By Sandeep Chaudhary
High SLR Ratios Among Nepali Banks Indicate Strong Liquidity Positions

In a recent analysis of the Statutory Liquidity Reserve (SLR) percentages of major Nepali banks, it was observed that many institutions significantly exceed the minimum requirement of 10%. The SLR, which mandates banks to maintain a certain percentage of their net demand and time liabilities in the form of liquid assets, is a critical measure to ensure liquidity and financial stability within the banking sector.
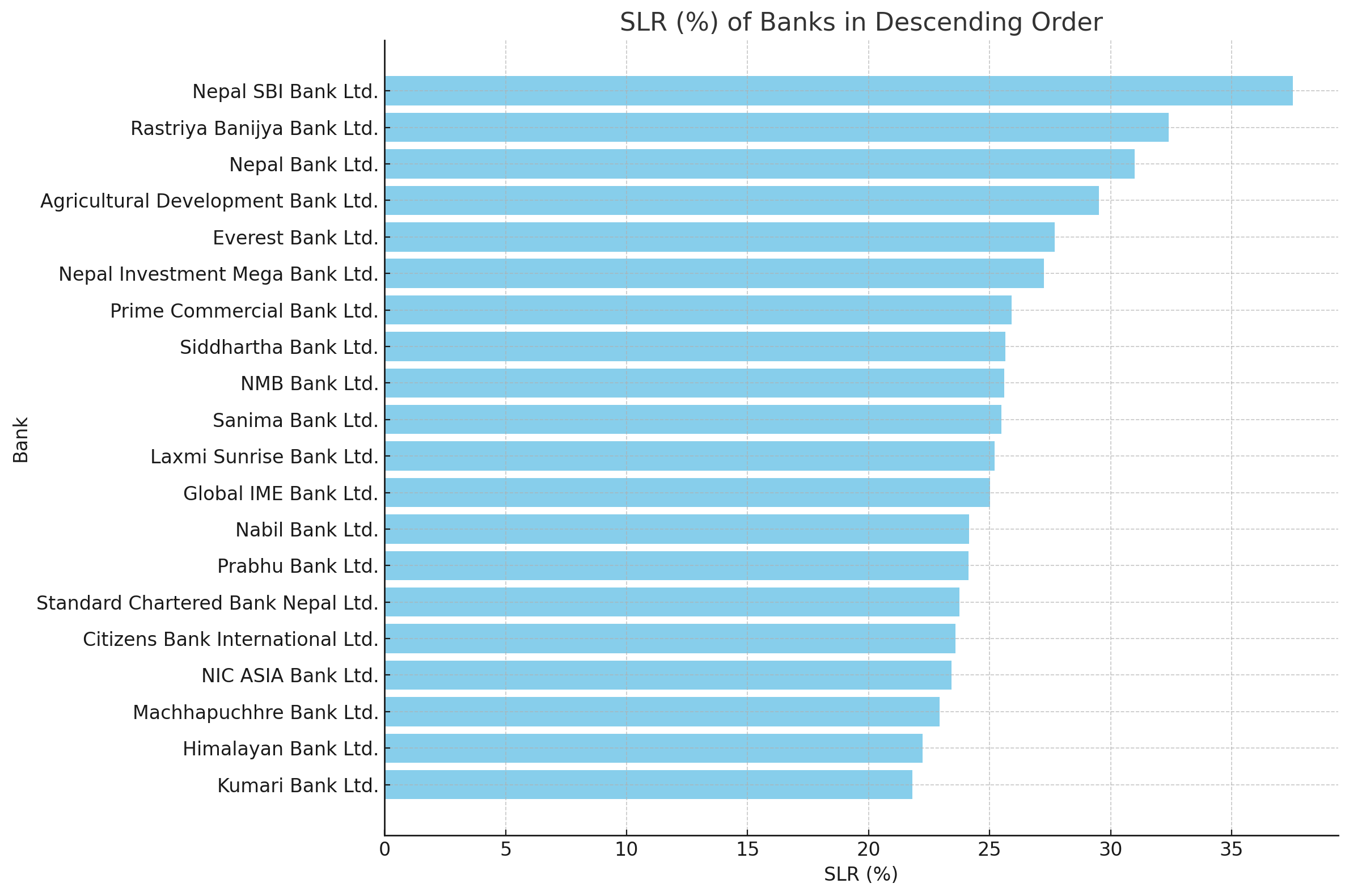
Leading the pack is Nepal SBI Bank Ltd. with an impressive SLR of 37.53%, far surpassing the regulatory minimum. This high reserve ensures that the bank has a substantial cushion of liquid assets, promoting financial stability and enhancing customer confidence.
Rastriya Banijya Bank Ltd. and Nepal Bank Ltd. follow closely with SLRs of 32.41% and 31% respectively. These banks demonstrate robust liquidity management, which is essential for meeting short-term obligations and providing a buffer against financial stress.
Agricultural Development Bank Ltd. also shows a strong liquidity position with an SLR of 29.52%, while Everest Bank Ltd. and Nepal Investment Mega Bank Ltd. maintain SLRs of 27.7% and 27.25% respectively. These figures are indicative of sound financial health and a proactive approach to managing liquidity risks.
Prime Commercial Bank Ltd. (25.91%), Siddhartha Bank Ltd. (25.66%), and NMB Bank Ltd. (25.60%) are other notable mentions, all maintaining SLRs well above the required threshold. Their adherence to high liquidity standards ensures their ability to handle financial fluctuations and continue lending activities even during economic downturns.
Other banks such as Sanima Bank Ltd. (25.48%), Laxmi Sunrise Bank Ltd. (25.2%), and Global IME Bank Ltd. (25.02%) also exhibit strong liquidity positions, reflecting their commitment to financial prudence and stability.
While Nabil Bank Ltd. (24.15%) and Prabhu Bank Ltd. (24.13%) have lower SLRs compared to their peers, they still maintain a comfortable margin above the minimum requirement, ensuring sufficient liquidity to meet their obligations.
The lower end of the spectrum includes Standard Chartered Bank Nepal Ltd. (23.75%), Citizens Bank International Ltd. (23.6%), NIC ASIA Bank Ltd. (23.43%), Machhapuchhre Bank Ltd. (22.93%), Himalayan Bank Ltd. (22.22%), and Kumari Bank Ltd. (21.81%). Despite having relatively lower SLRs, these banks still showcase commendable liquidity management, staying well above the regulatory benchmark.
The high SLR percentages across these banks highlight the strong liquidity positions within the Nepali banking sector. By maintaining substantial liquid reserves, these institutions not only comply with regulatory requirements but also reinforce their resilience against potential financial adversities, thereby ensuring sustained trust and stability in the banking system.









