By Sandeep Chaudhary
Nepal's Balance of Payments Analysis: Trends and Implications (2016/17 - 2023/24)

The latest data from Nepal's balance of payments (BoP) indicators reveal critical insights into the country's economic dynamics over the past several years. This period has been marked by significant fluctuations in key metrics such as the current account balance, balance on goods, services net, workers' remittances, net direct investment, and the overall BoP deficit. Here's an in-depth look at the trends and their implications.
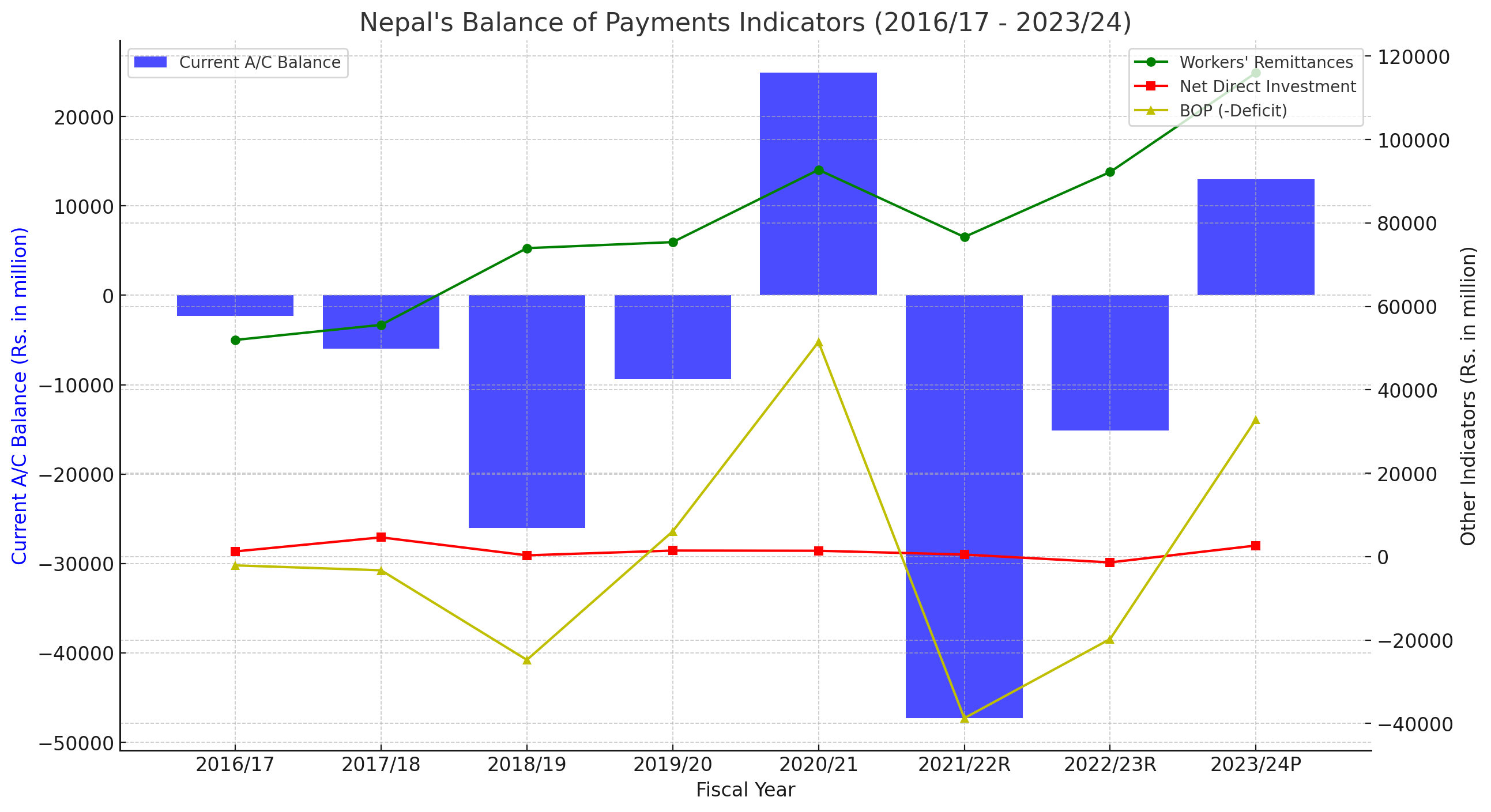
The chart above visually represents Nepal's key balance of payments indicators from fiscal years 2016/17 to 2023/24.
