By Sandeep Chaudhary
What is Gross National Disposable Income (GNDI) and Nepal's Gross National Disposable Income (GNDI) Trends

Gross National Disposable Income (GNDI) is an important economic indicator that provides a comprehensive picture of a nation's economic health. For Nepal, understanding GNDI is crucial as it encompasses not only the income generated within the country but also the net income received from abroad, including remittances, foreign aid, and investments. This holistic measure helps policymakers, economists, and the public to assess the nation's economic well-being more accurately.
What is GNDI?
GNDI is the total income available to the residents of a country for spending or saving. It is calculated by adding net primary income and net secondary income from the rest of the world to the Gross National Income (GNI). Here's a breakdown:
Gross National Income (GNI): This includes all income earned by a country's residents, whether within the country or abroad.
Net Primary Income: This involves income received from abroad, such as wages, salaries, and investment returns, minus similar payments made to the rest of the world.
Net Secondary Income: This includes transfers such as remittances from expatriates and foreign aid.
Formula for GNDI: GNDI=GNI+Net Primary Income+Net Secondary Income\
Importance of GNDI for Nepal
Nepal's economy heavily relies on remittances, which constitute a significant portion of its net secondary income. By understanding GNDI, we can better grasp the real disposable income available to Nepali households and the overall economic resilience of the country.
Economic Planning: GNDI provides a clearer picture for economic planning and development strategies. It helps in formulating policies that can improve living standards and promote sustainable growth.
Investment Decisions: A higher GNDI indicates more disposable income, which can attract both domestic and international investors looking for new opportunities.
Social Welfare: Understanding GNDI helps in assessing the potential for social welfare programs. Higher disposable income means the government can potentially invest more in health, education, and infrastructure.
Nepal's GNDI in Recent Years
In recent years, Nepal has seen a steady increase in its GNDI, primarily due to the influx of remittances from Nepali workers abroad. These remittances play a crucial role in stabilizing the economy, especially during times of internal economic challenges.
Remittances: With a large number of Nepalis working abroad, remittances form a substantial part of net secondary income. This inflow of funds has helped boost GNDI significantly.
