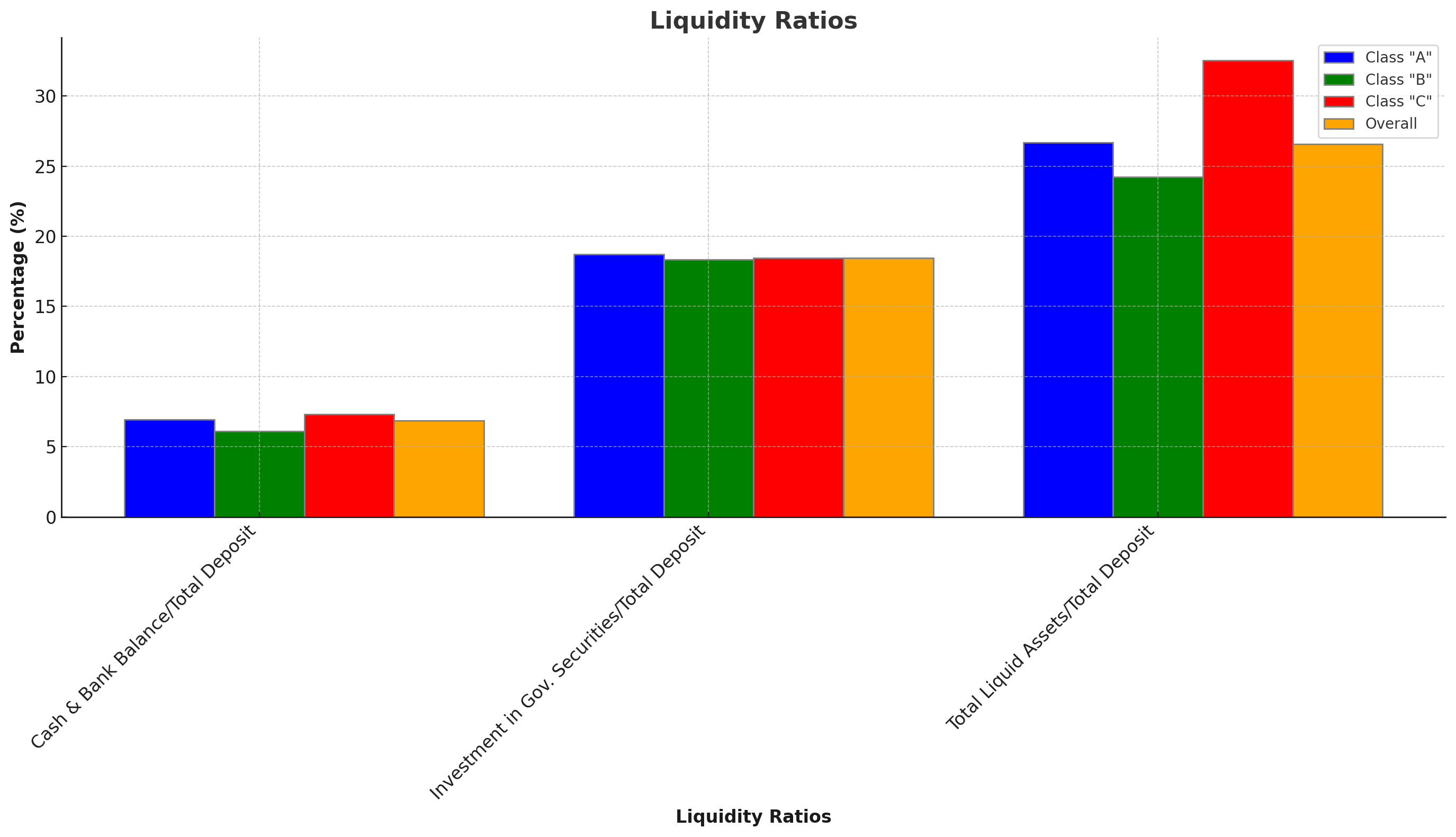
Liquidity ratios indicate healthy liquidity management across banks. The cash and bank balance to total deposit ratio is 6.88%, while investments in government securities represent 18.47% of total deposits. Notably, Class "C" banks maintain the highest liquidity with a total liquid assets to total deposit ratio of 32.54%.
