By Sandeep Chaudhary
Comprehensive Financial Analysis of NIC Asia Bank: Performance, Insights, and Strategic Implications
NICA's Annual EPS Shows Significant Fluctuations Over the Past Five Years
NICA, a prominent banking institution, has experienced significant variations in its Basic Earnings per Share (EPS) over the past five years. The data, which spans from Q3 2076/2077 to Q3 2080/2081, reveals a mixed performance, reflecting both periods of growth and decline.
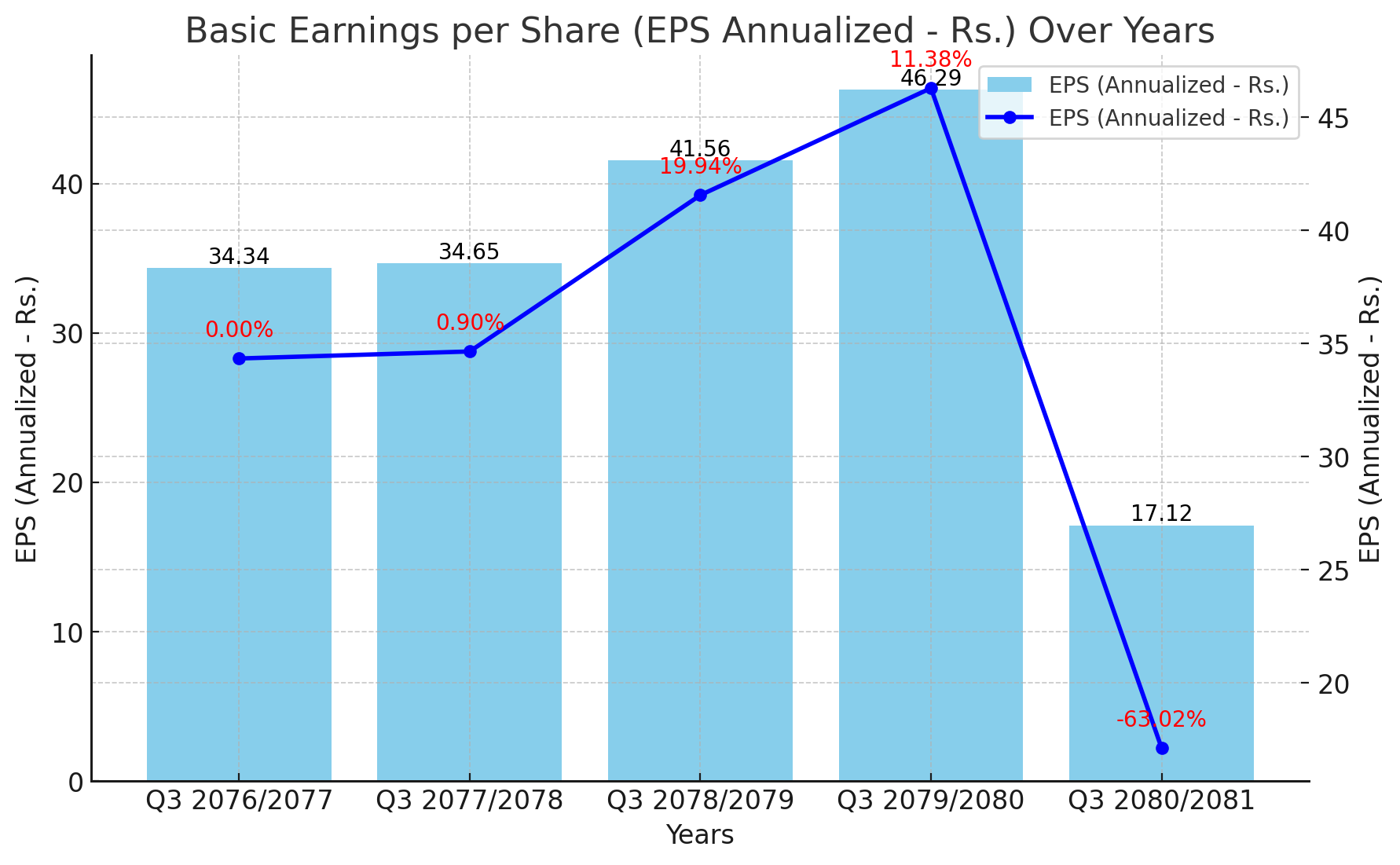
In Q3 2076/2077, NICA reported an EPS of Rs. 34.34. This value remained relatively stable into the next year, with a slight increase to Rs. 34.65 in Q3 2077/2078, marking a modest growth of 0.90%. This period of stability, however, was followed by a more substantial rise in Q3 2078/2079, where the EPS jumped to Rs. 41.56. This 19.94% increase indicated a strong performance and a positive outlook for the bank.