Foreign Aid: Nepal also receives considerable foreign aid, which contributes to its net secondary income. This aid supports various developmental projects, enhancing overall economic growth.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While Nepal's GNDI has been growing, challenges remain. The country needs to diversify its income sources and reduce dependency on remittances. Strengthening domestic industries and creating more local employment opportunities are vital steps toward sustainable economic growth.
In conclusion, Gross National Disposable Income (GNDI) is a vital measure for understanding the true economic standing of Nepal. By focusing on GNDI, policymakers can create more informed and effective strategies to enhance the nation's prosperity and ensure a higher quality of life for all its citizens.
Nepal's Gross National Disposable Income (GNDI) Trends: A Comprehensive Analysis
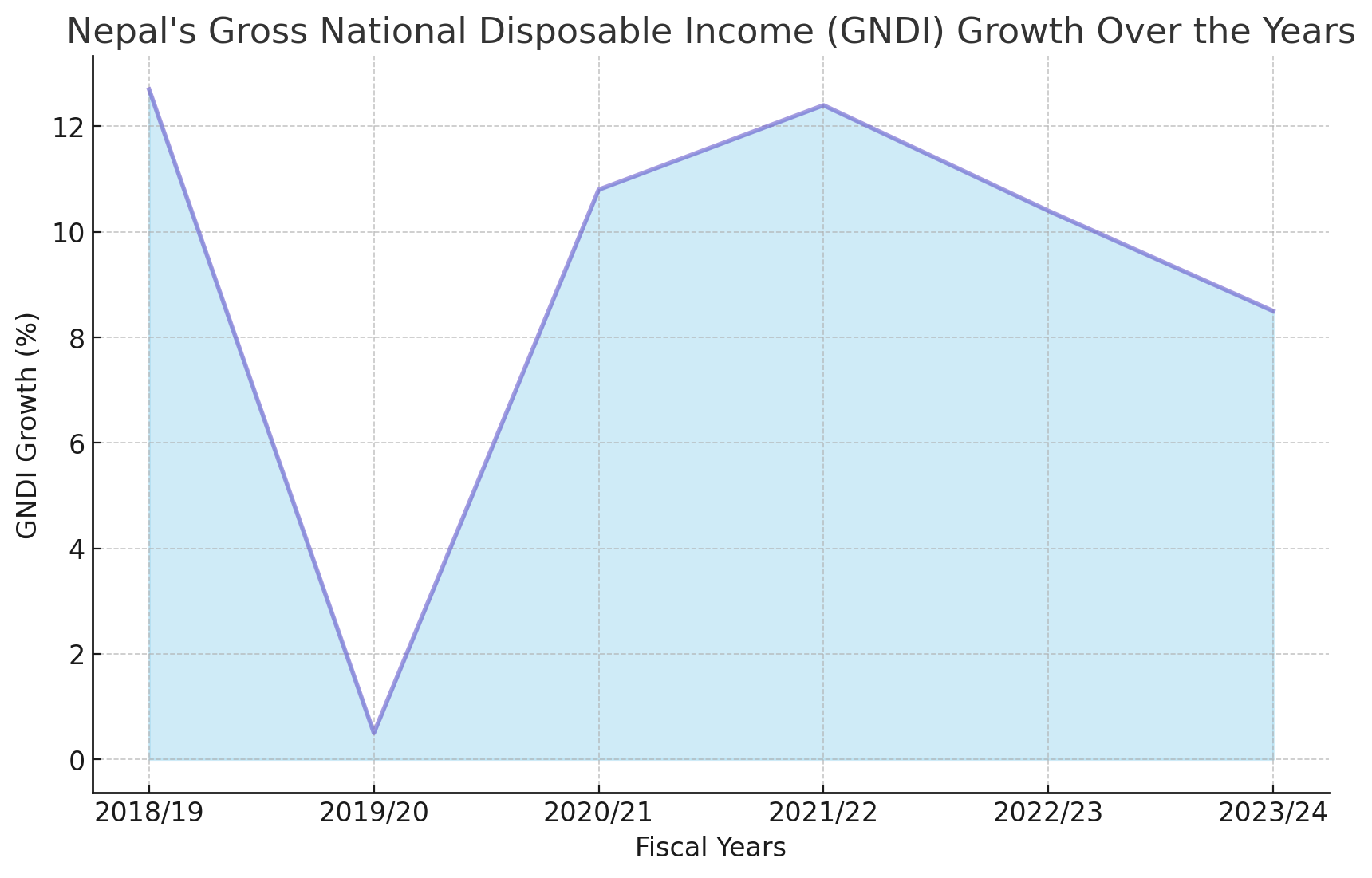
GNDI Trends from 2018/19 to 2023/24
2018/19: The GNDI growth stood at a robust 12.7%. This high growth rate reflects a period of strong economic activity and overall prosperity.
2019/20: A dramatic decline is observed, with the GNDI growth plummeting to a mere 0.5%. This sharp decrease can be attributed to various economic disruptions, including the global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
2020/21: The economy showed signs of recovery, with GNDI growth rebounding to 10.8%. This recovery indicates effective economic policies and resilience in the face of global challenges.
2021/22: The growth rate continued to improve, reaching 12.4%. This period likely benefited from ongoing recovery efforts and a stabilization of economic activities.
2022/23$: A slight dip occurred, with GNDI growth falling to 10.4%. This decline may reflect emerging challenges or a stabilization of the rapid recovery witnessed in the previous years.
2023/24$$: The GNDI growth is projected to be 8.5%. While still positive, this decrease suggests that the economy may be facing new hurdles or a normalization of growth rates post-recovery.
Interpretation and Implications
The fluctuation in Nepal's GNDI growth rates over these years provides a window into the country's economic health and resilience. The significant drop in 2019/20 underscores the impact of the pandemic, while the subsequent recovery highlights the country's ability to bounce back. However, the projected decline in 2023/24 growth indicates potential challenges ahead.
Policymakers need to delve deeper into the factors contributing to these fluctuations. Understanding the causes of the 2019/20 dip and the subsequent recovery can help in formulating strategies to sustain growth. Additionally, addressing the projected slowdown in 2023/24 will be crucial to ensure long-term economic stability and growth.
In conclusion, while Nepal's GNDI growth has shown remarkable resilience, the future will require careful economic planning and policy adjustments to maintain and enhance this growth trajectory.