Capital Adequacy
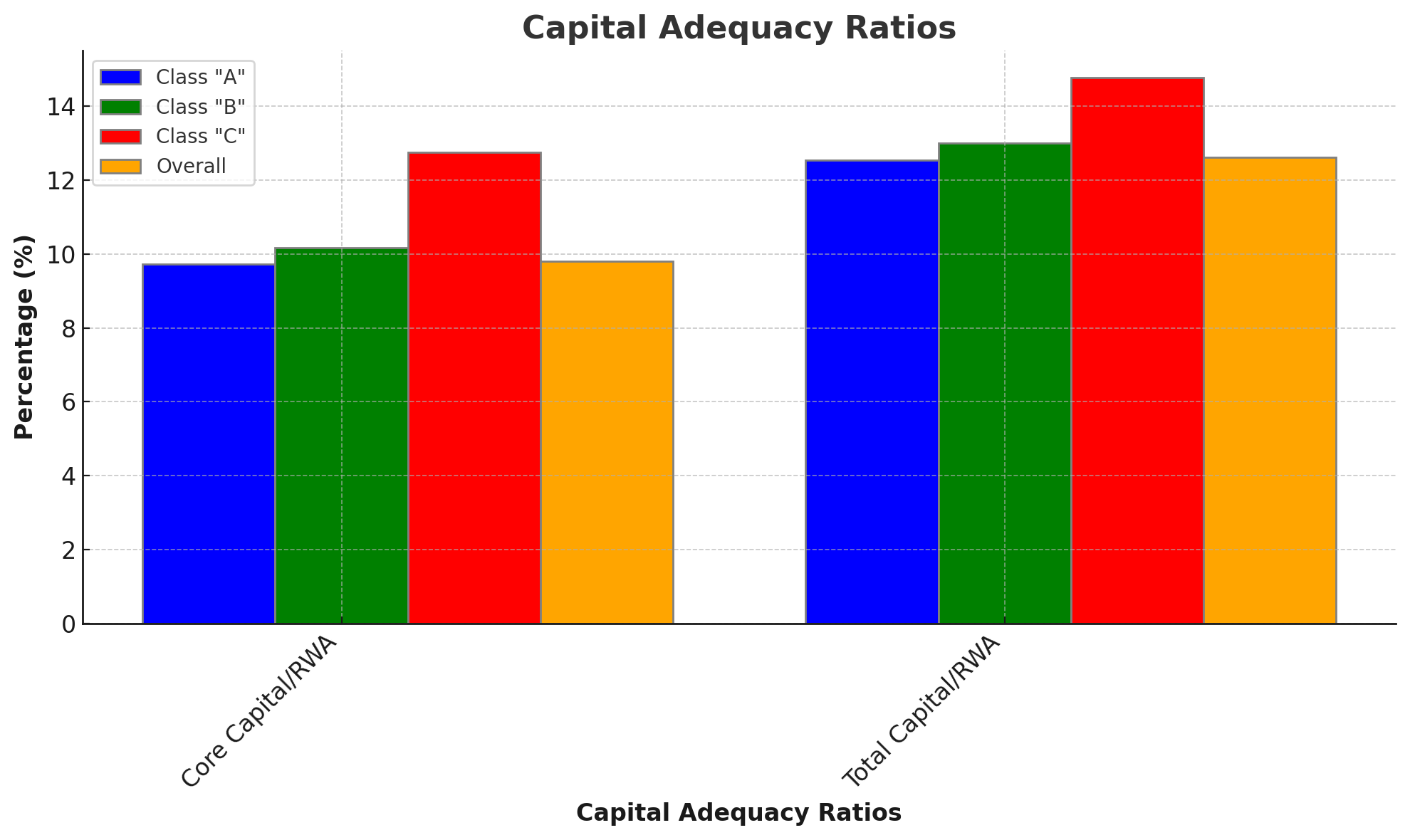
Capital adequacy ratios reveal that the banks are well-capitalized, with the overall Core Capital/RWA ratio at 9.81% and Total Capital/RWA ratio at 12.61%. Class "C" banks show the highest capital adequacy with ratios of 12.74% for Core Capital/RWA and 14.77% for Total Capital/RWA, ensuring a strong buffer against potential risks.