Interpretation:
Current Account Balance (Blue Bars):
The current account balance has shown significant fluctuations. After maintaining a negative balance for several years, there is a noticeable positive shift in 2023/24. This improvement is a positive sign indicating better financial health and possibly higher export or remittance inflows.
Workers' Remittances (Green Line):
Workers' remittances have generally increased over the years, highlighting the critical role of the Nepalese diaspora in the economy. The peak in remittances during 2022/23 underscores the importance of this income stream.
Net Direct Investment (Red Line):
Net direct investment shows variability but remains relatively low compared to other indicators. This reflects investor confidence fluctuations and the need for policy measures to attract more foreign investment.
BOP (-Deficit) (Yellow Line):
The BoP deficit reached a significant peak in 2020/21 but showed substantial improvement in 2022/23 and 2023/24, turning into a surplus in 2023/24. This turnaround suggests a stronger external position, potentially due to increased remittances and better trade balances.
Current Account Balance and Trade Deficit
Nepal's current account balance has experienced substantial volatility. Starting from a deficit of -2,315.3 million NPR in August 2016/17, the deficit expanded to -72,158.4 million NPR by July 2022/23, before turning positive in August 2023/24 with a surplus of 12,985.0 million NPR. This reversal indicates a significant improvement in the country's external sector, possibly driven by increased remittances and stronger export performance.
The balance on goods has persistently remained in deficit, reflecting Nepal's reliance on imports for essential goods and services. This deficit peaked at -1,661,975.4 million NPR in July 2021/22, highlighting the pressing need for policies to bolster domestic production and reduce import dependency.
Services Net and Workers' Remittances
The net services account has shown mixed results, with deficits and occasional surpluses. This fluctuation points to varying performance in sectors such as tourism, transportation, and financial services.
Workers' remittances have been a critical source of foreign exchange for Nepal, consistently showing positive growth. Despite a slight dip in some periods, remittances have generally increased, peaking at 1,220,559.5 million NPR in July 2022/23. This underscores the importance of the Nepalese diaspora in supporting the national economy.
Net Direct Investment and BoP Deficit
Net direct investment has also exhibited fluctuations but generally trended upwards, reflecting growing investor confidence in Nepal's economic prospects. However, the overall BoP deficit has been a concern, with substantial deficits observed in several fiscal years. The deficit narrowed to a surplus of 285,823.2 million NPR in July 2022/23, indicating improved external balances.
Interpretation and Implications
The data suggests that Nepal's economy is gradually stabilizing, with significant improvements in the current account and BoP balances in recent months. The positive shift in the current account balance and the narrowing of the BoP deficit are encouraging signs of economic resilience.
However, the persistent trade deficit underscores the need for structural reforms to enhance domestic production capabilities and reduce reliance on imports. Additionally, sustained growth in remittances highlights the need to create more opportunities for overseas employment while also developing strategies to channel these funds into productive investments domestically.
The fluctuating net services account suggests that further development and diversification of the service sector could provide a more stable source of foreign exchange earnings. Policies aimed at boosting tourism, improving service exports, and enhancing the business environment could be beneficial.
In conclusion, while the recent improvements in Nepal's BoP indicators are promising, addressing the underlying structural challenges will be crucial for sustaining economic stability and growth. Continued efforts to enhance domestic production, diversify exports, and attract foreign investment will be key to ensuring long-term economic resilience.









