By Sandeep Chaudhary
Significant Drop in Imports: Causes and Implications

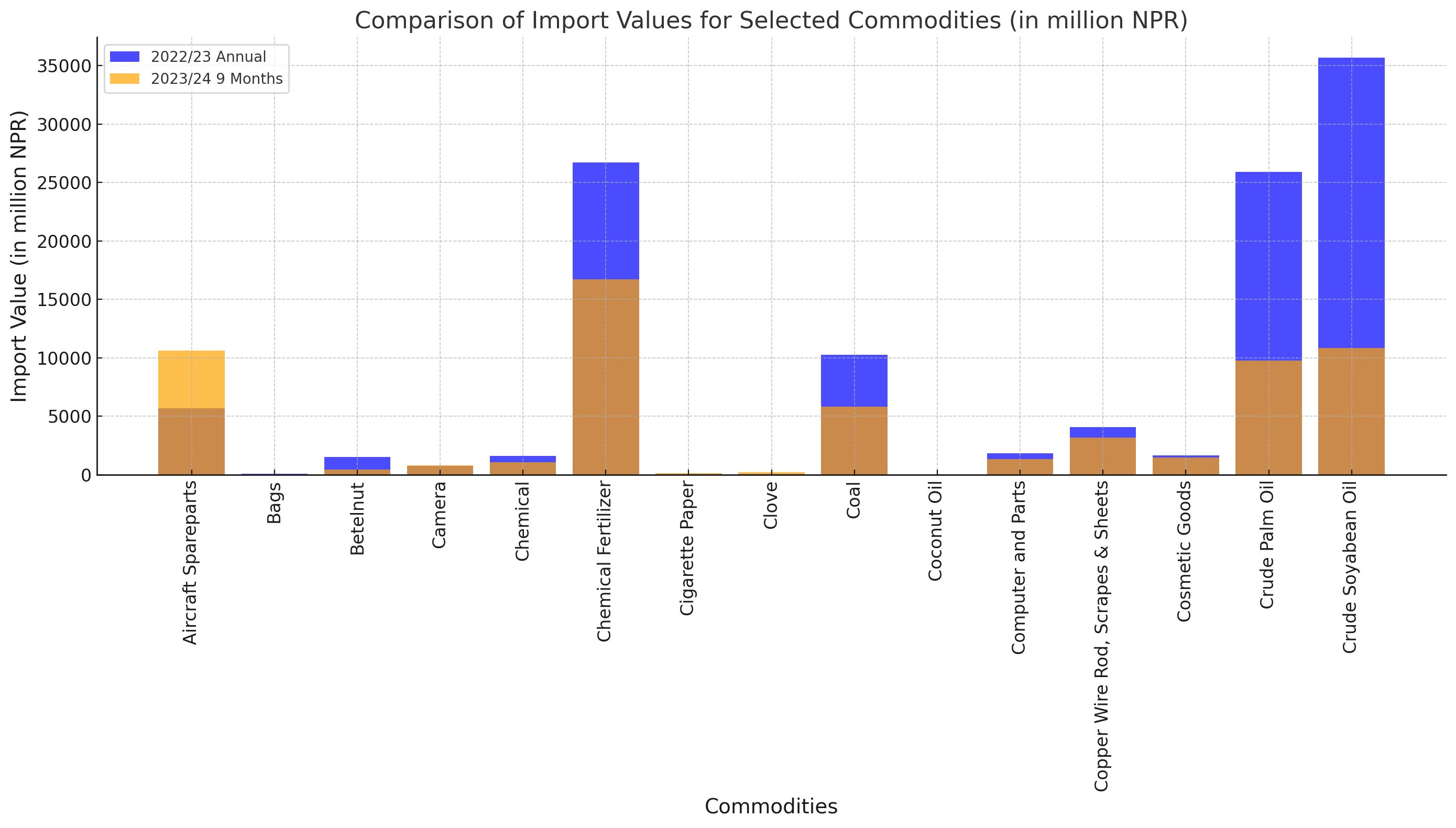
According to the latest data released by the Nepal Rastra Bank, there has been a notable decline in the import of major commodities in the first nine months of the fiscal year 2023/24. This information, presented in Table 16, highlights the import trends of various key commodities.
Key Highlights:
Overall Import Decline: The total imports for the fiscal year 2022/23 stood at NPR 290,660.7 million, which has dropped to NPR 169,694.1 million in the first nine months of 2023/24, marking a significant decline of 27.1%.
Notable Changes in Specific Commodities:
Aircraft Spareparts: This category saw a remarkable increase of 191%.
Betelnut: There was a drastic decline of 59%.
Crude Palm Oil: Imports fell by 55.7%.
Silver: This commodity experienced a 75.4% increase.
Medicine: There was a significant drop of 53.2%.
Causes of Decline:
Analysts suggest several key reasons behind this import decline:
Increased Domestic Production: Nepal has ramped up the production of various goods, reducing the need for imports.
Global Economic Slowdown: The global economic downturn has reduced the demand for imported goods.
Currency Issues: A shortage of foreign currency has made it challenging to finance imports.
Policy Changes: The government has implemented various policy measures aimed at curbing imports to balance the trade deficit.
Future Outlook:
Considering the sharp decline in imports, analysts recommend that the government adopts alternative strategies. Balancing imports while encouraging domestic production will be crucial. Policy adjustments may be needed to stabilize the economy and ensure sustainable growth.
Conclusion:
The significant drop in the import of major commodities could have various implications for Nepal's economy. While it may promote local production, immediate challenges need to be addressed, and long-term strategies should be developed to support economic stability. The government and the business sector must remain vigilant and proactive in managing these changes.









