By Sandeep Chaudhary
Nepal Stock Market Indicators Show Mixed Performance in Mid-April 2024

In a recently published report, Nepal Stock Market indicators reveal a mixed performance as of mid-April 2024. The Nepal Stock Exchange (NEPSE) index has shown a slight recovery with a closing value of 2025.7 points, marking a 4.7% increase from the previous year's mid-April value of 1934.5 points. However, it remains significantly lower compared to 2022's 2415.3 points, reflecting a -19.9% change over the two-year period.
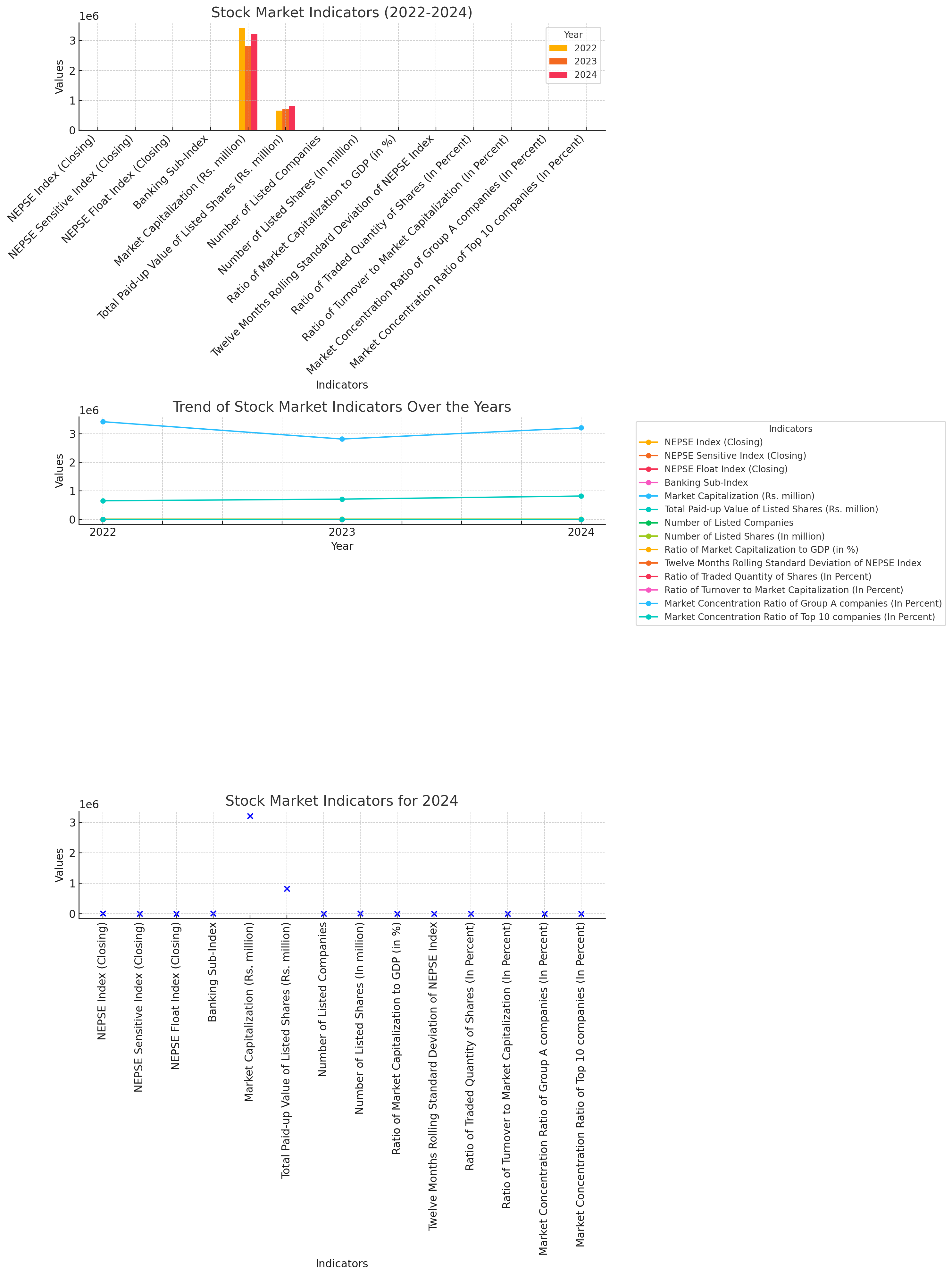
Here are three different visualizations of the stock market indicators for 2022, 2023, and 2024:
Bar Plot: This chart shows the comparison of stock market indicators for the years 2022, 2023, and 2024. Each indicator is represented by three bars, one for each year, allowing for a side-by-side comparison.
Line Plot: This chart illustrates the trend of stock market indicators over the three years. It helps to visualize the changes and trends for each indicator from 2022 to 2024.
Scatter Plot: This chart focuses on the values of stock market indicators for the year 2024. Each indicator is plotted as a point, providing a clear snapshot of the current state.
Similarly, the NEPSE Sensitive Index, which tracks the performance of blue-chip companies, closed at 358.2 points, experiencing a modest decline of -2.7% compared to the previous year and a more substantial -21.5% drop from 2022's 456.1 points.
The NEPSE Float Index, which measures the performance of freely tradable shares, recorded a value of 137.0 points in mid-April 2024. This index saw a small improvement of 1.0% over the last year but remains down by -17.7% from its 2022 value of 164.6 points.
In sector-specific performance, the Banking Sub-Index fell to 1059.2 points, showing a significant decline of -15.6% from the previous year and an even steeper drop of -34.0% compared to its 2022 value of 1604.4 points.
Market capitalization also exhibited a mixed trend. The total market capitalization stood at Rs. 3212008.1 million in mid-April 2024, which is an increase of 14.0% from the previous year but a -17.7% decline from 2022's Rs. 3426108.8 million. Meanwhile, the total paid-up value of listed shares surged by 15.2% over the previous year, reaching Rs. 819542.4 million.
The number of listed companies rose from 272 to 282 over the year, and the number of listed shares increased by 8.4% to 8267.4 million in mid-April 2024.
The report highlighted a notable improvement in the ratio of market capitalization to GDP, which stood at 56.3% in mid-April 2024. Despite this improvement over the previous year, it still marks a -12.5% decline from 2022's 68.8%.
Volatility in the NEPSE index decreased, with the twelve-month rolling standard deviation falling to 95.0 points from 140.4 points the previous year, reflecting a -32.4% change.
Trade activity saw a significant decrease, with the ratio of traded quantity of shares dropping to 17.1% from 12.3% over the past year, marking a -92.5% change. Similarly, the ratio of turnover to market capitalization fell by -64.4% to 11.7% in mid-April 2024.
The report also detailed market concentration ratios, with the concentration ratio of Group A companies decreasing to 38.1%, and the top 10 companies' concentration ratio falling to 25.8%.
Overall, while some indicators show positive trends and recovery signs, the Nepal stock market continues to grapple with challenges and volatility, reflecting the broader economic conditions and investor sentiments.