Financial Access
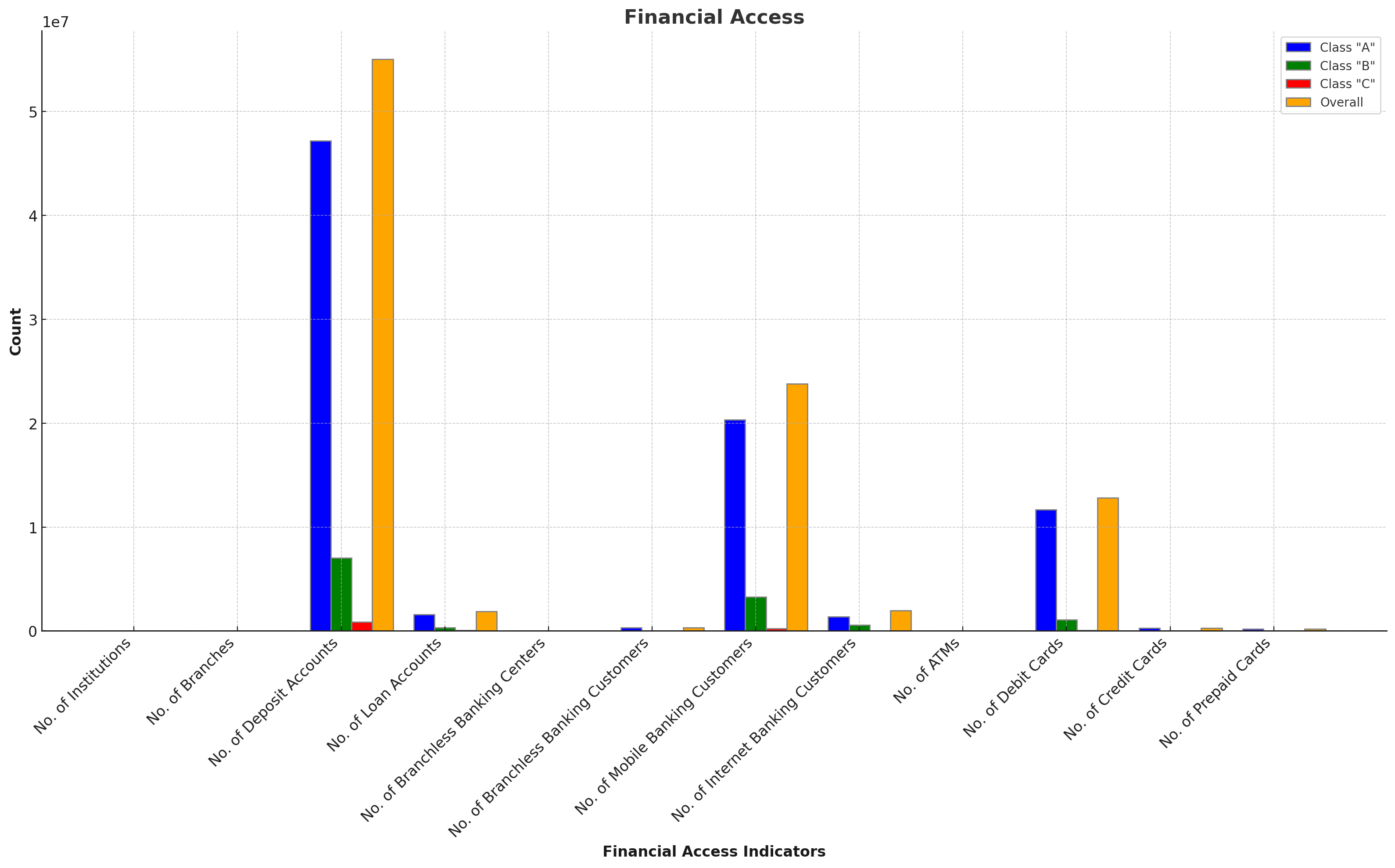
The banking sector continues to expand its reach, with 54 institutions serving over 55 million deposit accounts and 1.89 million loan accounts. Mobile banking and internet banking have shown significant growth, with over 23 million and 1.9 million customers, respectively. The number of ATMs stands at 5,163, enhancing accessibility for customers.