Continuing its upward trajectory, NICA recorded its highest EPS in Q3 2079/2080 at Rs. 46.29, reflecting an 11.38% growth from the previous year. This period marked the peak of NICA's earnings performance, suggesting robust operational efficiency and profitability.
However, the latest data for Q3 2080/2081 shows a drastic downturn, with the EPS plummeting to Rs. 17.12. This sharp decline of 63.02% is concerning and signals potential underlying issues that may need addressing. Several factors could have contributed to this decline, including market volatility, economic downturns, regulatory changes, or internal challenges within the bank.
Interpretation:
The fluctuations in NICA's EPS over the past five years highlight the dynamic nature of the banking sector and the challenges that financial institutions face in maintaining consistent profitability. The steady growth from Q3 2076/2077 to Q3 2079/2080 reflects a period of strong performance and effective management. However, the significant drop in Q3 2080/2081 raises questions about the sustainability of previous growth and the potential impact of external and internal factors on the bank's financial health.
Investors and stakeholders should closely monitor NICA's strategic responses to this downturn. Measures to stabilize and improve earnings, such as cost management, diversification of revenue streams, and enhancing operational efficiencies, will be crucial for regaining investor confidence and ensuring long-term profitability.
In summary, while NICA demonstrated strong earnings growth in the earlier years, the recent decline in EPS underscores the need for vigilance and strategic adjustments to navigate the challenges
