By Sandeep Chaudhary
Sharp Increase in Treasury Bills Rate Highlights Market Volatility

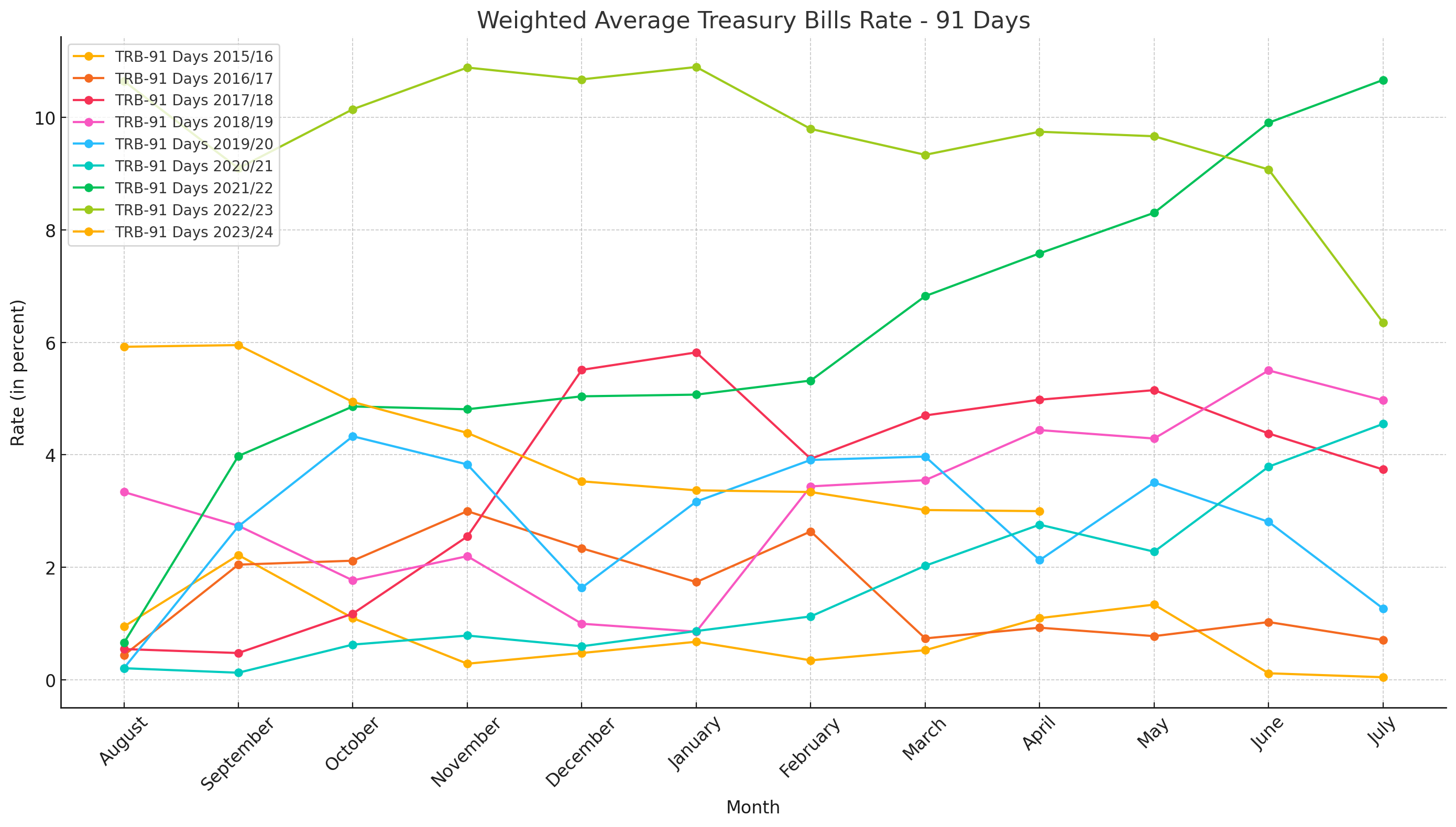
The latest data on the weighted average treasury bills rate reveals significant trends and insights into market conditions over the past years. The table illustrates the rates for both 91-day and 364-day treasury bills from mid-2015 to mid-2024, showing a notable increase in recent years.
Key Observations:
91-Day Treasury Bills:
The 91-day treasury bills rate has experienced a sharp rise in the 2022/23 and 2023/24 fiscal years, peaking at 10.88% in November 2022 and slightly declining to 6.35% by July 2024. This represents a substantial increase from the 2015/16 rates, which were as low as 0.05% in July 2016.
The annual average rate for 2023/24 stood at 9.51%, a significant jump from the previous year's 6.67%. This suggests heightened short-term borrowing costs and possibly increased market demand for shorter-term securities.
364-Day Treasury Bills:
Similarly, the 364-day treasury bills have shown an upward trajectory, with a notable peak of 11.92% in January 2023. The annual average rate for 2023/24 reached 9.02%, compared to 8.26% the previous year.
The rates have fluctuated over the years, with the lowest average annual rate being 1.03% in 2015/16, highlighting a broader trend of rising long-term borrowing costs.
Interpretation:
The increase in treasury bills rates reflects a variety of economic conditions. Higher rates generally indicate increased government borrowing costs, which can be attributed to factors such as inflationary pressures, changes in monetary policy, and overall market sentiment. The significant jump in the 91-day and 364-day rates in recent years suggests that the market is anticipating continued economic volatility and possibly higher inflation.
For investors, these rising rates could mean better returns on short-term investments, but they also signal caution as higher borrowing costs could impact corporate profits and consumer spending. The data underscores the importance of closely monitoring fiscal policies and market conditions as they evolve.
In conclusion, the rising treasury bills rates point to a more expensive borrowing environment, with potential implications for economic growth and stability. Investors and policymakers alike must stay vigilant and adaptive to navigate these changing conditions effectively.