Interest Rates
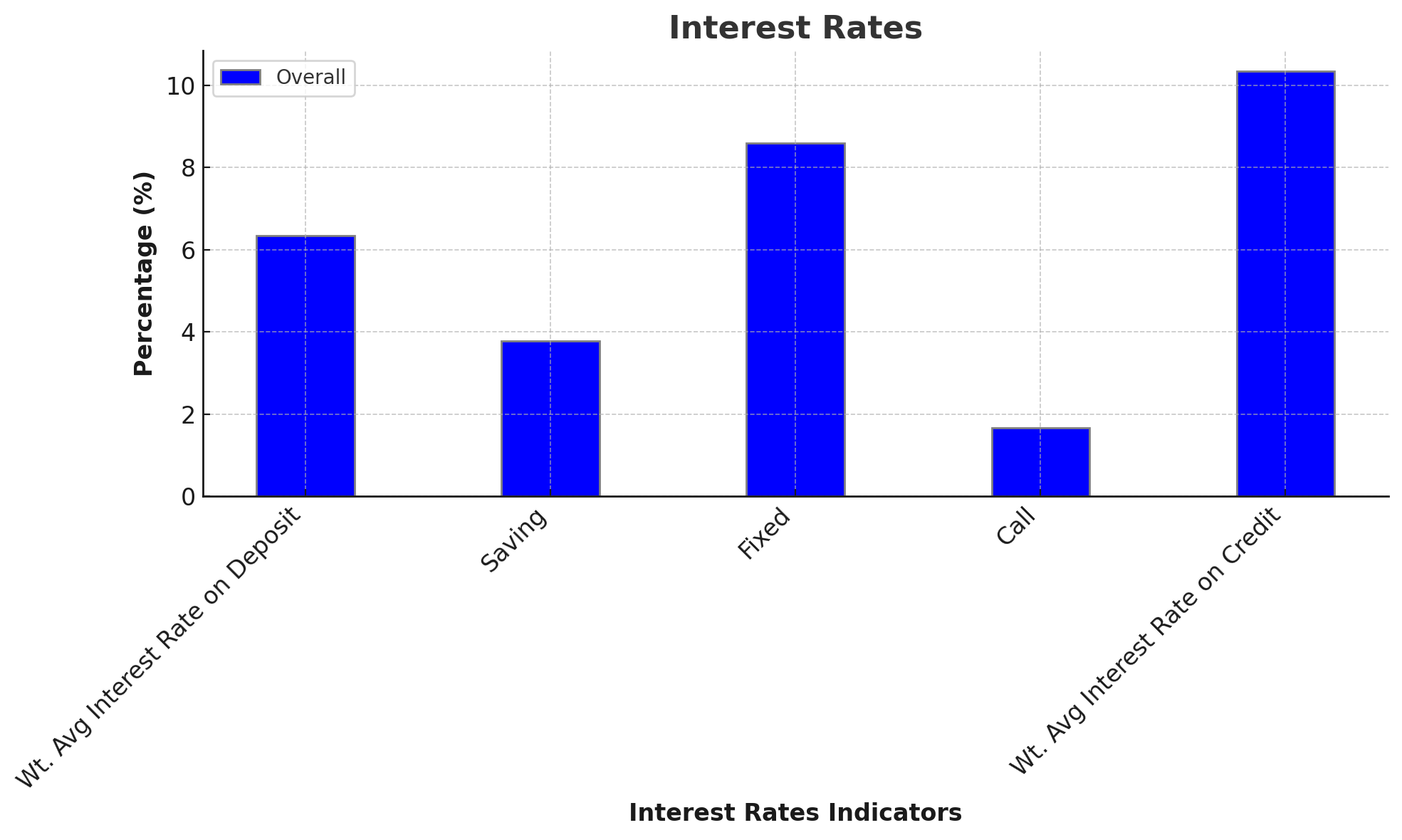
Interest rates remain competitive, with the weighted average interest rate on deposits at 6.35% and the weighted average interest rate on credit at 10.34%. This spread provides a reasonable margin for banks while ensuring attractive returns for depositors and manageable costs for borrowers.
Interpretation
The data underscores a stable and expanding banking sector in Nepal. The high deposit and credit ratios relative to GDP reflect strong public trust and active lending practices. Healthy liquidity and capital adequacy ratios suggest that banks are well-prepared to manage risks and sustain growth. The extensive reach of banking services, especially through mobile and internet banking, highlights the sector's commitment to financial inclusion.
Overall, the banking sector's performance as of mid-May 2024 indicates a resilient financial system capable of supporting economic growth and development in Nepal. With ongoing improvements in financial access and prudent management of liquidity and capital, the sector is well-positioned to navigate future challenges and opportunities.