Non-Performing Loan Analysis of NICA: A Concerning Trend
NICA, a prominent bank in the financial sector, has recently reported its non-performing loan (NPL) data for the last five fiscal years. The data reveals a worrying upward trend in the NPL to total loan ratio, indicating potential challenges for the bank in maintaining its asset quality.
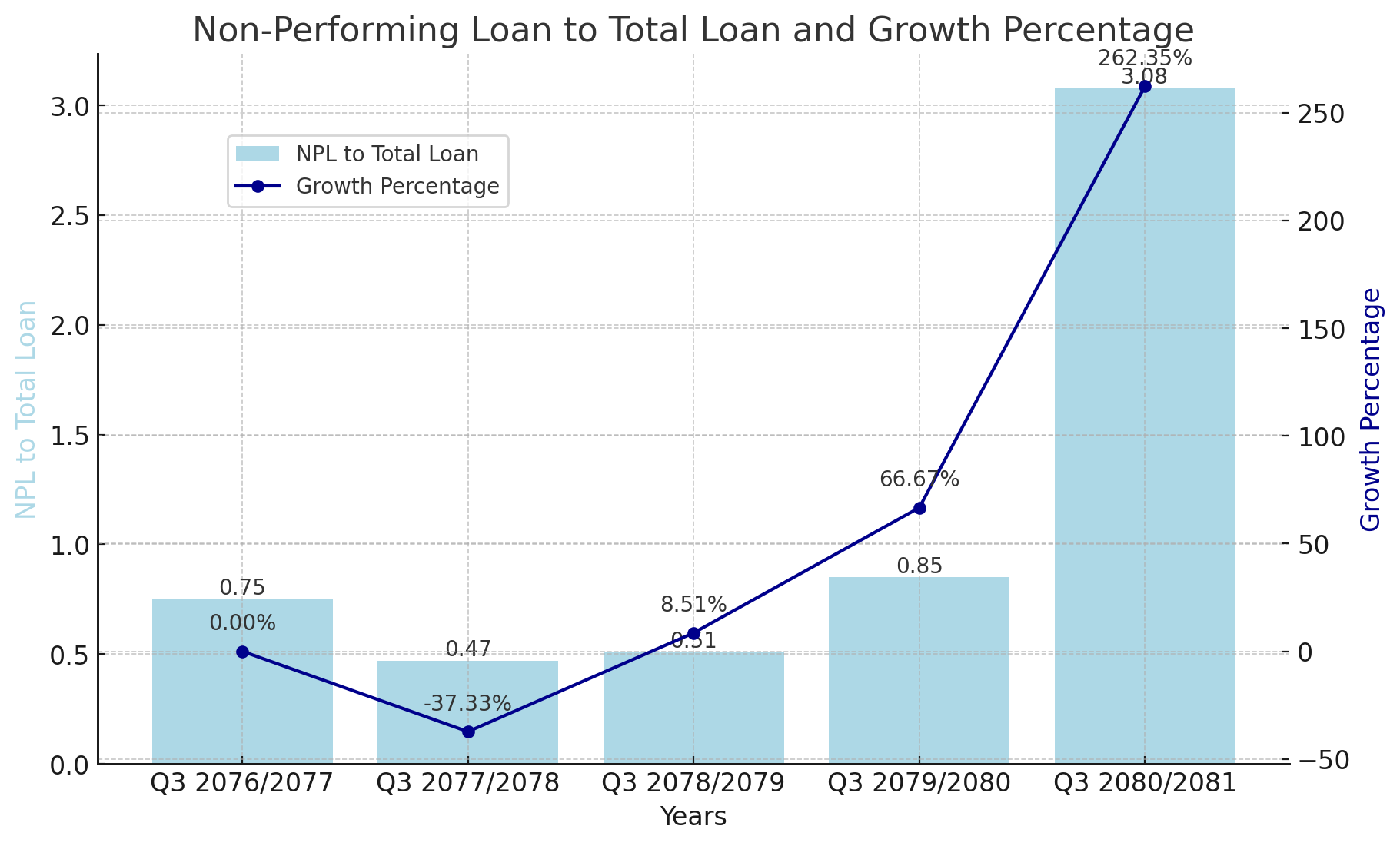
NPL Ratio Over the Years
Q3 2076/2077: The NPL ratio stood at 0.75%.
Q3 2077/2078: The ratio declined to 0.47%, a decrease of 37.33% from the previous year.
Q3 2078/2079: The ratio saw a slight increase to 0.51%, reflecting an 8.51% rise.
Q3 2079/2080: The ratio surged to 0.85%, marking a significant growth of 66.67%.
Q3 2080/2081: The NPL ratio dramatically jumped to 3.08%, an alarming increase of 262.35%.
Interpretation
The data highlights a disturbing trend in NICA's NPL ratio, which has seen a steep rise over the past two years. The significant increase in the NPL ratio from 0.85% to 3.08% between Q3 2079/2080 and Q3 2080/2081 suggests that the bank is facing substantial challenges in its loan portfolio. This sharp rise indicates that a larger portion of NICA's loans are not being repaid on time, which can lead to increased financial instability for the bank.
NICA's Net Worth Per Share Sees Significant Fluctuations Amid Market Changes
Kathmandu, June 18, 2024 – NICA, a leading entity in the banking sector, has demonstrated notable fluctuations in its net worth per share over the past five fiscal years. The analysis, covering Q3 2076/2077 to Q3 2080/2081, reveals significant variations reflective of underlying market conditions and strategic financial maneuvers.
