By Sandeep Chaudhary
Exports Of Major Commodities To Other Countries

Nepal's economy has shown mixed results in its foreign exports over the past fiscal year, as revealed by the latest report from the Nepal Rastra Bank. The data indicates a decline in the export of major commodities in the first nine months of the fiscal year 2023/24.
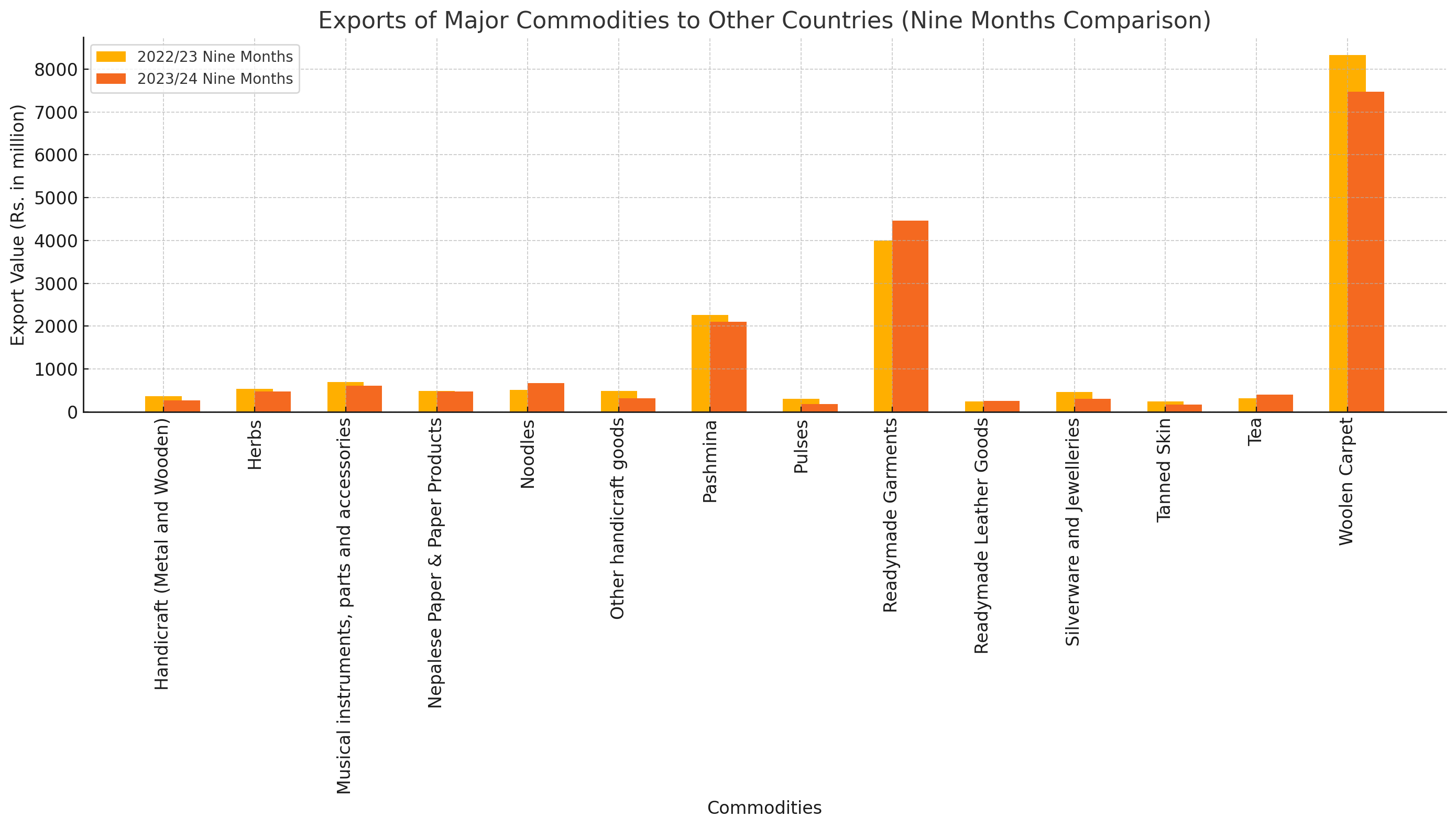
Decline in Major Commodities Exports In the first nine months, the export of major commodities decreased from Rs. 19,245.6 million to Rs. 18,205.2 million, marking a 5.4% drop.
Handicrafts and Herbs The export of metal and wooden handicrafts saw a significant decrease, falling by 25% to Rs. 272.3 million. Similarly, the export of herbs declined by 10.2%, reaching Rs. 482.4 million.
Musical Instruments and Nepalese Paper Products Exports of musical instruments and their parts fell by 12.4%, amounting to Rs. 612.6 million. Nepalese paper and paper products exports slightly decreased by 0.1%, totaling Rs. 483.1 million.
Other Sectors: Noodles and Handicrafts On a positive note, the export of noodles saw a substantial increase of 30.9%, reaching Rs. 670.2 million. However, other handicraft goods faced a steep decline of 33.9%, dropping to Rs. 321.0 million.
Pashmina and Pulses Pashmina exports fell by 6.8% to Rs. 2,109.4 million. Pulses experienced the largest decline among major commodities, with a drop of 40.5%, bringing the total to Rs. 181.6 million.
Readymade Garments and Leather Goods The export of readymade garments showed a positive trend, increasing by 11.8% to Rs. 4,465.1 million. Conversely, readymade leather goods saw a modest increase of 3.7%, totaling Rs. 252.6 million.
Silverware and Jewelry Silverware and jewelry exports faced a sharp decline of 35.1%, amounting to Rs. 302.3 million. Tanned skin exports also dropped significantly by 28.7%, reaching Rs. 173.8 million.
Tea and Woolen Carpet Tea exports saw a notable increase of 27.5%, totaling Rs. 407.6 million. Woolen carpet exports, however, decreased by 10.3%, bringing the total to Rs. 7,471.3 million.
Overall Performance The total exports, including other commodities, saw a slight decrease of 2%, amounting to Rs. 33,976.2 million in the first nine months of 2023/24 compared to Rs. 34,657.8 million in the same period of the previous year.
Interpretation The decline in major commodities' exports highlights the challenges faced by Nepal's export sector. Factors such as global economic conditions, demand fluctuations, and domestic production issues might have contributed to this trend. While some sectors like noodles and tea have shown resilience and growth, others, particularly handicrafts and pulses, have experienced significant setbacks. These mixed results underscore the need for strategic measures to enhance the competitiveness and diversification of Nepal's export portfolio.









