By Sandeep Chaudhary
Number of Nepalese Going for Foreign Employment as of 2023/24 (Nine-month Data)

Number of Nepalese going for Foreign Employment (Countrywise)" provides data on the annual and nine-month figures for foreign employment of Nepalese people across different countries for the years 2021/22, 2022/23, and 2023/24. Here is a detailed interpretation of the data:
Summary of Data
Countries Listed: 19 specific countries along with an 'Other' category.
Years:
2021/22 (Annual and Nine Months)
2022/23 (Annual and Nine Months)
2023/24 (Nine Months)
Metrics:
Number of Nepalese going for foreign employment annually and for nine months.
Percent Share of foreign employment for nine months in 2022/23 and 2023/24.
Percent Change during nine months from 2022/23 to 2023/24.
Key Points
Top Destination Countries (2023/24 Nine Months):
UAE: 91,695 (27.8% share, 131.1% increase from 2022/23 nine months).
Saudi Arabia: 53,561 (16.3% share, 35.2% increase from 2022/23 nine months).
Qatar: 31,501 (9.6% share, -0.9% change from 2022/23 nine months).
Malaysia: 99,959 (18.2% share, -68.0% change from 2022/23 nine months).
Significant Changes:
Romania: 203.7% increase from 2022/23 nine months.
Turkey: -87.0% decrease from 2022/23 nine months.
Japan: 101.8% increase from 2022/23 nine months.
Israel: -92.8% decrease from 2022/23 nine months.
Other: 185.6% increase from 2022/23 nine months.
Countries with Decreases:
Saudi Arabia: 63.5% decrease from 2022/23 nine months.
Qatar: 49.7% decrease from 2022/23 nine months.
Oman: 2.9% decrease from 2022/23 nine months.
Total Numbers:
For nine months of 2023/24: 329,422 (15.1% decrease from 2022/23 nine months).
For nine months of 2022/23: 387,839.
Observations
UAE and Saudi Arabia are consistently among the top destinations for Nepalese seeking foreign employment.
Malaysia shows a significant drop in the number of Nepalese workers from 2022/23 to 2023/24.
Some countries like Romania and Japan are showing substantial growth, indicating emerging destinations for Nepalese workers.
The overall total for nine months of 2023/24 shows a decrease compared to 2022/23, suggesting a decline in foreign employment during this period.
This data can be crucial for policymakers to understand trends in foreign employment, identify emerging markets, and address any issues related to the decline or increase in specific regions.
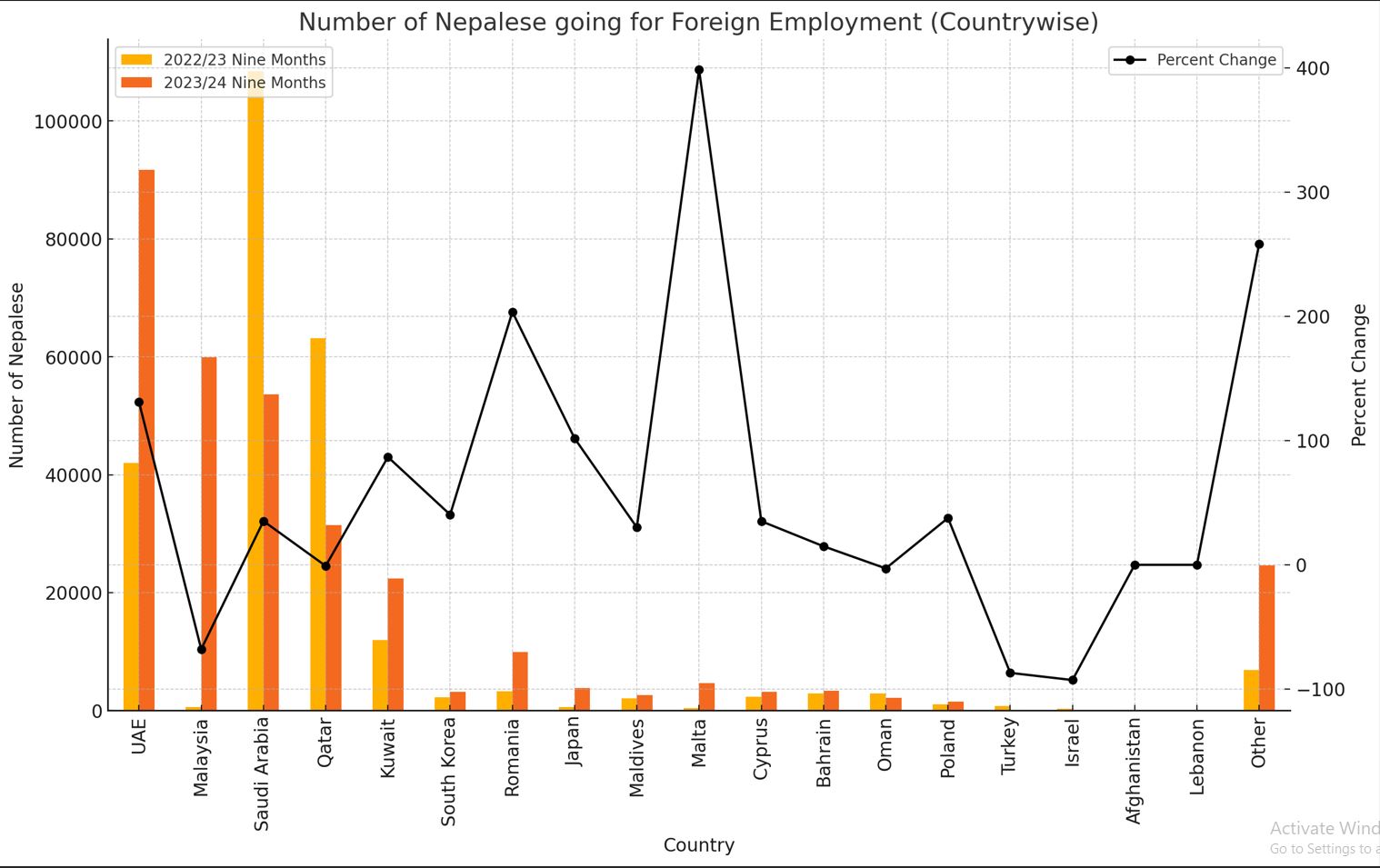
Key Elements:
Bar Chart: Displays the number of Nepalese workers going for foreign employment in 2022/23 and 2023/24 (nine months) for each country.
Line Chart: Illustrates the percent change in the number of workers from 2022/23 to 2023/24 (nine months).
The chart above visually represents the number of Nepalese going for foreign employment to various countries during the nine months of 2022/23 and 2023/24.
Key Insights from the Chart:
Number of Nepalese Workers:
UAE saw a significant increase from 41,963 in 2022/23 to 91,695 in 2023/24.
Malaysia and Saudi Arabia also show substantial numbers, though Malaysia had a notable decrease.
Qatar and Kuwait have stable or slightly varied figures.
Romania and Japan have sharp increases, indicating rising trends in these countries.
Percent Change:
Romania, Japan, and Other categories show the highest positive percent changes, suggesting emerging or improving markets for Nepalese workers.
Malaysia, Turkey, and Israel exhibit significant negative changes, indicating a decline in Nepalese workers going to these countries.
The combination of bar charts for the number of workers and a line chart for percent change provides a comprehensive overview of trends in foreign employment for Nepalese across different countries