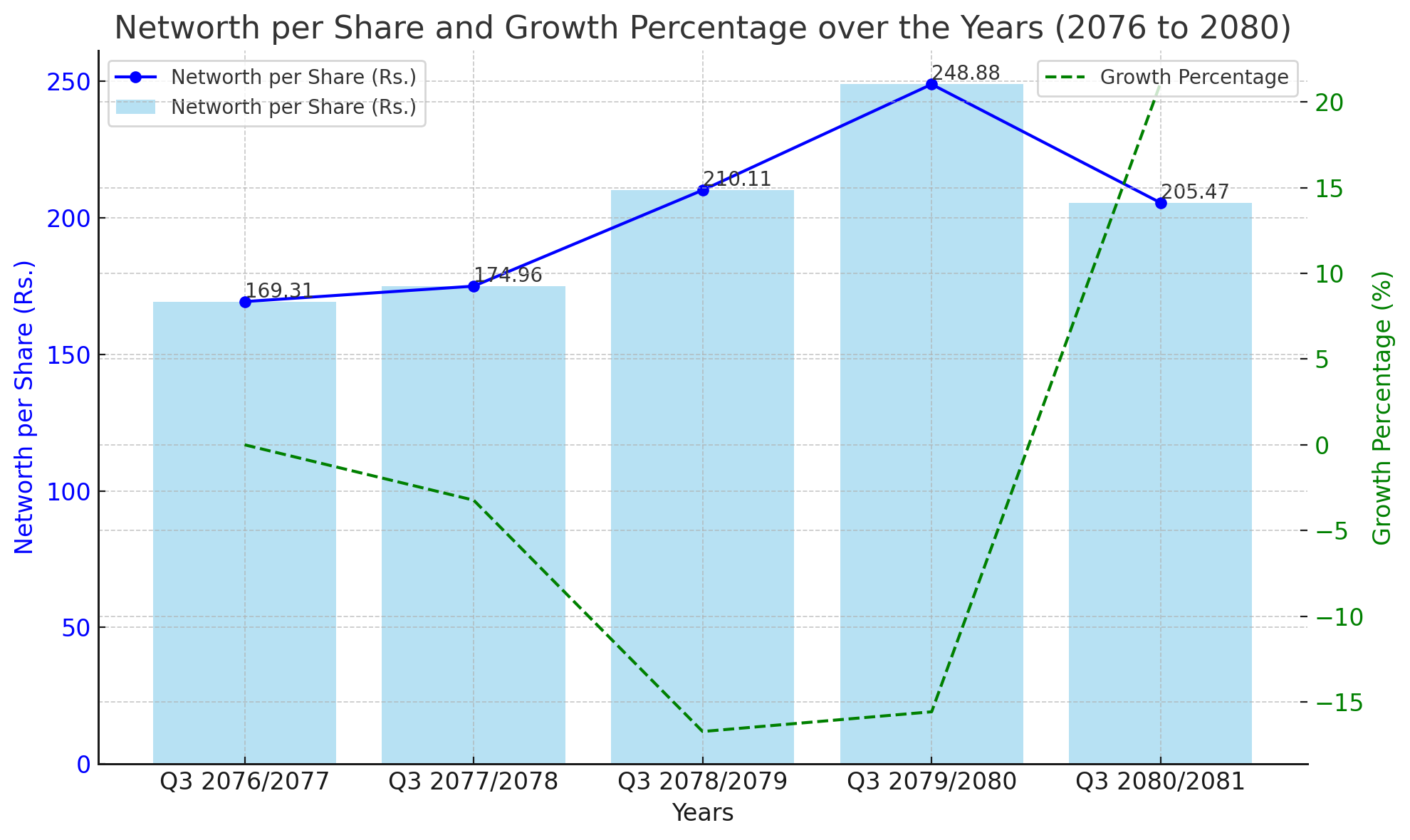
Consistent Growth Followed by Decline
Starting from Q3 2076/2077, NICA's net worth per share stood at Rs. 169.31. Over the next three years, the company saw a steady increase, reaching Rs. 174.96 in Q3 2077/2078 and Rs. 210.11 in Q3 2078/2079. This upward trajectory culminated in a peak of Rs. 248.88 by Q3 2079/2080, marking a substantial growth of 47.1% from the base year.
However, the trend took a downturn in Q3 2080/2081, with the net worth per share falling to Rs. 205.47, a decline of 17.4% from the previous year's peak. This decline highlights the challenges faced by the banking sector amid fluctuating economic conditions and possibly internal adjustments within the company.
Volatile Growth Rates
The growth percentages over the years showcase the volatility in NICA's financial performance. The most significant growth was observed between Q3 2078/2079 and Q3 2079/2080, where the net worth per share surged by 18.4%. Conversely, the subsequent year saw a sharp decline of 17.4%, indicating potential market or operational challenges.
Interpretation and Market Implications
The data indicates that while NICA has experienced periods of robust growth, the recent decline suggests a need for strategic realignments. The peak in Q3 2079/2080 might have been driven by favorable market conditions, effective management strategies, or a combination of both. The subsequent drop, however, raises questions about the sustainability of such growth and the impact of external economic factors.
Financial analysts suggest that NICA's fluctuations are indicative of broader market trends affecting the banking sector. The volatility in growth rates underscores the importance of adaptive strategies to navigate the dynamic economic landscape.
