By Dipesh Ghimire
Analysis of Nepal's Macroeconomic Indicators (2019/20 to 2024/25)
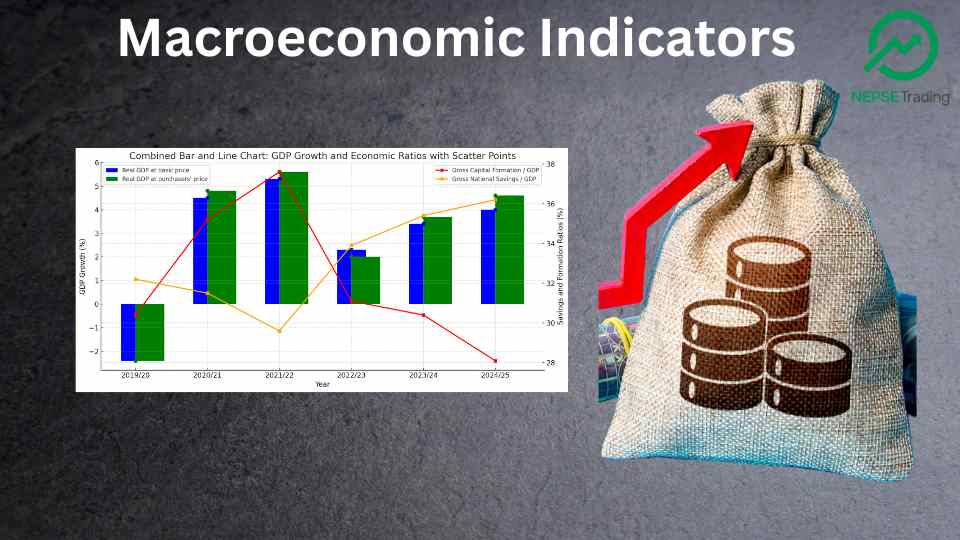
Nepal’s economy has experienced a fluctuating trajectory over the past few years, with a significant decline in GDP during the COVID-19 pandemic, followed by gradual recovery and growth. The country's economic indicators from fiscal years 2019/20 to 2024/25 reflect a series of challenges and improvements in key sectors such as GDP growth, national savings, and capital formation.

1. Real GDP Growth:
The Real GDP growth at basic price saw a notable downturn in the fiscal year 2019/20, with a contraction of -2.4% due to the COVID-19 pandemic's economic impact. However, there was a strong rebound in the following years. In 2020/21, real GDP growth surged to 4.5%, and it continued its upward trajectory, reaching 5.3% in 2021/22. The growth, however, slowed down to 2.3% in 2022/23 and further to 3.4% in 2023/24, reflecting ongoing challenges such as inflationary pressures and global economic uncertainties. The projections for 2024/25 suggest a return to 4.0% growth, showing optimism for a stable recovery.
2. Real GDP at Purchasers' Price:
The Real GDP at purchasers' price mirrors a similar trend, starting with -2.4% in 2019/20, followed by a recovery in 2020/21 (4.8%), and a steady increase reaching 5.6% in 2021/22. This indicator peaked at 2.0% in 2022/23, and projections suggest it will grow to 3.7% in 2023/24, further highlighting the slow recovery in purchasing power. The anticipated rate for 2024/25 is 4.6%, signaling gradual improvement in consumer purchasing power.
3. Nominal GDP Growth:
Nominal GDP growth was 0.8% in 2019/20, but there was a significant jump to 11.9% in 2020/21, showing the effect of inflation and rising prices. This trend continued in 2021/22, with a 14.3% growth rate, and is projected to stabilize at 7.8% in 2022/23 and 6.4% in 2023/24. The nominal GDP will likely stay strong in the coming years with a forecast of 7.0% for 2024/25.
4. Gross National Income (GNI):
The Gross National Income (GNI), which reflects the total income earned by the residents of Nepal, including remittances, saw a steady rise from 0.9% in 2019/20 to 11.2% in 2020/21 and 14.4% in 2021/22. However, the growth rate slowed down in subsequent years, with 8.5% projected in 2023/24. The trend reflects increasing remittances that contribute to national income but also highlights slowing income growth from other sectors.
5. Gross Capital Formation and National Savings:
A critical indicator for economic growth is Gross Capital Formation / GDP, which measures the investment in physical assets. This ratio peaked at 37.6% in 2021/22, reflecting robust investments but is expected to decline to 28.1% by 2024/25, possibly due to slower investments in infrastructure and other sectors.
Conversely, Gross National Savings / GDP showed a steady decline from 32.2% in 2019/20 to 29.6% in 2021/22. The savings rate is expected to increase to 35.4% by 2023/24 and stabilize at 36.2% by 2024/25, indicating a higher inclination to save, possibly due to economic uncertainties.
6. Gross Domestic Product (Current Price):
In terms of monetary value, Nepal's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in current prices has consistently risen. From Rs 3887.7 billion in 2019/20, it reached Rs 4352.6 billion in 2020/21, and it continues to grow, expected to reach Rs 6107.2 billion by 2024/25. This indicates a nominal increase in the economy's total size, driven by inflation and nominal growth in various sectors.
The macroeconomic data from 2019/20 to 2024/25 paints a mixed picture of recovery and challenges. Nepal's GDP growth, while recovering, has shown signs of slowing, particularly in 2022/23 and 2023/24. However, the positive outlook for 2024/25 suggests the country will return to stable growth.
Key challenges include the sluggish growth in capital formation and the lower-than-expected growth in national savings, which could impact long-term investments. On a positive note, the increase in Gross National Income (GNI) and rising savings rates highlight a shift towards financial stability and resilience.
Nepal's economy will need to navigate external pressures, such as global inflation and supply chain disruptions, while focusing on strengthening domestic investments and savings to maintain a steady recovery in the coming years. The data suggests that the country's economic recovery post-pandemic is promising, with an optimistic outlook for 2024/25.









