By Trading view
Major Changes in Import Duties Announced in Nepal’s Finance Bill 2081
The Government of Nepal has introduced significant changes in import duty structures through the newly released Finance Bill for Fiscal Year 2081/82. These revisions target key goods ranging from agricultural produce to medical supplies and industrial raw materials. The updated import tariff framework aims to protect domestic industries, curb unnecessary imports, and adjust to global price trends.
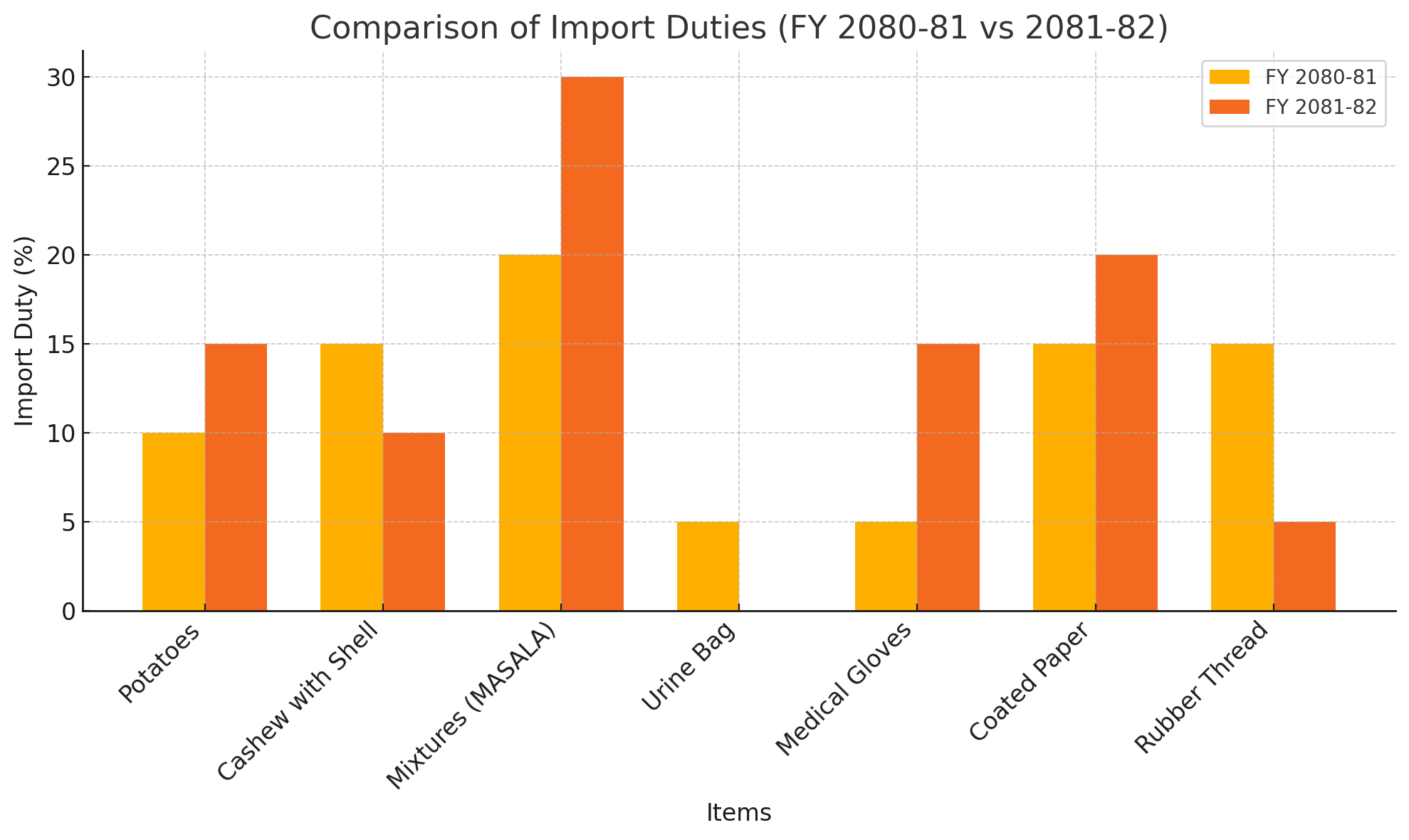
One of the most notable changes is the increase in import duty on frozen vegetables, particularly potatoes (sub-heading 0710.10.00), which saw an increment from 10% to 15%. This move is likely aimed at promoting local agricultural production and reducing reliance on imported food staples.
In contrast, the duty on cashew nuts with shells (0801.31.00) has been reduced from 15% to 10%, making them slightly cheaper to import. This could benefit food and nut processing industries that rely on imported raw nuts. However, other nuts like coconuts and Brazil nuts remain under the same classification without specific duty changes mentioned.
Spices such as ginger, saffron, turmeric, thyme, bay leaves, and curry under heading 09.10 have not seen any duty adjustments. But in a significant move, the import duty on mixed spices (Mixtures - MASALA) (0910.91.00) has been raised from 20% to 30%, likely to encourage local spice blends and mixtures produced within Nepal.
Changes are also visible in plastic and rubber product categories. For instance, urine bags (3926.90.31), which earlier carried a 5% import duty, are now exempted from duty altogether in the current fiscal year. This shift may support healthcare infrastructure and improve access to essential medical products.
Rubber-based clothing accessories and medical apparel under heading 40.15 saw a noteworthy increase in import duties. Products like gloves and mitts made of vulcanized rubber have maintained an unspecified rate, but medical-grade articles like surgical gloves (4015.12.00) have seen their duty increase from 5% to 15%, potentially to promote local production or manage healthcare import costs.
Industrial sectors that rely on coated paper will now face higher import costs as the duty on kaolin-coated paper and paperboard (heading 48.10) has been increased from 15% to 20%. Similarly, rubber thread and cord, textile covered (5604.10.00), now attract a 5% import duty, down from the previous 15%, suggesting support for textile and elastic component manufacturing.
Overall, the Finance Bill 2081 has adjusted import tariffs in a way that appears to balance between protecting domestic producers and easing access to essential imports. With notable increases in some sectors like spices and paper, and reductions or exemptions in healthcare and textile inputs, these changes reflect the government’s strategic trade and economic priorities for the upcoming fiscal year.