Future Outlook
Investors and stakeholders are closely monitoring NICA's next steps. The company's ability to stabilize its net worth per share and return to a growth trajectory will be crucial in regaining investor confidence. Strategic initiatives aimed at mitigating market risks and enhancing operational efficiency will play a vital role in shaping NICA's financial future.
As NICA navigates these challenges, the banking sector remains a focal point for economic observers, with implications for broader market stability and growth.
Decline in Return on Equity Reflects Challenges for NICA Bank
NICA Bank, a prominent player in the Nepali banking sector, has witnessed a significant decline in its Return on Equity (ROE) over the past five fiscal years. The ROE, a key financial indicator of profitability, has dropped from 20.28% in Q3 2076/2077 to a concerning 8.33% in Q3 2080/2081, highlighting the challenges faced by the bank in maintaining its profitability.
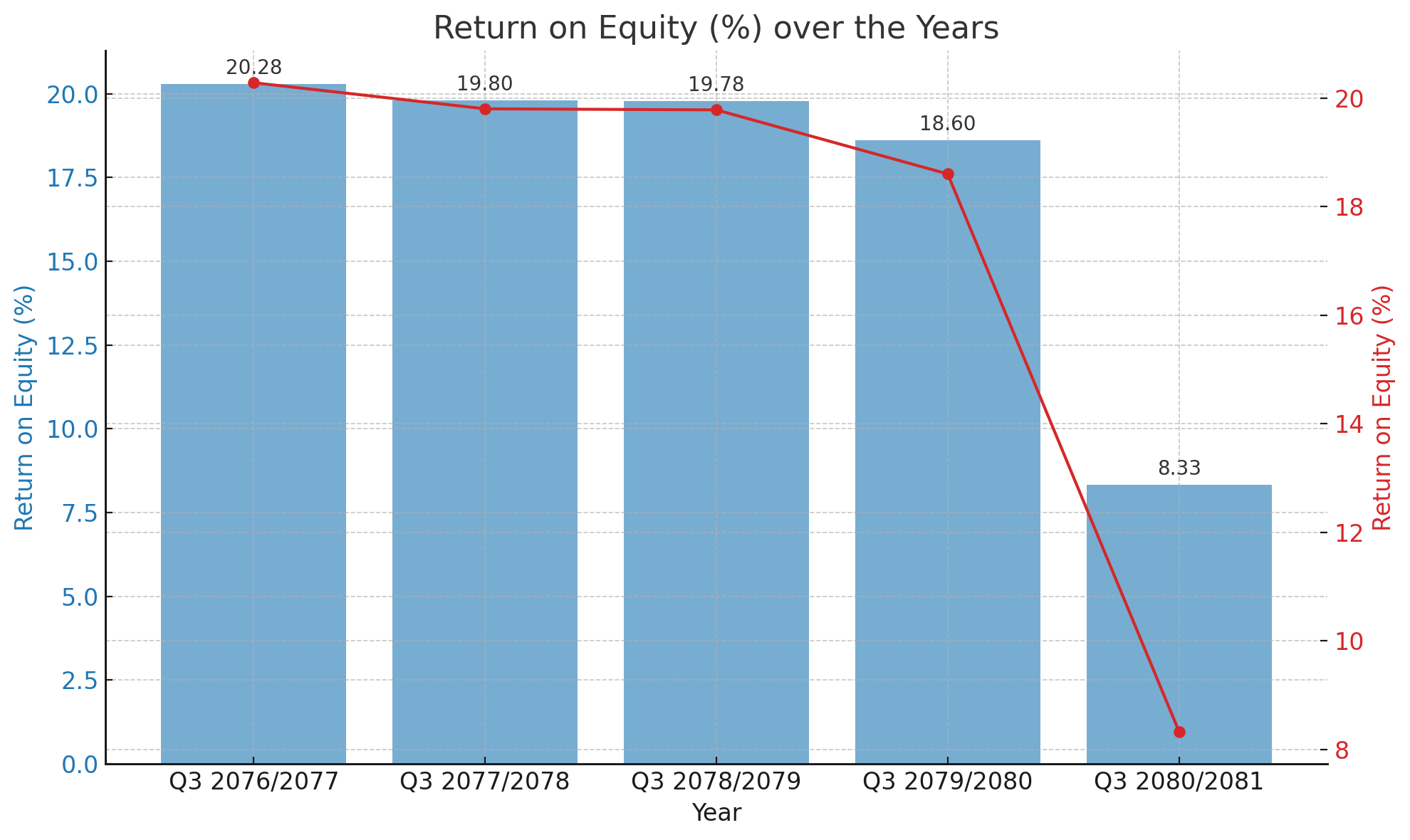
Decline in ROE Over the Years
The historical data shows a gradual decline in ROE:
Q3 2076/2077: 20.28%
Q3 2077/2078: 19.8%
Q3 2078/2079: 19.78%
Q3 2079/2080: 18.6%
Q3 2080/2081: 8.33%
The sharpest decline occurred between Q3 2079/2080 and Q3 2080/2081, where the ROE plummeted by approximately 55.22%. This drastic reduction suggests underlying issues that need to be addressed to restore the bank's financial health.
