By Sandeep Chaudhary
The Essential Role of the Net Liquidity Ratio in Banking Stability

The Net Liquidity Ratio is a vital metric for assessing a bank's ability to meet its short-term obligations using its liquid assets. As per Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB) guidelines, maintaining a minimum Net Liquidity Ratio of 20% is crucial for ensuring financial stability and depositor confidence.
This ratio measures the proportion of a bank’s liquid assets relative to its total deposits. Liquid assets include cash, cash equivalents, and high-quality liquid instruments that can be quickly converted into cash with minimal loss. By maintaining a Net Liquidity Ratio of at least 20%, banks can ensure they have enough liquidity to meet immediate withdrawal requests and other short-term liabilities.
The formula used to calculate this ratio is:
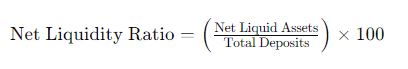
This formula highlights the importance of net liquid assets, which are derived by subtracting short-term liabilities from total liquid assets. By focusing on truly available liquid assets, banks can better manage their liquidity risks.
Adhering to the NRB’s minimum Net Liquidity Ratio requirement is essential for several reasons. It ensures that banks have sufficient liquidity to meet short-term demands, reducing the risk of a liquidity crunch. It also promotes sound risk management practices, helping banks navigate financial uncertainties more effectively. Regulatory compliance is another critical aspect, as failing to meet the NRB’s minimum ratio requirements can result in penalties and loss of depositor confidence. Lastly, a robust Net Liquidity Ratio enhances the overall stability of the banking sector, contributing to a more resilient financial system.
In conclusion, the Net Liquidity Ratio is a critical measure for assessing a bank's liquidity position and its ability to meet short-term obligations. By adhering to NRB guidelines and maintaining a minimum ratio of 20%, banks can ensure sufficient liquidity, manage risks effectively, and promote depositor confidence, thereby contributing to the overall stability and health of the banking sector.









