By Sandeep Chaudhary
Banks Mandated to Allocate 13% of Loans to Agriculture by Mid-2023, 14% by Mid-2024

In a bid to bolster the agricultural sector, commercial banks are under strict mandates to allocate a significant portion of their total credit to agriculture. By mid-July 2022, banks are required to dedicate at least 12 percent of their lending to this vital sector. This quota is set to increase incrementally, reaching 13 percent by mid-July 2023, 14 percent by mid-July 2024, and 15 percent by mid-July 2025.
As of mid-April 2022, commercial banks have made substantial progress towards meeting these targets. Currently, 12.28 percent of their total credit, amounting to Rs. 490.15 billion, has been directed towards agricultural loans. This level of disbursement demonstrates the banking sector's commitment to supporting agricultural development and ensuring sustainable growth.
Analysis of Current Data
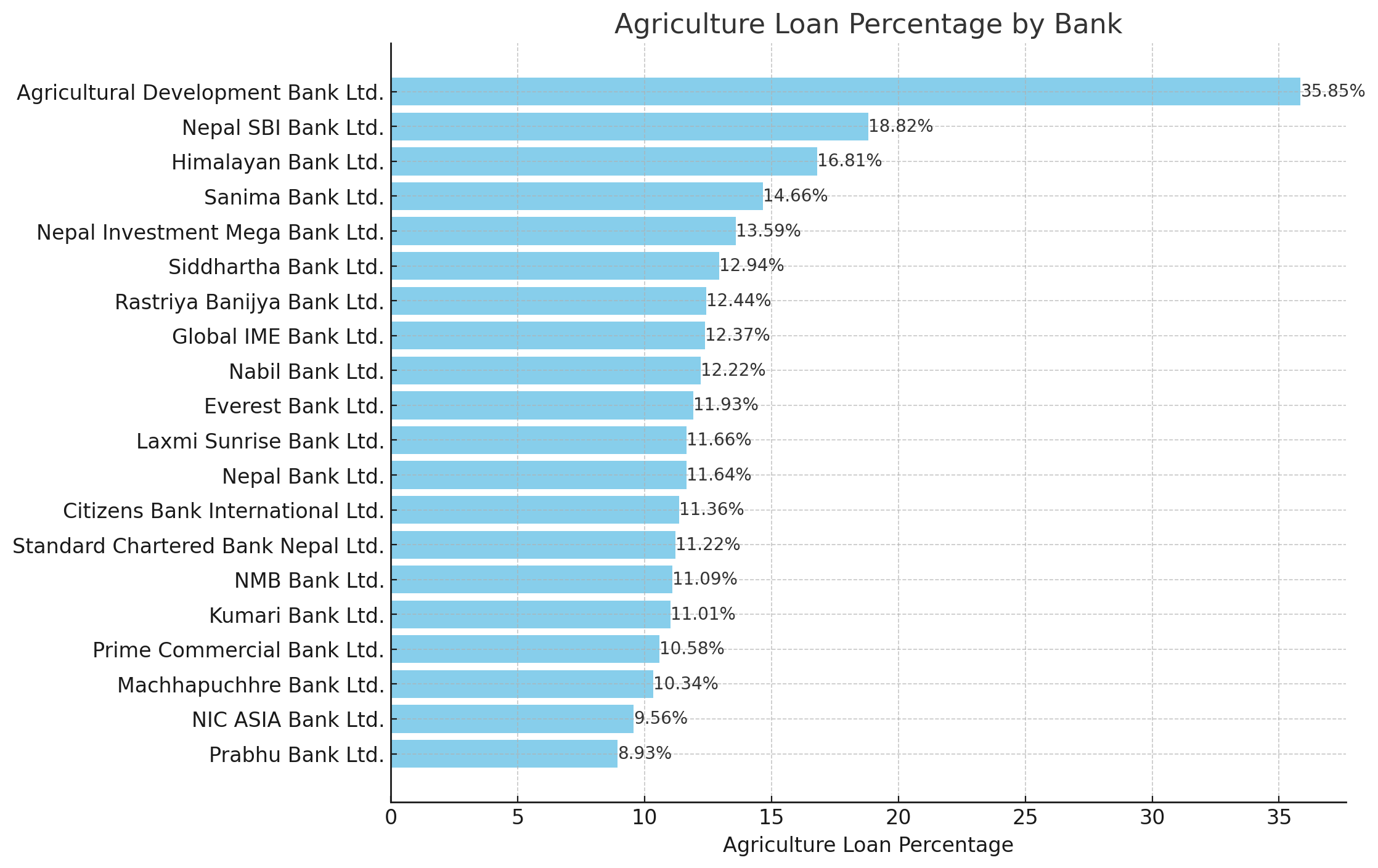
Analyzing the recent data on prescribed sector lending by commercial banks reveals a mixed landscape of compliance and commitment towards agricultural lending:
Agricultural Development Bank Ltd. leads significantly with 35.85 percent of its total lending directed towards agriculture, far exceeding the current requirement of 12 percent. This shows a strong institutional focus on agricultural financing.
Nepal SBI Bank Ltd. and Himalayan Bank Ltd. also show commendable figures, with 18.82 percent and 16.81 percent of their lending dedicated to agriculture, respectively. These banks are well ahead of the regulatory requirement, indicating robust support for the agricultural sector.
On the lower end of the spectrum, Prabhu Bank Ltd. and NIC ASIA Bank Ltd. have allocated 8.93 percent and 9.56 percent of their total credit to agriculture, respectively. While these figures are below the 12 percent threshold for 2022, they highlight areas where further efforts are needed to meet the mandated targets.
The overall sector average stands at 13.15 percent, which is slightly above the required 12 percent. This suggests that, collectively, banks are on track to meet or exceed the regulatory expectations for agricultural lending. However, individual performances vary, with some banks needing to intensify their focus on this sector.
The phased increase in lending requirements reflects the government's strategic focus on agriculture, recognizing its crucial role in the national economy. With these targets in place, commercial banks are expected to continue their efforts to support farmers and agricultural enterprises, contributing to enhanced productivity and economic stability in the sector.
As the deadlines approach, banks are likely to ramp up their agricultural lending programs, offering more tailored financial products to meet the diverse needs of the agricultural community. This proactive approach is not only essential for compliance but also pivotal in fostering long-term economic resilience.
In conclusion, while the banking sector shows a positive trend towards meeting agricultural lending targets, there is still room for improvement among certain institutions. Continued efforts and strategic initiatives will be key to achieving the upcoming milestones and supporting the growth and sustainability of Nepal's agricultural sector.