Interpreting the Decline
Several factors could be contributing to this decline:
Increased Competition: The banking sector in Nepal has seen an influx of new players, intensifying competition and impacting profit margins.
Economic Slowdown: A sluggish economy can lead to lower demand for loans and other banking services, affecting profitability.
Regulatory Changes: New regulations may have imposed additional costs or restrictions, reducing the bank's ability to generate profits.
Operational Inefficiencies: There may be inefficiencies within the bank's operations, leading to higher costs and reduced profitability.
Growth Rate Analysis
The growth rate data further underscores the bank's challenges. After a steady period, the growth rate turned negative, culminating in a significant decline of -55.22% in the most recent year. This negative growth indicates that the bank's ability to generate profits has not only stalled but reversed, raising concerns among investors and stakeholders.
Strategic Measures Needed
To combat these challenges, NICA Bank must implement strategic measures:
Cost Optimization: Streamlining operations to reduce costs without compromising service quality.
Innovative Products: Introducing new, innovative financial products to attract and retain customers.
Digital Transformation: Embracing digital banking solutions to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
Market Expansion: Exploring new markets and customer segments to diversify income sources.
Conclusion
The decline in NICA Bank's ROE is a wake-up call for the management to reassess and realign their strategies. By addressing the underlying issues and adopting a proactive approach, NICA Bank can work towards reversing the trend and restoring its profitability in the coming years.
NICA Bank's Distributable Profit Per Share Analysis Over the Years
Analyzing the Trends and Implications for Investors
NICA Bank, a prominent entity in the banking sector, has exhibited fluctuating distributable profit per share (DPS) over the past five fiscal years. The analysis of the bank's DPS reveals significant insights into its financial health and operational performance.
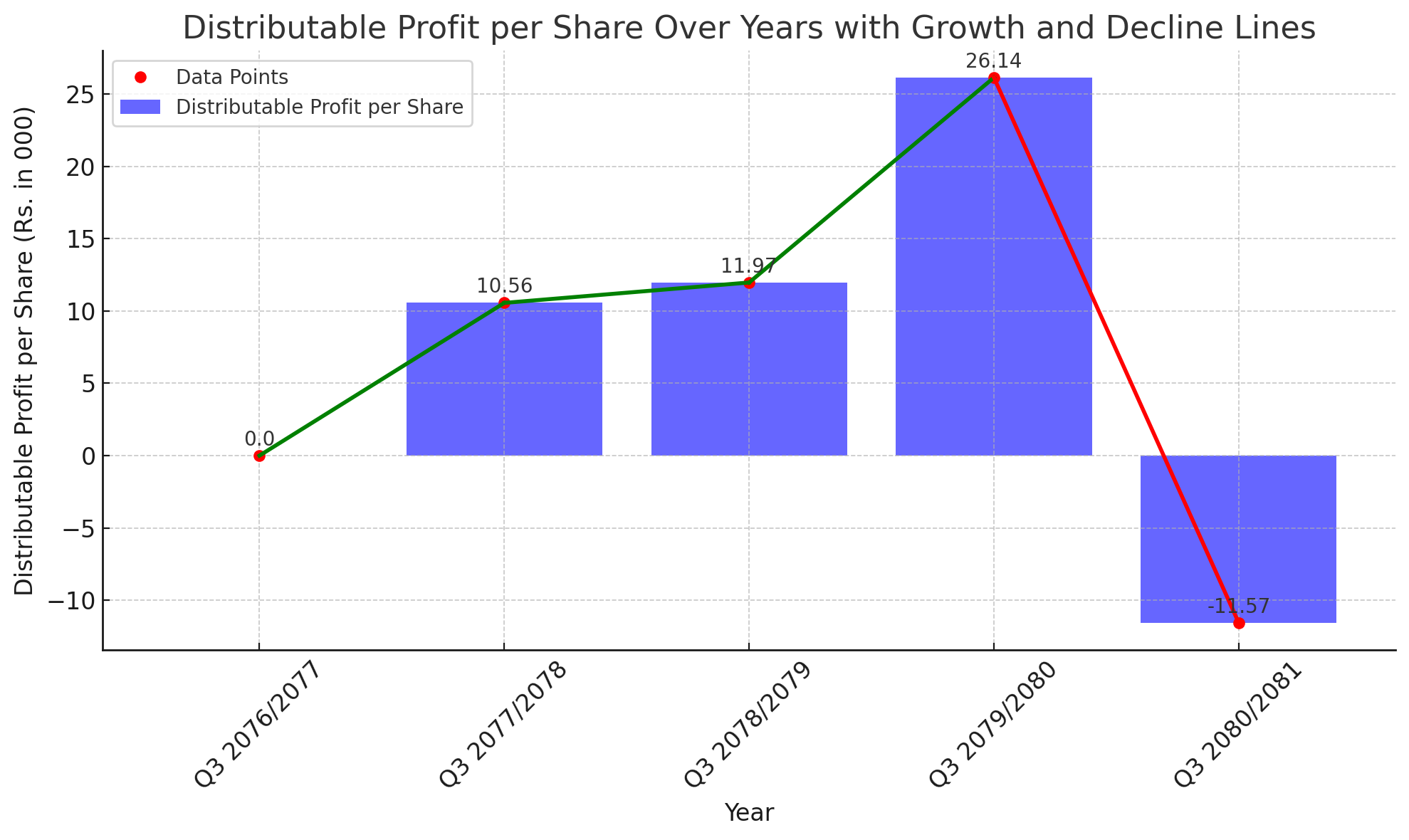
Yearly Breakdown:
Q3 2076/2077: The bank reported a DPS of Rs. 0. This neutral figure indicates a baseline year with neither profit distribution nor loss incurred per share.
