By Sandeep Chaudhary
Public Issue Approval by SEBON (Mid-July 2023 - Mid-April 2024)
The Securities Board of Nepal (SEBON) has announced the public issue approvals for various securities from mid-July 2023 to mid-April 2024. The approvals span different types of securities including right shares, ordinary shares, mutual funds, and debentures. The total approved amount stands at a substantial Rs. 24,776.3 million. Here is a detailed breakdown of the approvals:
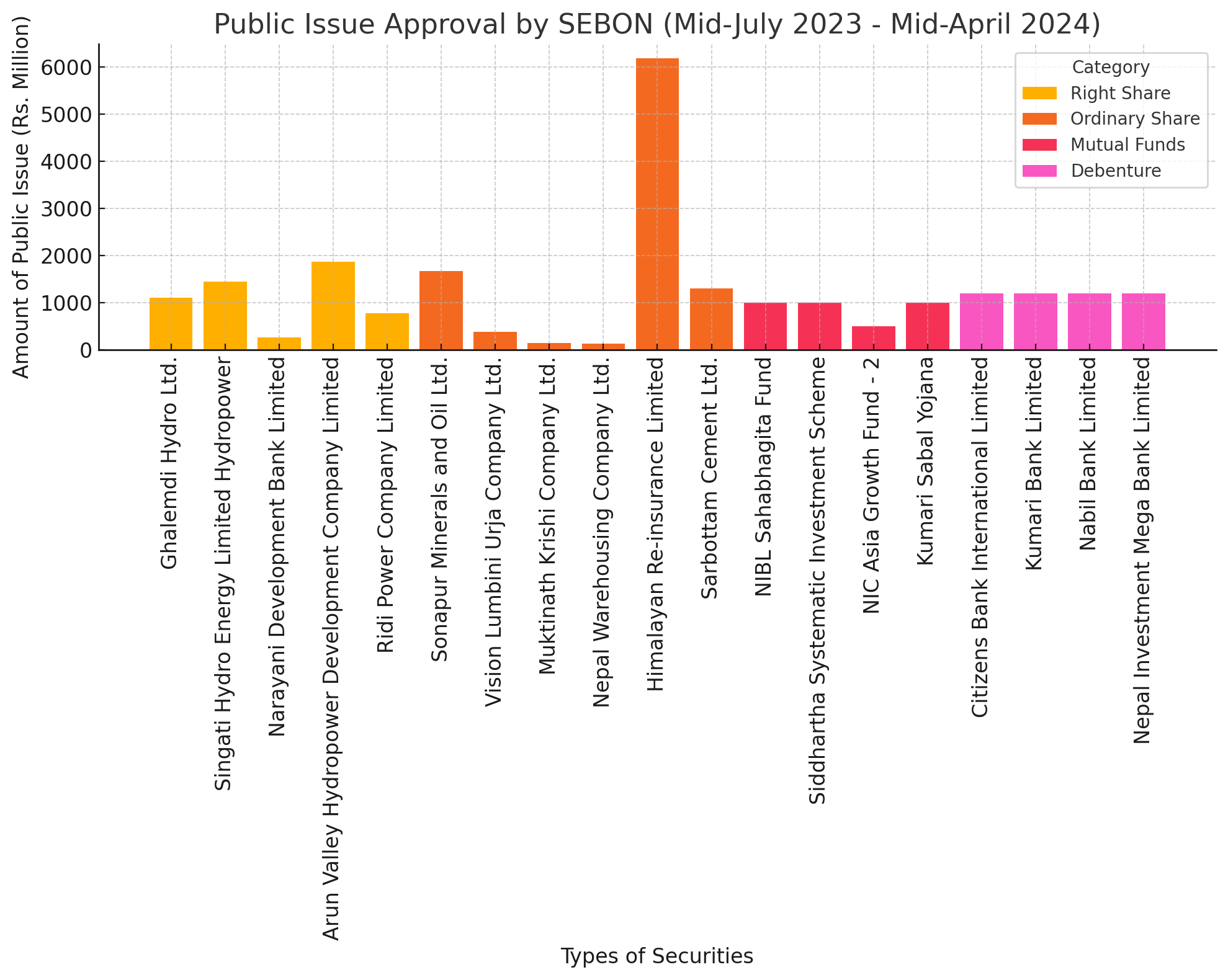
Here is the visual representation of the public issue approvals by SEBON from mid-July 2023 to mid-April 2024. The bar chart categorizes the types of securities and displays the amount of public issue for each, highlighting the significant approvals in different categories
Right Shares
A total of five companies have received approval for right shares, amounting to Rs. 5,454.9 million. The approvals are as follows:
Ghalemdi Hydro Ltd. – Rs. 1100.0 million, approved on 18/08/2080.
Singati Hydro Energy Limited Hydropower – Rs. 1450.0 million, approved on 11/09/2080.
Narayani Development Bank Limited – Rs. 262.5 million, approved on 19/10/2080.
Arun Valley Hydropower Development Company Limited – Rs. 1868.0 million, approved on 9/9/2080.
Ridi Power Company Limited – Rs. 774.5 million, approved on 19/08/2080.
Ordinary Shares
The approval for ordinary shares amounts to Rs. 9,805.4 million, with the following companies receiving the nod:
Sonapur Minerals and Oil Ltd. – Rs. 1666.1 million, approved on 17/04/2080.
Vision Lumbini Urja Company Ltd. – Rs. 382.5 million, approved on 19/05/2080.
Muktinath Krishi Company Ltd. – Rs. 140.3 million, approved on 16/06/2080.
Nepal Warehousing Company Ltd. – Rs. 137.5 million, approved on 19/06/2080.
Himalayan Re-insurance Limited – Rs. 6180.9 million, approved on 13/07/2080.
Sarbottam Cement Ltd. – Rs. 1299.2 million, approved on 10/08/2080.
Mutual Funds
Four mutual funds have received approval, totaling Rs. 3,500.0 million:
NIBL Sahabhagita Fund (Open End) – Rs. 1000.0 million, approved on 25/05/2080.
Siddhartha Systematic Investment Scheme – Rs. 1000.0 million, approved on 29/05/2080.
NIC Asia Growth Fund - 2 – Rs. 500.0 million, approved on 12/06/2080.
Kumari Sabal Yojana (Close End) – Rs. 1000.0 million, approved on 18/08/2080.
Debentures
The approval for debentures amounts to Rs. 6,016.0 million, distributed among four companies:
Citizens Bank International Limited – Rs. 1200.0 million for 10 years at 10%, approved on 29/05/2080.
Kumari Bank Limited – Rs. 1200.0 million for 10 years at 10%, approved on 8/06/2080.
Nabil Bank Limited – Rs. 1200.0 million for 7 years at 9%, approved on 19/08/2080.
Nepal Investment Mega Bank Limited – Rs. 1200.0 million for 10 years at 10%, approved on 19/08/2080.
This approval by SEBON reflects a significant boost in the public issuance of various securities, supporting the growth and development of the financial market in Nepal.









