By Sandeep Chaudhary
NIC ASIA Bank Leads in CD Ratio Among Nepali Banks

NIC ASIA Bank has the highest Credit-Deposit (CD) ratio among Nepali banks at 86.11%, according to recent data. Kumari Bank follows with 85.36%, and Prime Commercial Bank is third with 85.10%. Citizens Bank International and Nabil Bank round out the top five with CD ratios of 84.21% and 83.97%, respectively. The high CD ratios indicate a strong lending environment and effective deposit management in Nepal's banking sector.
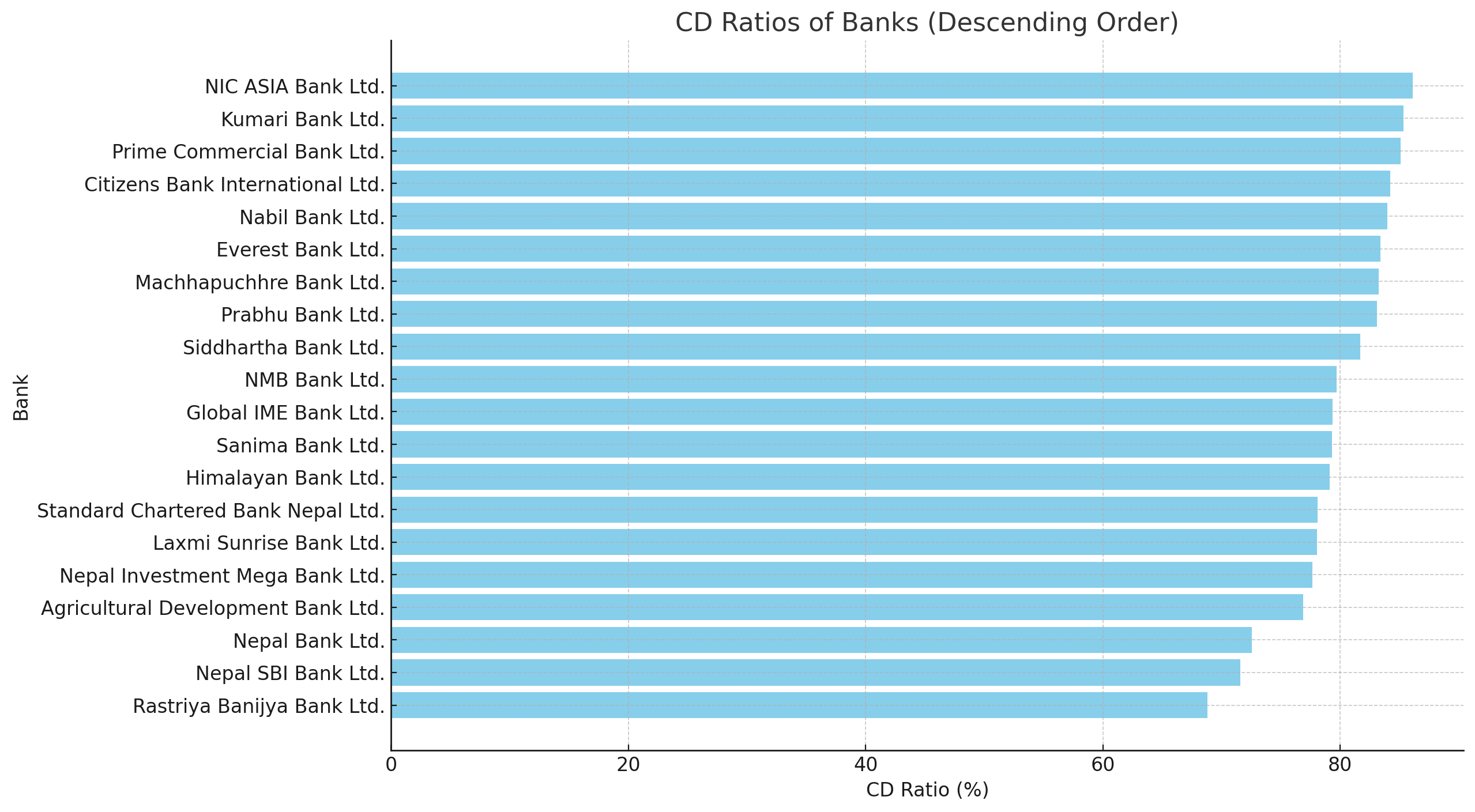
Kathmandu, June 15 – NIC ASIA Bank has secured the top position in the Credit-Deposit (CD) ratio among Nepali banks. According to the latest data, NIC ASIA Bank has achieved an impressive CD ratio of 86.11%, the highest among all banks in Nepal.
Kumari Bank follows closely with a CD ratio of 85.36%, placing it in the second position. Prime Commercial Bank comes in third with a CD ratio of 85.10%. Citizens Bank International stands at the fourth position with a CD ratio of 84.21%.
Notably, Nabil Bank holds the fifth position with a CD ratio of 83.97%. Similarly, Everest Bank and Machhapuchhre Bank have achieved CD ratios of 83.42% and 83.26%, respectively, securing their positions among the top banks.
Other banks like Prabhu Bank, Siddhartha Bank, and NMB Bank have also shown strong performances with CD ratios of 83.09%, 81.68%, and 79.72%, respectively.
The overall high CD ratios indicate a robust lending environment in the banking sector of Nepal, reflecting the banks' confidence in the market and their ability to manage deposits efficientlyy