Q3 2077/2078: Marking a positive turn, NICA Bank achieved a DPS of Rs. 10.56. This growth signifies effective financial strategies and operational efficiency improvements.
Q3 2078/2079: The upward trend continued, with a slight increase in DPS to Rs. 11.97. Consistent growth suggests stable revenue streams and controlled expenditure.
Q3 2079/2080: A remarkable surge saw the DPS soaring to Rs. 26.14. This significant leap indicates a period of exceptional profitability, potentially driven by strategic investments, increased market share, or cost optimizations.
Q3 2080/2081: In stark contrast to the previous year's performance, the DPS plummeted to -Rs. 11.57. This decline points to a challenging financial period for the bank, possibly due to economic downturns, increased loan defaults, or heightened operational costs.
Interpretation:
Growth Phases: The periods from Q3 2076/2077 to Q3 2079/2080 reflect a healthy growth trajectory. The consistent rise in DPS indicates the bank's ability to enhance its profitability and deliver value to its shareholders.
Decline Phase: The sharp decline in Q3 2080/2081 warrants closer scrutiny. Factors contributing to this downturn could include external economic pressures, internal mismanagement, or significant one-time financial hits. Investors must consider these aspects to understand the bank's current financial stability and future outlook.
Investor Outlook:
For current and potential investors, the mixed DPS results necessitate a cautious approach. While the bank demonstrated robust growth for several years, the recent downturn raises questions about its resilience in adverse conditions.
Short-term Strategy: Investors might adopt a wait-and-see approach, monitoring the bank's quarterly reports for signs of recovery or further decline.
Long-term Strategy: For those with a long-term investment horizon, understanding the underlying causes of the recent dip and the bank's strategic response will be crucial in making informed decisions.
In conclusion, while NICA Bank has shown strong growth capabilities, the recent negative turn in its DPS underscores the importance of thorough financial analysis and strategic planning for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring sustained profitability.









