By Sandeep Chaudhary
Effective Management of Non-Performing Loans (NPL) According to NRB Guidelines

Non-Performing Loans (NPL) are a critical concern for banks, indicating loans where the borrower is not making scheduled payments of interest or principal. As per Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB) guidelines, loans overdue for more than 90 days are classified as non-performing. Effective management of NPLs is essential for maintaining the financial health of banks and ensuring their continued ability to lend.
Classification and Provisioning
NRB requires banks to classify their loans based on the number of days overdue and to maintain provisions to cover potential losses. Loans overdue for 91 to 180 days are classified as substandard and require a 25% provision. Loans overdue for 181 to 365 days are classified as doubtful and require a 50% provision. Loans overdue for more than 365 days are classified as loss loans and require a 100% provision.
Calculating the NPL Ratio
The NPL ratio is a key metric used to evaluate the quality of a bank's loan portfolio. The formula to calculate the NPL ratio is:
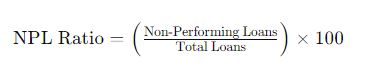
This ratio provides insights into the proportion of a bank's loans that are at risk of default. A high NPL ratio indicates potential issues with credit quality and can impact the bank's profitability and capital adequacy.
Importance of NPL Management
Managing NPLs is crucial for several reasons. It ensures the financial stability of banks by preventing the erosion of capital and profitability. It also helps in mitigating credit risk, ensuring a healthy loan portfolio. Adhering to NRB guidelines on NPLs ensures regulatory compliance, avoiding penalties and enhancing depositor confidence. Additionally, effective NPL management means more capital is available for lending, supporting economic growth.
In conclusion, managing Non-Performing Loans (NPL) is essential for maintaining the financial health and stability of banks. By adhering to NRB guidelines and implementing effective NPL management practices, banks can mitigate risks, comply with regulatory standards, and promote depositor confidence, thereby contributing to the overall stability and resilience of the banking sector.